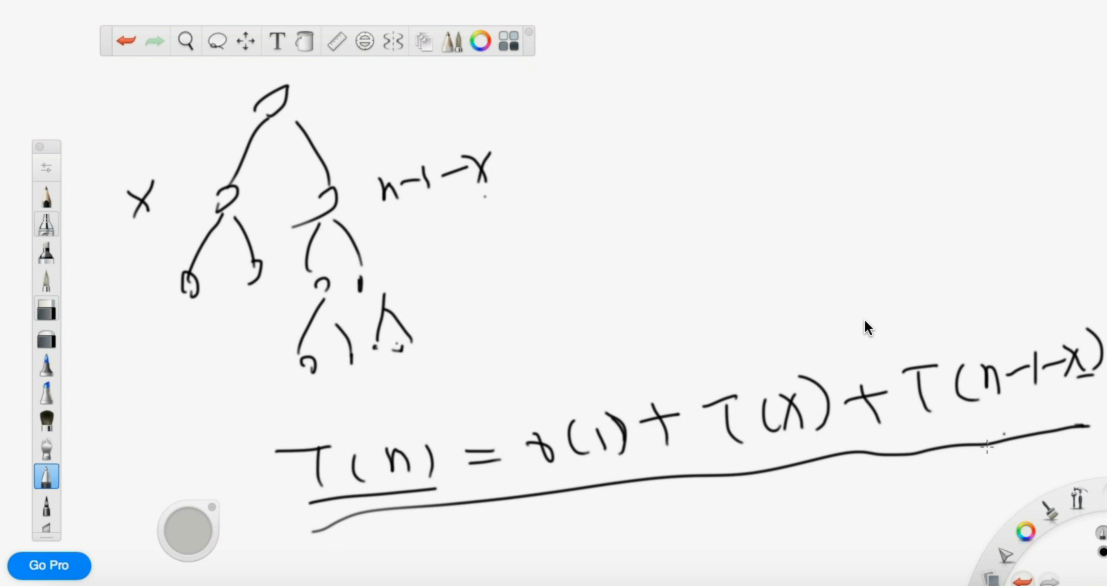Binary Tree & Divide Conquer Template
Outline
- Time Complexity Training ii
- Traverse in Binary Tree
- Preorder / Inorder / Postorder
DFS in Binary Tree
Preorder / Inorder / Postorder
Introduce Divide Conquer Algorithm
Non-recursion vs Traverse vs Divide Conquer
Binary Search Tree
- Insert / Remove / Find / Validate
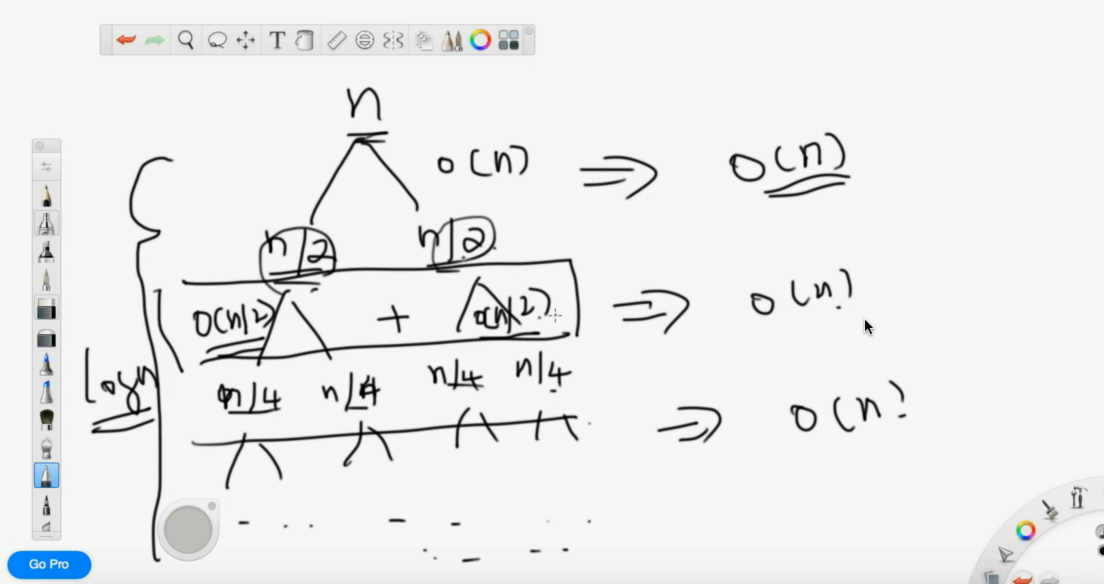
Time Complexity Training ii
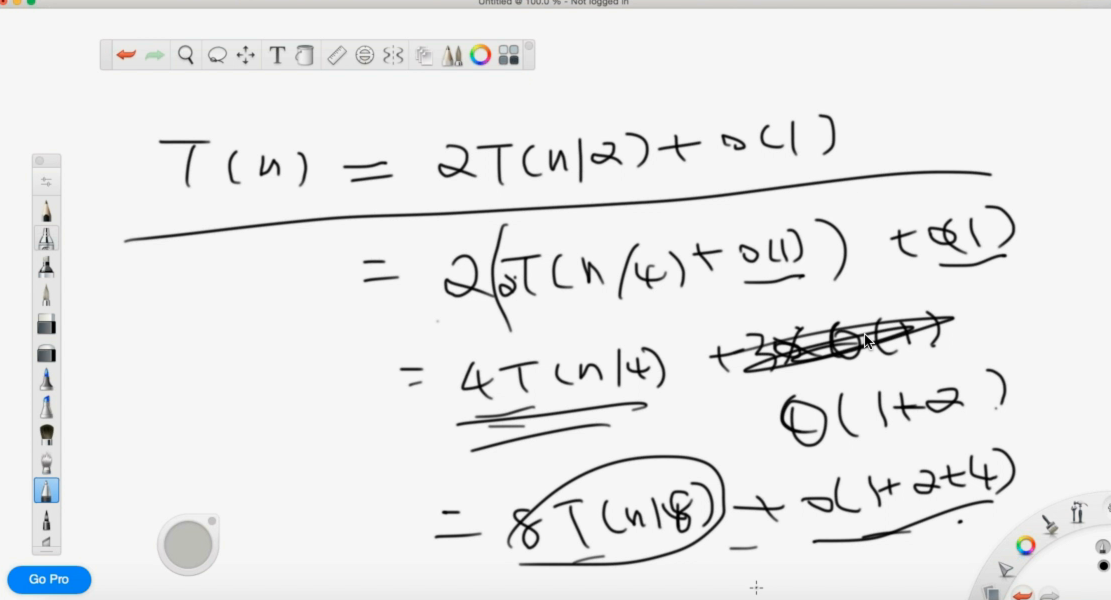
- 通过 O(n) 的时间,把 n 的时间,变为了两个 n/2 的问题,复杂度是多少?
T(n) = 2T(n/2) + O(n) = 2(T(n/4) + O(n/2)) + O(n) = … = nxT(n/n) + o(nlogn) = O(nlogn)
Merge Sort 就是 O(nlogn)
- 通过 O(1) 的时间,把 n 的问题,变成了两个 n/2 的问题,复杂度是多少?
T(n) = 2T(n/2) + O(1) = 2(2T(n/4) + O(1)) + O(1)
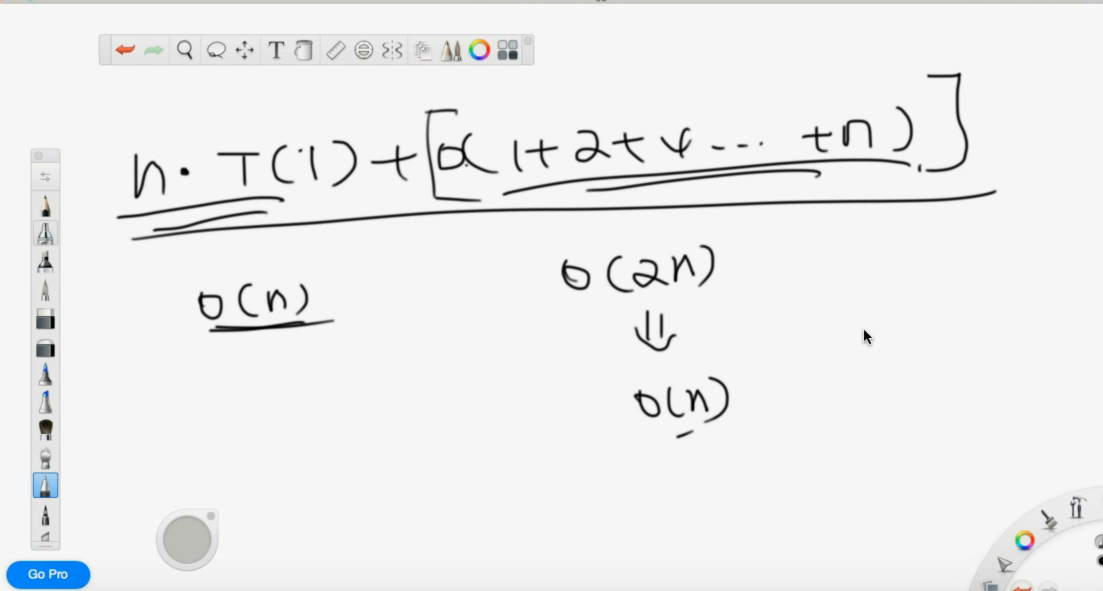
= nxT(1) + O(1+2+4+…+n) = O(n) + O(2n) = O(n)
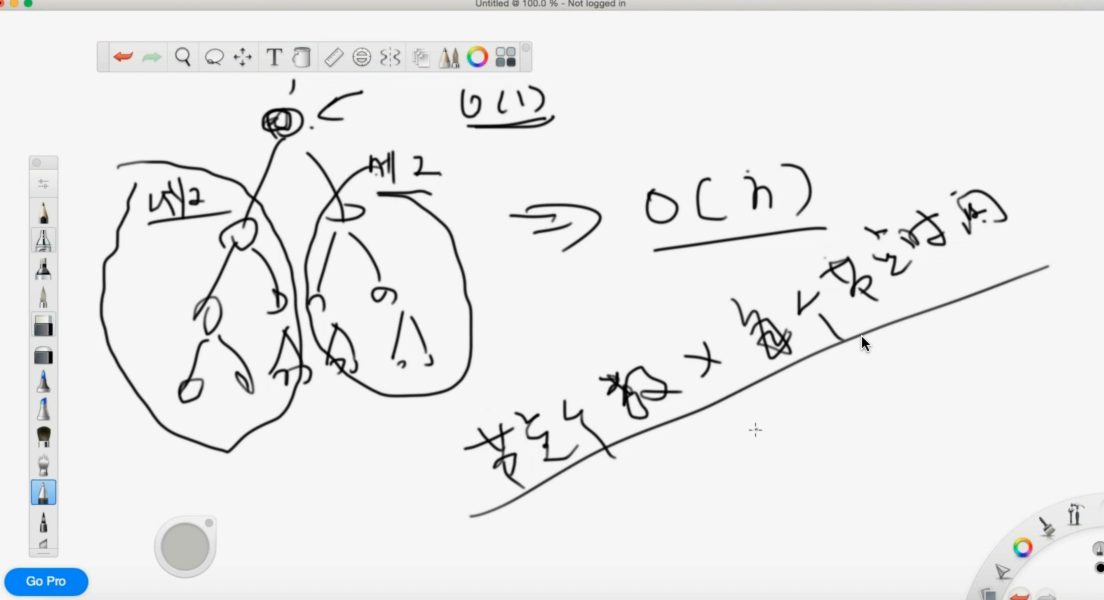
二叉树上的问题
节点个数 x 每个节点时间
利用二叉树的形状来分析时间复杂度。
这颗树有 logn 层,每个 n -> n/2 是 O(n) 所以最后是 logn*O(n) 即 O(nlogn)
Template Traverse a Binary Tree
Traverse vs Divide Conquer
They are both Recursion Algorithm
Result in parameter vs Result in return value
Top down vs Bottom up
- Merge Sort / Quick Sort
- 90% Binary Tree Problems!!
1
2
3
4
5
1
/ \
2 3
/ \
4 5
- Preorder 前序遍历
- 1 245 3 根左右
- Inorder 中序遍历
- 425 1 3 左 根 右
- Postorder 后序遍历
- 452 3 1 左 右 根
Preorder
https://www.lintcode.com/problem/binary-tree-preorder-traversal/
https://www.jiuzhang.com/solutions/binary-tree-preorder-traversal/
Inorder
https://www.lintcode.com/en/problem/binary-tree-inorder-traversal/
https://www.jiuzhang.com/solutions/binary-tree-inorder-traversal/
Postorder
https://www.lintcode.com/en/problem/binary-tree-postorder-traversal/
https://www.jiuzhang.com/solutions/binary-tree-postorder-traversal/
如果面试面你一个二叉树的遍历,那么面试官希望你用非递归的版本来写,因为递归的版本太简单了。
- 出一个小的数据,跑一下这个三个程序。
递归的几个要素?三要素
- 递归的定义:把 root 为根的 preorder 加入 result 里面
- 递归的拆解,把大象放冰箱总共分几步。
- 递归的出口:这个参数你小到不能再小了的处理。
- 递归的调用,如果要再添加一个要素的话,就是递归你怎么 call 的
Template Recursion
Binary Tree Preorder Traversal
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
//Version 1: Traverse
/**
* Definition for binary tree
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ArrayList<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
ArrayList<Integer> result = new ArrayList<Integer>();
traverse(root, result);
return result;
} // end preorderTraversal
// 把root为跟的preorder加入result里面
private void traverse(TreeNode root, ArrayList<Integer> result) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
result.add(root.val);
traverse(root.left, result);
traverse(root.right, result);
} // end traverse
} // end Solution
分治的方法
让A去做一件事情,B做另一件事情,最后A和B的结果汇总一下,就是总结果。
- 递归的定义:返回以 root 为根的二叉树的 preorder
- 递归和分治的区别?结果在参数的位置,分治是返回结果
Template Divide Conquer
Binary Tree Preorder Traversal
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
//Version 2: Divide & Conquer
/**
* Definition for binary tree
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ArrayList<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
ArrayList<Integer> result = new ArrayList<Integer>();
// null or leaf
if (root == null) {
return result;
}
// Divide
ArrayList<Integer> left = preorderTraversal(root.left);
ArrayList<Integer> right = preorderTraversal(root.right);
// Conquer
result.add(root.val);
result.addAll(left);
result.addAll(right);
return result;
} // end preorderTraversal
} // end Solution
!!! Template Non-Recursion (Recommend)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
// Version 0: Non-Recursion (Recommend)
/**
* Definition for binary tree
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<TreeNode>();
List<Integer> preorder = new ArrayList<Integer>();
if (root == null) {
return preorder;
}
stack.push(root);
while (!stack.empty()) {
TreeNode node = stack.pop();
preorder.add(node.val);
if (node.right != null) {
stack.push(node.right);
}
if (node.left != null) {
stack.push(node.left);
}
}
return preorder;
} // end preorderTraversal
} // end Solution
独孤九剑 —— 破枪式
碰到二叉树的问题,就想想整棵树在该问题上的结果和左右儿子在该问题上的结果之间的联系是什么
Maximum Depth of Binary Tree
Lintcode https://www.lintcode.com/problem/maximum-depth-of-binary-tree/
Leetcode https://leetcode.cn/problems/maximum-depth-of-binary-tree/
Solution https://www.jiuzhang.com/solutions/maximum-depth-of-binary-tree/
Related Question: Minimum Depth of Binary Tree
递归的版本
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
/**
* Definition of TreeNode:
* public class TreeNode {
* public int val;
* public TreeNode left, right;
* public TreeNode(int val) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = this.right = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
/**
* @param root: The root of binary tree.
* @return: An integer.
*/
private int depth;
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
depth = 0;
helper(root, 1);
return depth;
} // end maxDepth
private void helper(TreeNode node, int curtDepth) {
if (node == null) {
return;
}
if (curtDepth > depth) {
depth = curtDepth;
}
helper(node.left, curtDepth + 1);
helper(node.right, curtDepth + 1);
} // end helper
} // end Solution
在工程中呢,会尽量减少全局变量的使用,算是不好的一个 coding pattern 吧
Divide Conquer 呢
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
/**
* Definition of TreeNode:
* public class TreeNode {
* public int val;
* public TreeNode left, right;
* public TreeNode(int val) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = this.right = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
/**
* @param root: The root of binary tree.
* @return: An integer
*/
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null){
return 0;
}
int leftDepth = maxDepth(root.left);
int rightDepth = maxDepth(root.right);
return Math.max(leftDepth, rightDepth) + 1;
} // end maxDepth
} // end Solution
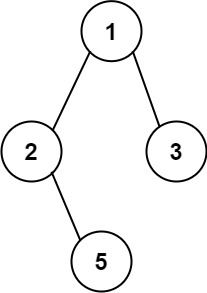
Binary Tree Paths
Leetcode https://leetcode.com/problems/binary-tree-paths/
Solution https://www.jiuzhang.com/problem/binary-tree-paths/
Descripton
Given the root of a binary tree, return all root-to-leaf paths in *any order*.
A leaf is a node with no children.
Example 1:
Input: root = [1, 2, 3, null, 5]
Output: [“1->2->5”, “1->3”]
Example 2:
Input: root = [1]
Output: [“1”]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [1, 100].
- -100 <= Node.val <= 100
Solutions
- Divide Conquer
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
public class Solution {
// 1. 递归的定义:求出 root 为根的所有 r2l path
public List<String> binaryTreePaths(TreeNode root) {
List<String> paths = new ArrayList<String>();
// 3. 递归的出口
if (root == null) {
return paths;
}
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) {
paths.add("" + root.val);
return paths;
}
// 2. 递归的拆解
List<String> leftPaths = binaryTreePaths(root.left);
List<String> rightPaths = binaryTreePaths(root.right);
for (String path : leftPaths) {
paths.add(root.val + "->" + path);
}
for (String path : rightPaths) {
paths.add(root.val + "->" + path);
}
return paths;
} // end binaryTreePaths
} // end Solution
- Recursion
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
/**
* @param root the root of the binary tree
* @return all root-to-leaf paths
*/
public List<String> binaryTreePaths(TreeNode root) {
List<String> result = new ArrayList<String>();
if (root == null) {
return result;
}
helper(root, String.valueOf(root.val), result);
return result;
} // end binaryTreePaths
private void helper(TreeNode root, String path, List<String> result) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) {
result.add(path);
return;
}
if (root.left != null) {
helper(root.left, path + "->" + String.valueOf(root.left.val), result);
}
if (root.right != null) {
helper(root.right, path + "->" + String.valueOf(root.right.val), result);
}
} // end helper
} // end Solution
Minimum Subtree
Lintcode https://www.lintcode.com/problem/596/ 这道题要VIP
Solution https://www.jiuzhang.com/problem/minimum-subtree/
Description
Given a binary tree, find the subtree with minimum sum. Return the root of the subtree.
Notice
LintCode will print the subtree which root is your return node. It’s guaranteed that there is only one subtree with minimum sum and the given binary tree is not an empty tree.
Example
Given a binary tree:
1
/ \
-5 2
/ \ / \
0 2 -4 -5
return the node1.
Solutions
两种solution区别为记录截止到每一层的最小树的方式不同:第一种方法为用返回值变量带着走,第二种方法用class的变量记录。
- Result Type
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
// solution 1
/**
* Definition of TreeNode:
* public class TreeNode {
* public int val;
* public TreeNode left, right;
* public TreeNode(int val) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = this.right = null;
* }
* }
*/
class ResultType {
public TreeNode minSubtree;
public int sum, minSum;
public ResultType(TreeNode minSubtree, int minSum, int sum) {
this.minSubtree = minSubtree;
this.minSum = minSum;
this.sum = sum;
}
}
public class Solution {
/**
* @param root the root of binary tree
* @return the root of the minimum subtree
*/
public TreeNode findSubtree(TreeNode root) {
ResultType result = helper(root);
return result.minSubtree;
}
public ResultType helper(TreeNode node) {
if (node == null) {
return new ResultType(null, Integer.MAX_VALUE, 0);
}
ResultType leftResult = helper(node.left);
ResultType rightResult = helper(node.right);
ResultType result = new ResultType(
node,
leftResult.sum + rightResult.sum + node.val,
leftResult.sum + rightResult.sum + node.val
);
if (leftResult.minSum < result.minSum) {
result.minSum = leftResult.minSum;
result.minSubtree = leftResult.minSubtree;
}
if (rightResult.minSum < result.minSum) {
result.minSum = rightResult.minSum;
result.minSubtree = rightResult.minSubtree;
}
return result;
}
}
- Divide Conquer
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
// solution 2
/**
* Definition of TreeNode:
* public class TreeNode {
* public int val;
* public TreeNode left, right;
* public TreeNode(int val) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = this.right = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
/**
* @param root the root of binary tree
* @return the root of the minimum subtree
*/
public TreeNode minSubtree;
public int minSum = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
public TreeNode findSubtree(TreeNode root) {
// Write your code here
getSum(root);
return minSubtree;
}
private int getSum(TreeNode node){
if(node == null) {
return 0;
}
int left = getSum(node.left);
int right = getSum(node.right);
int curtSum = left + right + node.val;
if(curtSum < minSum) {
this.minSubtree = node;
this.minSum = curtSum;
}
return curtSum;
}
}
public class Solution {
private TreeNode subtree = null;
private int subTreeSum = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
/**
* @param root the root of binary tree
* @return the root of the minimum subtree
*/
public TreeNode findSubtree(TreeNode root) {
helper(root);
return subtree;
}
// 1. return root's sum
private int helper(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
// divide + conquer + merge
// 分治
int sum = helper(root.left) + helper(root.right) + root.val;
// 打擂台(遍历 traverse)
// traverse (compare with global variable)
if (sum < subtreeSum) {
subtreeSum = sum;
subtree = root;
}
return sum;
} // end helper
} // end Solution
Result Type
问:什么时候用?
当返回的东西多余一个变量的时候,这时候就要返回一个类对象,里面包含你计算的东西了。
1
2
3
4
class ResultType {
int var1;
int var2;
} // end ResultType
Balanced Binary Tree
Lintcode https://www.lintcode.com/problem/balanced-binary-tree/
Leetcode https://www.leetcode.com/problems/balanced-binary-tree/
Solution https://www.jiuzhang.com/solutions/balanced-binary-tree/
When we need ResultType?
Description
Given a binary tree, determine if it is height-balanced.
For this problem, a height-balanced binary tree is defined as a binary tree in which the depth of the two subtree of every node never differ by more than 1.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
如下,是一个平衡的二叉树。
1
/ \
2 3
如下,是一个不平衡的二叉树。1的左右子树高度差2
1
\
2
/ \
3 4
Solutions
- Version 1: with ResultType
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
// Version 1: with ResultType
/**
* Definition of TreeNode:
* public class TreeNode {
* public int val;
* public TreeNode left, right;
* public TreeNode(int val) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = this.right = null;
* }
* }
*/
class ResultType {
public boolean isBalanced;
public int maxDepth;
public ResultType(boolean isBalanced, int maxDepth) {
this.isBalanced = isBalanced;
this.maxDepth = maxDepth;
}
}
public class Solution {
/**
* @param root: The root of binary tree.
* @return: True if this Binary tree is Balanced, or false.
*/
public boolean isBalanced(TreeNode root) {
return helper(root).isBalanced;
} // end isBalanced
private ResultType helper(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return new ResultType(true, 0);
}
ResultType left = helper(root.left);
ResultType right = helper(root.right);
// subtree not balance
if (!left.isBalanced || !right.isBalanced) {
return new ResultType(false, -1);
}
// root not balance
if (Math.abs(left.maxDepth - right.maxDepth) > 1) {
return new ResultType(false, -1);
}
return new ResultType(true, Math.max(left.maxDepth, right.maxDepth) + 1);
} // end helper
} // end Solution
- Version 2: without ResultType
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
// Version 2: without ResultType
public class Solution {
public boolean isBalanced(TreeNode root) {
return maxDepth(root) != -1;
}
private int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
int left = maxDepth(root.left);
int right = maxDepth(root.right);
if (left == -1 || right == -1 || Math.abs(left-right) > 1) {
return -1;
}
return Math.max(left, right) + 1;
}
}
看起来是更简单一点,这种方法在面试的时候不推荐!!
函数的返回的时候返回有二义性!!!一会代表 maxDepth 一会又代表 -1 不是平衡的。
那我们应该把变量 hard code 到每一行里面。就像下面写的。
Subtree with Maximum Average
Leetcode https://leetcode.com/problems/maximum-average-subtree/
Leetcode Discuss https://leetcode.com/discuss/interview-question/349617
Solution https://www.jiuzhang.com/problem/subtree-with-maximum-average/
Description
Given a binary tree, find the subtree with maximum average. Return the root of the subtree.
LintCode will print the subtree which root is your return node. It’s guaranteed that there is only one subtree with maximum average.
Example 1
Input:
{1,-5,11,1,2,4,-2}
Output:11
Explanation:
The tree is look like this:
1
/ \
-5 11
/ \ / \
1 2 4 -2
The average of subtree of 11 is 4.3333, is the maximun.
Example 2
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
Input:
{1,-5,11}
Output:11
Explanation:
1
/ \
-5 11
The average of subtree of 1,-5,11 is 2.333,-5,11. So the subtree of 11 is the maximun.
Solutions
避免精度问题:root.sum / root.num > ans.sum / ans.num 的判断移项成乘法:root.sum ans.num > ans.sum root.num
- version 1: Traverse + Divide Conquer
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
// version 1: Traverse + Divide Conquer
public class Solution {
private class ResultType {
public int sum, size;
public ResultType(int sum, int size) {
this.sum = sum;
this.size = size;
}
}
private TreeNode subtree = null;
private ResultType subtreeResult = null;
/**
* @param root the root of binary tree
* @return the root of the maximum average of subtree
*/
public TreeNode findSubtree2(TreeNode root) {
helper(root);
return subtree;
}
private ResultType helper(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return new ResultType(0, 0);
}
// 分治法计算左右子树的平均值
ResultType left = helper(root.left);
ResultType right = helper(root.right);
// 当前subtree的结果是左右两颗子树的和的平均值加上自身
ResultType result = new ResultType(
left.sum + right.sum + root.val,
left.size + right.size + 1
);
// 打擂台比较得到最大平均值的子树
if (subtree == null ||
subtreeResult.sum * result.size < result.sum * subtreeResult.size
) {
subtree = root;
subtreeResult = result;
}
return result;
}
}
Lowest Common Ancestor
Leetcode https://leetcode.cn/problems/lowest-common-ancestor-of-a-binary-tree/
Solution https://www.jiuzhang.com/problem/lowest-common-ancestor/
with parent pointer vs no parent pointer
follow up: LCA 2 && 3
Description
Given the root and two nodes in a Binary Tree. Find the lowest common ancestor(LCA) of the two nodes.
The lowest common ancestor is the node with largest depth which is the ancestor of both nodes.
Solutions
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
// Version : Divide & Conquer
public class Solution {
// 在root为根的二叉树中找A,B的LCA:
// 如果找到了就返回这个LCA
// 如果只碰到A,就返回A
// 如果只碰到B,就返回B
// 如果都没有,就返回null
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode node1, TreeNode node2) {
if (root == null || root == node1 || root == node2) {
return root;
}
// Divide
TreeNode left = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, node1, node2);
TreeNode right = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, node1, node2);
// Conquer
if (left != null && right != null) {
return root;
}
if (left != null) {
return left;
}
if (right != null) {
return right;
}
return null;
}
}
- 如果 A 和 B 都存在 root 下面,return lca(A, B)
- 如果 只有 A 在,return A
- 如果 只有 B 在,return B
- 如果都不在,return null
如果 TreeNode 存储了 parent 指针,就会更快的解决这个问题。
1
2
3
4
5
public class Solution {
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor() {
} // end lowestCommonAncestor
} // end Solution
Lowest Common Ancestor II
Description
Given the root and two nodes in a Binary Tree. Find the lowest common ancestor(LCA) of the two nodes.
The lowest common ancestor is the node with largest depth which is the ancestor of both nodes.
The node has an extra attribute parent which point to the father of itself. The root’s parent is null.
Example
For the following binary tree:
4
/ \
3 7
/ \
5 6
LCA(3, 5) =4
LCA(5, 6) =7
LCA(6, 7) =7
Solutions
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
/**
* Definition of ParentTreeNode:
*
* class ParentTreeNode {
* public ParentTreeNode parent, left, right;
* }
*/
public class Solution {
/**
* @param root: The root of the tree
* @param A, B: Two node in the tree
* @return: The lowest common ancestor of A and B
*/
public ParentTreeNode lowestCommonAncestorII(ParentTreeNode root,
ParentTreeNode A,
ParentTreeNode B) {
if(root == null || A == null || B == null) return null;
ArrayList<ParentTreeNode> pathA = getPathToRoot(A);
ArrayList<ParentTreeNode> pathB = getPathToRoot(B);
ParentTreeNode LCA = null;
int a = pathA.size() - 1;
int b = pathB.size() - 1;
while(a >= 0 && b >= 0) {
if(pathA.get(a) != pathB.get(b)) {
break;
}
LCA = pathA.get(a);
a--;
b--;
} // end while loop
return LCA;
} // end lowestCommonAncestorII
private ArrayList<ParentTreeNode> getPathToRoot(ParentTreeNode node) {
ArrayList<ParentTreeNode> path = new ArrayList();
if(node == null) {
return path;
}
while(node != null) {
path.add(node);
node = node.parent;
} // end while loop
return path;
} // end getPathToRoot
} // end Solution
Lowest Common Ancestor III
更好的程序风格,用 ResultType
Description
Given the root and two nodes in a Binary Tree. Find the lowest common ancestor(LCA) of the two nodes. The nearest common ancestor of two nodes refers to the nearest common node among all the parent nodes of two nodes (including the two nodes). Return null if LCA does not exist.
node A or node B may not exist in tree. Each node has a different value
Example1
Input:
{4, 3, 7, #, #, 5, 6}
3 5
5 6
6 7
5 8
Output:
4
7
7
null
Explanation:
4
/ \
3 7
/ \
5 6
LCA(3, 5) = 4
LCA(5, 6) = 7
LCA(6, 7) = 7
LCA(5, 8) = null
Example2
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
Input:
{1}
1 1
Output:
1
Explanation:
The tree is just a node, whose value is 1.
Solutions
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
/**
* Definition of TreeNode:
* public class TreeNode {
* public int val;
* public TreeNode left, right;
* public TreeNode(int val) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = this.right = null;
* }
* }
*/
class ResultType {
public boolean a_exist, b_exist;
public TreeNode node;
ResultType(boolean a, boolean b, TreeNode n) {
a_exist = a;
b_exist = b;
node = n;
}
}
public class Solution {
/**
* @param root The root of the binary tree.
* @param A and B two nodes
* @return: Return the LCA of the two nodes.
*/
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor3(TreeNode root, TreeNode A, TreeNode B) {
// write your code here
ResultType rt = helper(root, A, B);
if (rt.a_exist && rt.b_exist)
return rt.node;
else
return null;
} // end lowestCommonAncestor3
public ResultType helper(TreeNode root, TreeNode A, TreeNode B) {
if (root == null)
return new ResultType(false, false, null);
ResultType left_rt = helper(root.left, A, B);
ResultType right_rt = helper(root.right, A, B);
boolean a_exist = left_rt.a_exist || right_rt.a_exist || root == A;
boolean b_exist = left_rt.b_exist || right_rt.b_exist || root == B;
if (root == A || root == B)
return new ResultType(a_exist, b_exist, root);
if (left_rt.node != null && right_rt.node != null)
return new ResultType(a_exist, b_exist, root);
if (left_rt.node != null)
return new ResultType(a_exist, b_exist, left_rt.node);
if (right_rt.node != null)
return new ResultType(a_exist, b_exist, right_rt.node);
return new ResultType(a_exist, b_exist, null);
} // end helper
} // end Solution
Binary Search Tree
二叉查找树,简称“BST”,又名“二叉搜索树”“排序二叉树”
BST 基本性质
从定义出发:
- 左子树都比根节点小
- 右子树都不小于根节点
从效果出发:
- 中序遍历 in-order traversal 是“不下降”序列
性质:
- 如果一棵二叉树的中序遍历不是“不下降”序列,则一定不是BST
- 如果一颗二叉树的中序遍历是不下降,也未必是BST
Notes:
只有平衡二叉树(Balanced Binary Tree)高度是logn
Validate Binary Search Tree
Leetcode https://leetcode.cn/problems/validate-binary-search-tree/
Lintcode https://www.lintcode.com/problem/validate-binary-search-tree/
Solution https://www.jiuzhang.com/solutions/validate-binary-search-tree/
Traverse vs Divide Conquer
Description
Given a binary tree, determine if it is a valid binary search tree (BST).
Assume a BST is defined as follows:
- The left subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys less than the node’s key.
- The right subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys greater than the node’s key.
- Both the left and right subtrees must also be binary search trees.
- A single node tree is a BST
Example 1:
Input:
tree = {-1}
Output:
true
Explanation:
For the following binary tree(only one node):
-1
This is a binary search tree.
Example 2:
Input:
tree = {2,1,4,#,#,3,5}
Output:
true
Explanation:
For the following binary tree:
2
/ \
1 4
/ \
3 5
This is a binary search tree.
Solutions
- Divide Conquer
但是 minValue 和 maxValue 用 minNode 和 maxNode 来代替。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
/**
* Definition of TreeNode:
* public class TreeNode {
* public int val;
* public TreeNode left, right;
* public TreeNode(int val) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = this.right = null;
* }
* }
*/
class ResultType {
public boolean isBST;
public TreeNode maxNode, minNode;
public ResultType(boolean isBST) {
this.isBST = isBST;
this.maxNode = null;
this.minNode = null;
}
}
public class Solution {
/**
* @param root: The root of binary tree.
* @return: True if the binary tree is BST, or false
*/
public boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root) {
return divideConquer(root).isBST;
}
private ResultType divideConquer(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return new ResultType(true);
}
ResultType left = divideConquer(root.left);
ResultType right = divideConquer(root.right);
if (!left.isBST || !right.isBST) {
return new ResultType(false);
}
if (left.maxNode != null && left.maxNode.val >= root.val) {
return new ResultType(false);
}
if (right.minNode != null && right.minNode.val <= root.val) {
return new ResultType(false);
}
// is bst
ResultType result = new ResultType(true);
result.minNode = left.minNode != null ? left.minNode : root;
result.maxNode = right.maxNode != null ? right.maxNode : root;
return result;
}
}
- 采用非递归(Non-recursion / Iteration)版本的遍历法 时间复杂度O(n)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
public class Solution {
/**
* @param root: The root of binary tree.
* @return: True if the binary tree is BST, or false
*/
public boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root) {
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
while (root != null) {
stack.push(root);
root = root.left;
}
TreeNode lastNode = null;
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
// compare to last node
TreeNode node = stack.peek();
if (lastNode != null && lastNode.val >= node.val) {
return false;
}
lastNode = node;
// move to next
if (node.right == null) {
node = stack.pop();
while (!stack.isEmpty() && stack.peek().right == node) {
node = stack.pop();
}
} else {
node = node.right;
while (node != null) {
stack.push(node);
node = node.left;
}
}
}
return true;
}
}
- version 3 Divide and Conquer
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
public class Solution {
/**
* @param root: The root of binary tree.
* @return: True if the binary tree is BST, or false
*/
public boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root) {
// write your code here
return divConq(root, Long.MIN_VALUE, Long.MAX_VALUE);
} // end isBalidBST
private boolean divConq(TreeNode root, long min, long max){
if (root == null){
return true;
}
if (root.val <= min || root.val >= max){
return false;
}
return divConq(root.left, min, Math.min(max, root.val)) &&
divConq(root.right, Math.max(min, root.val), max);
} // end divConq
} // end Solution
Convert Binary Search Tree to Doubly Linked List
Lintcode https://www.lintcode.com/problem/1534/
Leetcode https://leetcode.com/problems/convert-binary-search-tree-to-sorted-doubly-linked-list/
Solution https://www.jiuzhang.com/problem/convert-binary-search-tree-to-doubly-linked-list/
Description
Convert a binary search tree to doubly linked list with in-order traversal.
Solutions
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
/**
* Definition of TreeNode:
* public class TreeNode {
* public int val;
* public TreeNode left, right;
* public TreeNode(int val) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = this.right = null;
* }
* }
* Definition for Doubly-ListNode.
* public class DoublyListNode {
* int val;
* DoublyListNode next, prev;
* DoublyListNode(int val) {
* this.val = val;
* this.next = this.prev = null;
* }
* }
*/
class ResultType {
DoublyListNode first, last;
public ResultType(DoublyListNode first, DoublyListNode last) {
this.first = first;
this.last = last;
}
}
public class Solution {
/**
* @param root: The root of tree
* @return: the head of doubly list node
*/
public DoublyListNode bstToDoublyList(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return null;
}
ResultType result = helper(root);
return result.first;
}
//中序遍历函数
public ResultType helper(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return null;
}
ResultType left = helper(root.left);
ResultType right = helper(root.right);
DoublyListNode node = new DoublyListNode(root.val);
ResultType result = new ResultType(null, null);
//构造单链表
if (left == null) {
result.first = node;
} else {
result.first = left.first;
left.last.next = node;
node.prev = left.last;
}
if (right == null) {
result.last = node;
} else {
result.last = right.last;
right.first.prev = node;
node.next = right.first;
}
return result;
}
}
- 根据二叉搜索树的中序遍历得到双向链表的节点值,最后构建一个新的双向链表即可。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
/**
* Definition of TreeNode:
* public class TreeNode {
* public int val;
* public TreeNode left, right;
* public TreeNode(int val) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = this.right = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
/**
* @param root: root of a tree
* @return: head node of a doubly linked list
*/
public TreeNode treeToDoublyList(TreeNode root) {
// Write your code here.
if (root == null) {
return null;
}
List<TreeNode> list = new ArrayList<>();
helper(root, list);
TreeNode head = list.get(0);
TreeNode tail = list.get(list.size() - 1);
head.left = tail;
tail.right = head;
return head;
}
private void helper(TreeNode node, List<TreeNode> list) {
if (node == null) {
return;
}
helper(node.left, list);
list.add(node);
if (list.size() >= 2) {
int n = list.size();
TreeNode a = list.get(n - 2);
TreeNode b = list.get(n - 1);
a.right = b;
b.left = a;
}
helper(node.right, list);
}
}
Flatten Binary Tree to Linked List
将二叉树拆成链表
Lintcode https://www.lintcode.com/problem/453/
Solution https://www.jiuzhang.com/problem/flatten-binary-tree-to-linked-list/
二叉树的结构变化的题目,依然用分治法!
Description
Flatten a binary tree to a fake “linked list” in pre-order traversal.
Here we use the right pointer in TreeNode as the next pointer in ListNode.
Don’t forget to mark the left child of each node to null. Or you will get Time Limit Exceeded or Memory Limit Exceeded.
Example 1:
Input:{1,2,5,3,4,#,6}
Output:{1,#,2,#,3,#,4,#,5,#,6}
Explanation:
1
/ \
2 5
/ \ \
3 4 6
1
\
2
\
3
\
4
\
5
\
6
Example 2:
1
2
3
4
5
Input:{1}
Output:{1}
Explanation:
1
1
Follow up
Do it in-place without any extra memory.
Solutions
- traversal
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
// solution 2: traversal
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
private TreeNode lastNode;
public void flatten(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
if (lastNode != null) {
lastNode.right = root;
lastNode.left = null;
}
lastNode = root;
TreeNode right = root.right;
flatten(root.left);
flatten(right);
}
}
- version 2 Divide and Conquer
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
// solution 1 : Divide & Conquer
class Solution {
public void flatten(TreeNode root) {
helper(root);
}
private TreeNode helper(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return null;
}
TreeNode leftLast = helper(root.left);
TreeNode rightLast = helper(root.right);
if (leftLast != null) {
leftLast.right = root.right;
root.right = root.left;
root.left = null;
}
if (rightLast != null) {
return rightLast;
}
if (leftLast != null) {
return leftLast;
}
return root;
}
}
Related Questions
- Binary Search Tree Iterator
- In-order Successor in Binary Search Tree
- Search Range in Binary Search Tree
- Insert Node in a Binary Search Tree
- Remove Node in a Binary Search Tree
Conclusions
- 用树形分析法计算时间复杂度
- 递归是深度优先搜索算法(DFS)的一种实现形式
- DFS可以使用非递归的方式实现
二叉树上的递归 Recursion in Binary Tree
遍历法 Traverse
分治法 Divide Conquer
二叉搜索树
性质:中序遍历是“不下降”序列
功能:O(h)的时间查找,删除,插入
- 必背程序:非递归版本的 preorder, inorder
- 分治法实际上是后序遍历序列。