Netty 核心模块组件
Netty 核心模块组件
6.1 Bootstrap、ServerBootstrap
Bootstrap意思是引导,一个Netty应用通常由一个Bootstrap开始,主要作用是配置整个Netty程序,串联各个组件,Netty中Bootstrap类是客户端程序的启动引导类,ServerBootstrap是服务端启动引导类。- 常见的方法有
public ServerBootstrap group(EventLoopGroup parentGroup, EventLoopGroup childGroup),该方法用于服务器端,用来设置两个EventLooppublic B group(EventLoopGroup group),该方法用于客户端,用来设置一个EventLooppublic B channel(Class<? extends C> channelClass),该方法用来设置一个服务器端的通道实现public <T> B option(ChannelOption<T> option, T value),用来给ServerChannel添加配置public <T> ServerBootstrap childOption(ChannelOption<T> childOption, T value),用来给接收到的通道添加配置public ServerBootstrap childHandler(ChannelHandler childHandler),该方法用来设置业务处理类(自定义的handler)public ChannelFuture bind(int inetPort),该方法用于服务器端,用来设置占用的端口号public ChannelFuture connect(String inetHost, int inetPort),该方法用于客户端,用来连接服务器端
6.2 Future、ChannelFuture
Netty 中所有的 IO 操作都是异步的,不能立刻得知消息是否被正确处理。但是可以过一会等它执行完成或者直接注册一个监听,具体的实现就是通过 Future 和 ChannelFutures,他们可以注册一个监听,当操作执行成功或失败时监听会自动触发注册的监听事件
常见的方法有
Channel channel(),返回当前正在进行IO操作的通道ChannelFuture sync(),等待异步操作执行完毕
6.3 Channel
Netty网络通信的组件,能够用于执行网络I/O操作。- 通过
Channel可获得当前网络连接的通道的状态 - 通过
Channel可获得网络连接的配置参数(例如接收缓冲区大小) Channel提供异步的网络I/O操作(如建立连接,读写,绑定端口),异步调用意味着任何I/O调用都将立即返回,并且不保证在调用结束时所请求的I/O操作已完成- 调用立即返回一个
ChannelFuture实例,通过注册监听器到ChannelFuture上,可以I/O操作成功、失败或取消时回调通知调用方 - 支持关联
I/O操作与对应的处理程序 - 不同协议、不同的阻塞类型的连接都有不同的
Channel类型与之对应,常用的Channel类型:NioSocketChannel,异步的客户端TCPSocket连接。NioServerSocketChannel,异步的服务器端TCPSocket连接。NioDatagramChannel,异步的UDP连接。NioSctpChannel,异步的客户端Sctp连接。NioSctpServerChannel,异步的Sctp服务器端连接,这些通道涵盖了UDP和TCP网络IO以及文件IO。
6.4 Selector
Netty基于Selector对象实现I/O多路复用,通过Selector一个线程可以监听多个连接的Channel事件。- 当向一个
Selector中注册Channel后,Selector内部的机制就可以自动不断地查询(Select)这些注册的Channel是否有已就绪的I/O事件(例如可读,可写,网络连接完成等),这样程序就可以很简单地使用一个线程高效地管理多个Channel
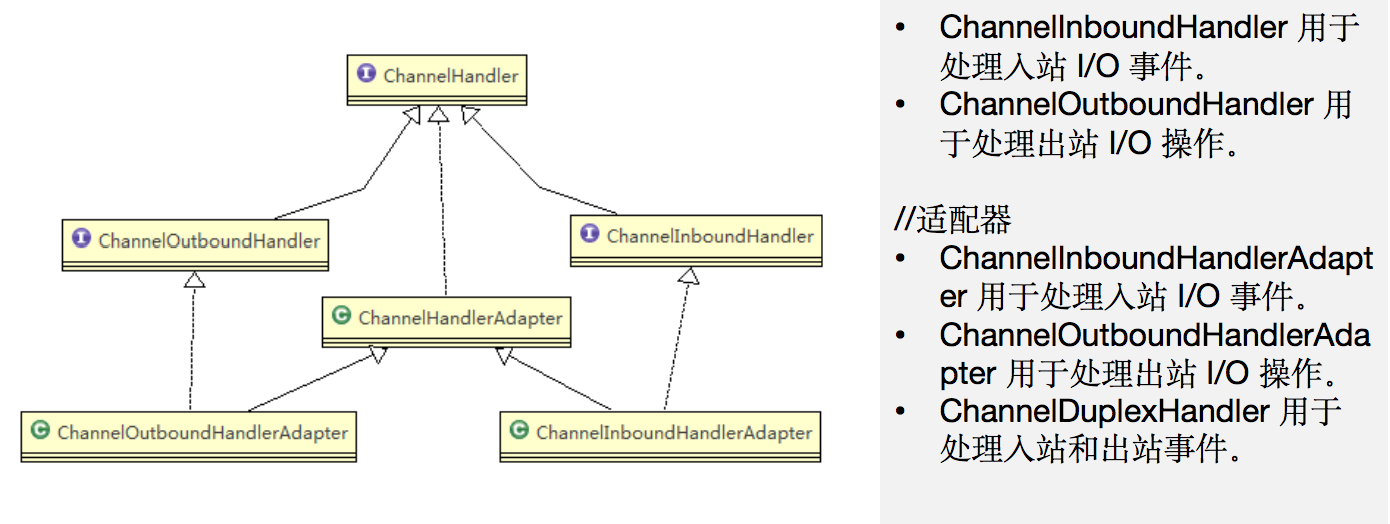
6.5 ChannelHandler 及其实现类
ChannelHandler是一个接口,处理I/O事件或拦截I/O操作,并将其转发到其ChannelPipeline(业务处理链)中的下一个处理程序。ChannelHandler本身并没有提供很多方法,因为这个接口有许多的方法需要实现,方便使用期间,可以继承它的子类ChannelHandler及其实现类一览图(后)
- 我们经常需要自定义一个
Handler类去继承ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter,然后通过重写相应方法实现业务逻辑,我们接下来看看一般都需要重写哪些方法
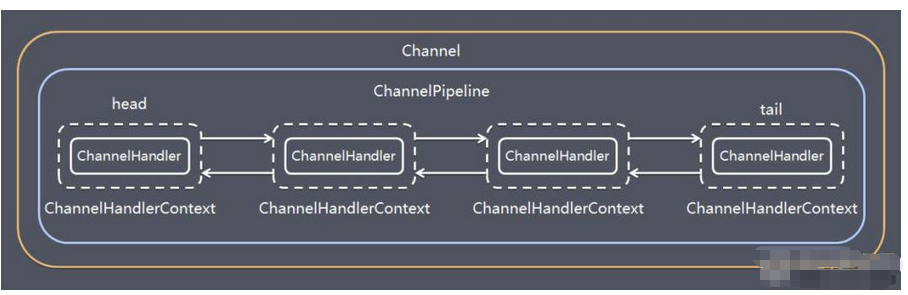
6.6 Pipeline 和 ChannelPipeline
ChannelPipeline 是一个重点:
ChannelPipeline是一个Handler的集合,它负责处理和拦截inbound或者outbound的事件和操作,相当于一个贯穿Netty的链。(也可以这样理解:ChannelPipeline是保存ChannelHandler的List,用于处理或拦截Channel的入站事件和出站操作)ChannelPipeline实现了一种高级形式的拦截过滤器模式,使用户可以完全控制事件的处理方式,以及Channel中各个的ChannelHandler如何相互交互- 在
Netty中每个Channel都有且仅有一个ChannelPipeline与之对应,它们的组成关系如下
- 常用方法
ChannelPipeline addFirst(ChannelHandler... handlers),把一个业务处理类(handler)添加到链中的第一个位置ChannelPipeline addLast(ChannelHandler... handlers),把一个业务处理类(handler)添加到链中的最后一个位置
6.7 ChannelHandlerContext
- 保存
Channel相关的所有上下文信息,同时关联一个ChannelHandler对象 - 即
ChannelHandlerContext中包含一个具体的事件处理器ChannelHandler,同时ChannelHandlerContext中也绑定了对应的pipeline和Channel的信息,方便对ChannelHandler进行调用。 - 常用方法
ChannelFuture close(),关闭通道ChannelOutboundInvoker flush(),刷新ChannelFuture writeAndFlush(Object msg),将数据写到ChannelPipeline中当前ChannelHandler的下一个ChannelHandler开始处理(出站)
6.8 ChannelOption
Netty在创建Channel实例后,一般都需要设置ChannelOption参数。ChannelOption参数如下:
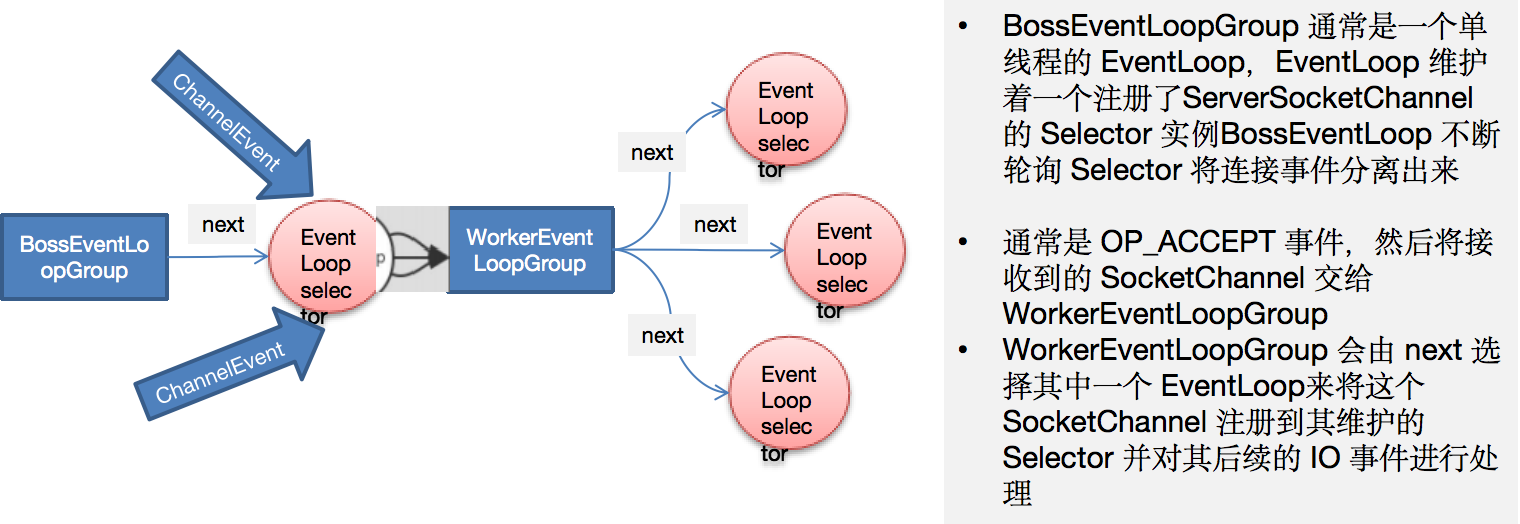
6.9 EventLoopGroup 和其实现类 NioEventLoopGroup
EventLoopGroup是一组EventLoop的抽象,Netty为了更好的利用多核CPU资源,一般会有多个EventLoop同时工作,每个EventLoop维护着一个Selector实例。EventLoopGroup提供next接口,可以从组里面按照一定规则获取其中一个EventLoop来处理任务。在Netty服务器端编程中,我们一般都需要提供两个EventLoopGroup,例如:BossEventLoopGroup和WorkerEventLoopGroup。- 通常一个服务端口即一个
ServerSocketChannel对应一个Selector和一个EventLoop线程。BossEventLoop负责接收客户端的连接并将SocketChannel交给WorkerEventLoopGroup来进行IO处理,如下图所示
- 常用方法
public NioEventLoopGroup(),构造方法public Future<?> shutdownGracefully(),断开连接,关闭线程
6.10 Unpooled 类
Netty提供一个专门用来操作缓冲区(即Netty的数据容器)的工具类- 常用方法如下所示
- 举例说明
Unpooled获取Netty的数据容器ByteBuf的基本使用【案例演示】
案例 1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
package com.atguigu.netty.buf;
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled;
public class NettyByteBuf01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建一个ByteBuf
//说明
//1. 创建 对象,该对象包含一个数组arr , 是一个byte[10]
//2. 在netty 的buffer中,不需要使用flip 进行反转
// 底层维护了 readerindex 和 writerIndex
//3. 通过 readerindex 和 writerIndex 和 capacity, 将buffer分成三个区域
// 0---readerindex 已经读取的区域
// readerindex---writerIndex , 可读的区域
// writerIndex -- capacity, 可写的区域
ByteBuf buffer = Unpooled.buffer(10);
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
buffer.writeByte(i);
}
System.out.println("capacity=" + buffer.capacity());//10
//输出
// for(int i = 0; i<buffer.capacity(); i++) {
// System.out.println(buffer.getByte(i));
// }
for (int i = 0; i < buffer.capacity(); i++) {
System.out.println(buffer.readByte());
}
System.out.println("执行完毕");
}
}
案例 2
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
package com.atguigu.netty.buf;
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled;
import java.nio.charset.Charset;
public class NettyByteBuf02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建ByteBuf
ByteBuf byteBuf = Unpooled.copiedBuffer("hello,world!", Charset.forName("utf-8"));
//使用相关的方法
if (byteBuf.hasArray()) { // true
byte[] content = byteBuf.array();
//将 content 转成字符串
System.out.println(new String(content, Charset.forName("utf-8")));
System.out.println("byteBuf=" + byteBuf);
System.out.println(byteBuf.arrayOffset()); // 0
System.out.println(byteBuf.readerIndex()); // 0
System.out.println(byteBuf.writerIndex()); // 12
System.out.println(byteBuf.capacity()); // 36
//System.out.println(byteBuf.readByte()); //
System.out.println(byteBuf.getByte(0)); // 104
int len = byteBuf.readableBytes(); //可读的字节数 12
System.out.println("len=" + len);
//使用for取出各个字节
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
System.out.println((char) byteBuf.getByte(i));
}
//按照某个范围读取
System.out.println(byteBuf.getCharSequence(0, 4, Charset.forName("utf-8")));
System.out.println(byteBuf.getCharSequence(4, 6, Charset.forName("utf-8")));
}
}
}
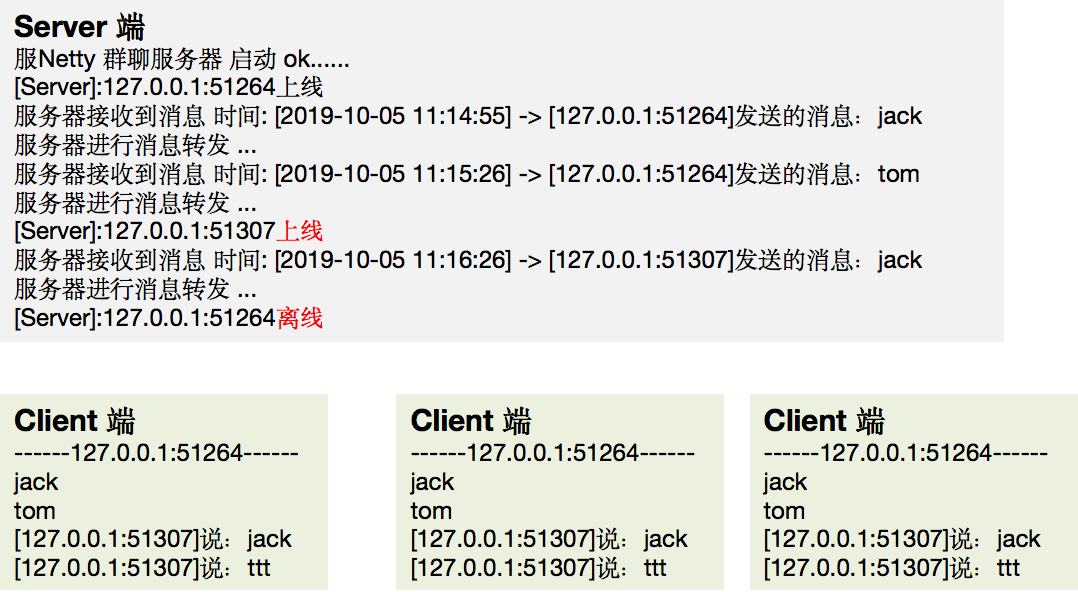
6.11 Netty 应用实例-群聊系统
实例要求:
- 编写一个
Netty群聊系统,实现服务器端和客户端之间的数据简单通讯(非阻塞) - 实现多人群聊
- 服务器端:可以监测用户上线,离线,并实现消息转发功能
- 客户端:通过
channel可以无阻塞发送消息给其它所有用户,同时可以接受其它用户发送的消息(有服务器转发得到) - 目的:进一步理解
Netty非阻塞网络编程机制 - 看老师代码演示
代码如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
220
221
222
223
224
225
226
227
228
229
230
231
232
233
234
235
236
237
238
239
240
package com.atguigu.netty.groupchat;
import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.*;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel;
import io.netty.handler.codec.string.StringDecoder;
import io.netty.handler.codec.string.StringEncoder;
public class GroupChatServer {
private int port; //监听端口
public GroupChatServer(int port) {
this.port = port;
}
//编写run方法,处理客户端的请求
public void run() throws Exception {
//创建两个线程组
EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(1);
EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(); //8个NioEventLoop
try {
ServerBootstrap b = new ServerBootstrap();
b.group(bossGroup, workerGroup)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 128)
.childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true)
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
//获取到pipeline
ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline();
//向pipeline加入解码器
pipeline.addLast("decoder", new StringDecoder());
//向pipeline加入编码器
pipeline.addLast("encoder", new StringEncoder());
//加入自己的业务处理handler
pipeline.addLast(new GroupChatServerHandler());
}
});
System.out.println("netty 服务器启动");
ChannelFuture channelFuture = b.bind(port).sync();
//监听关闭
channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} finally {
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
new GroupChatServer(7000).run();
}
}
package com.atguigu.netty.groupchat;
import io.netty.channel.Channel;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.channel.SimpleChannelInboundHandler;
import io.netty.channel.group.ChannelGroup;
import io.netty.channel.group.DefaultChannelGroup;
import io.netty.util.concurrent.GlobalEventExecutor;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
public class GroupChatServerHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<String> {
//public static List<Channel> channels = new ArrayList<Channel>();
//使用一个hashmap 管理
//public static Map<String, Channel> channels = new HashMap<String,Channel>();
//定义一个channle 组,管理所有的channel
//GlobalEventExecutor.INSTANCE) 是全局的事件执行器,是一个单例
private static ChannelGroup channelGroup = new DefaultChannelGroup(GlobalEventExecutor.INSTANCE);
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
//handlerAdded 表示连接建立,一旦连接,第一个被执行
//将当前channel 加入到 channelGroup
@Override
public void handlerAdded(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
Channel channel = ctx.channel();
//将该客户加入聊天的信息推送给其它在线的客户端
/*
该方法会将 channelGroup 中所有的channel 遍历,并发送 消息,
我们不需要自己遍历
*/
channelGroup.writeAndFlush("[客户端]" + channel.remoteAddress() + " 加入聊天" + sdf.format(new java.util.Date()) + " \n");
channelGroup.add(channel);
}
//断开连接, 将xx客户离开信息推送给当前在线的客户
@Override
public void handlerRemoved(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
Channel channel = ctx.channel();
channelGroup.writeAndFlush("[客户端]" + channel.remoteAddress() + " 离开了\n");
System.out.println("channelGroup size" + channelGroup.size());
}
//表示channel 处于活动状态, 提示 xx上线
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
System.out.println(ctx.channel().remoteAddress() + " 上线了~");
}
//表示channel 处于不活动状态, 提示 xx离线了
@Override
public void channelInactive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
System.out.println(ctx.channel().remoteAddress() + " 离线了~");
}
//读取数据
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, String msg) throws Exception {
//获取到当前channel
Channel channel = ctx.channel();
//这时我们遍历channelGroup, 根据不同的情况,回送不同的消息
channelGroup.forEach(ch -> {
if (channel != ch) { //不是当前的channel,转发消息
ch.writeAndFlush("[客户]" + channel.remoteAddress() + " 发送了消息" + msg + "\n");
} else {//回显自己发送的消息给自己
ch.writeAndFlush("[自己]发送了消息" + msg + "\n");
}
});
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
//关闭通道
ctx.close();
}
}
package com.atguigu.netty.groupchat;
import io.netty.bootstrap.Bootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.*;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioSocketChannel;
import io.netty.handler.codec.string.StringDecoder;
import io.netty.handler.codec.string.StringEncoder;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class GroupChatClient {
//属性
private final String host;
private final int port;
public GroupChatClient(String host, int port) {
this.host = host;
this.port = port;
}
public void run() throws Exception {
EventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap()
.group(group)
.channel(NioSocketChannel.class)
.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
//得到pipeline
ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline();
//加入相关handler
pipeline.addLast("decoder", new StringDecoder());
pipeline.addLast("encoder", new StringEncoder());
//加入自定义的handler
pipeline.addLast(new GroupChatClientHandler());
}
});
ChannelFuture channelFuture = bootstrap.connect(host, port).sync();
//得到channel
Channel channel = channelFuture.channel();
System.out.println("-------" + channel.localAddress() + "--------");
//客户端需要输入信息,创建一个扫描器
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
while (scanner.hasNextLine()) {
String msg = scanner.nextLine();
//通过channel 发送到服务器端
channel.writeAndFlush(msg + "\r\n");
}
} finally {
group.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
new GroupChatClient("127.0.0.1", 7000).run();
}
}
package com.atguigu.netty.groupchat;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.channel.SimpleChannelInboundHandler;
public class GroupChatClientHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<String> {
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, String msg) throws Exception {
System.out.println(msg.trim());
}
}
6.12 Netty 心跳检测机制案例
实例要求:
- 编写一个
Netty心跳检测机制案例,当服务器超过3秒没有读时,就提示读空闲 - 当服务器超过
5秒没有写操作时,就提示写空闲 - 实现当服务器超过
7秒没有读或者写操作时,就提示读写空闲 - 代码如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
package com.atguigu.netty.heartbeat;
import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelPipeline;
import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel;
import io.netty.handler.logging.LogLevel;
import io.netty.handler.logging.LoggingHandler;
import io.netty.handler.timeout.IdleStateHandler;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class MyServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//创建两个线程组
EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(1);
EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(); //8个NioEventLoop
try {
ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
serverBootstrap.group(bossGroup, workerGroup);
serverBootstrap.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class);
serverBootstrap.handler(new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.INFO));
serverBootstrap.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline();
//加入一个netty 提供 IdleStateHandler
/*
说明
1. IdleStateHandler 是netty 提供的处理空闲状态的处理器
2. long readerIdleTime : 表示多长时间没有读, 就会发送一个心跳检测包检测是否连接
3. long writerIdleTime : 表示多长时间没有写, 就会发送一个心跳检测包检测是否连接
4. long allIdleTime : 表示多长时间没有读写, 就会发送一个心跳检测包检测是否连接
5. 文档说明
triggers an {@link IdleStateEvent} when a {@link Channel} has not performed
* read, write, or both operation for a while.
* 6. 当 IdleStateEvent 触发后 , 就会传递给管道 的下一个handler去处理
* 通过调用(触发)下一个handler 的 userEventTiggered , 在该方法中去处理 IdleStateEvent(读空闲,写空闲,读写空闲)
*/
pipeline.addLast(new IdleStateHandler(7000, 7000, 10, TimeUnit.SECONDS));
//加入一个对空闲检测进一步处理的handler(自定义)
pipeline.addLast(new MyServerHandler());
}
});
//启动服务器
ChannelFuture channelFuture = serverBootstrap.bind(7000).sync();
channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} finally {
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}
package com.atguigu.netty.heartbeat;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter;
import io.netty.handler.timeout.IdleStateEvent;
public class MyServerHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
/**
* @param ctx 上下文
* @param evt 事件
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public void userEventTriggered(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object evt) throws Exception {
if (evt instanceof IdleStateEvent) {
//将 evt 向下转型 IdleStateEvent
IdleStateEvent event = (IdleStateEvent) evt;
String eventType = null;
switch (event.state()) {
case READER_IDLE:
eventType = "读空闲";
break;
case WRITER_IDLE:
eventType = "写空闲";
break;
case ALL_IDLE:
eventType = "读写空闲";
break;
}
System.out.println(ctx.channel().remoteAddress() + "--超时时间--" + eventType);
System.out.println("服务器做相应处理..");
//如果发生空闲,我们关闭通道
// ctx.channel().close();
}
}
}
6.13 Netty 通过 WebSocket 编程实现服务器和客户端长连接
实例要求:
Http协议是无状态的,浏览器和服务器间的请求响应一次,下一次会重新创建连接。- 要求:实现基于
WebSocket的长连接的全双工的交互 - 改变
Http协议多次请求的约束,实现长连接了,服务器可以发送消息给浏览器 - 客户端浏览器和服务器端会相互感知,比如服务器关闭了,浏览器会感知,同样浏览器关闭了,服务器会感知
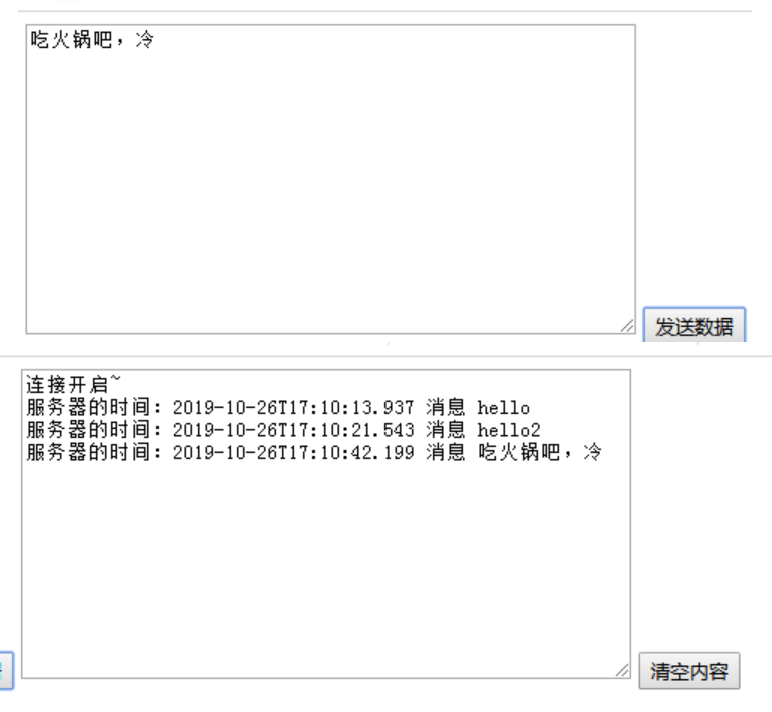
- 运行界面
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
package com.atguigu.netty.websocket;
import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelPipeline;
import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel;
import io.netty.handler.codec.http.HttpObjectAggregator;
import io.netty.handler.codec.http.HttpServerCodec;
import io.netty.handler.codec.http.websocketx.WebSocketServerProtocolHandler;
import io.netty.handler.logging.LogLevel;
import io.netty.handler.logging.LoggingHandler;
import io.netty.handler.stream.ChunkedWriteHandler;
public class MyServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//创建两个线程组
EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(1);
EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(); //8个NioEventLoop
try {
ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
serverBootstrap.group(bossGroup, workerGroup);
serverBootstrap.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class);
serverBootstrap.handler(new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.INFO));
serverBootstrap.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline();
//因为基于http协议,使用http的编码和解码器
pipeline.addLast(new HttpServerCodec());
//是以块方式写,添加ChunkedWriteHandler处理器
pipeline.addLast(new ChunkedWriteHandler());
/*
说明
1. http数据在传输过程中是分段, HttpObjectAggregator ,就是可以将多个段聚合
2. 这就就是为什么,当浏览器发送大量数据时,就会发出多次http请求
*/
pipeline.addLast(new HttpObjectAggregator(8192));
/*
说明
1. 对应websocket ,它的数据是以 帧(frame) 形式传递
2. 可以看到WebSocketFrame 下面有六个子类
3. 浏览器请求时 ws://localhost:7000/hello 表示请求的uri
4. WebSocketServerProtocolHandler 核心功能是将 http协议升级为 ws协议 , 保持长连接
5. 是通过一个 状态码 101
*/
pipeline.addLast(new WebSocketServerProtocolHandler("/hello2"));
//自定义的handler ,处理业务逻辑
pipeline.addLast(new MyTextWebSocketFrameHandler());
}
});
//启动服务器
ChannelFuture channelFuture = serverBootstrap.bind(7000).sync();
channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} finally {
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}
package com.atguigu.netty.websocket;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.channel.SimpleChannelInboundHandler;
import io.netty.handler.codec.http.websocketx.TextWebSocketFrame;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
//这里 TextWebSocketFrame 类型,表示一个文本帧(frame)
public class MyTextWebSocketFrameHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<TextWebSocketFrame> {
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, TextWebSocketFrame msg) throws Exception {
System.out.println("服务器收到消息 " + msg.text());
//回复消息
ctx.channel().writeAndFlush(new TextWebSocketFrame("服务器时间" + LocalDateTime.now() + " " + msg.text()));
}
//当web客户端连接后, 触发方法
@Override
public void handlerAdded(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
//id 表示唯一的值,LongText 是唯一的 ShortText 不是唯一
System.out.println("handlerAdded 被调用" + ctx.channel().id().asLongText());
System.out.println("handlerAdded 被调用" + ctx.channel().id().asShortText());
}
@Override
public void handlerRemoved(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
System.out.println("handlerRemoved 被调用" + ctx.channel().id().asLongText());
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
System.out.println("异常发生 " + cause.getMessage());
ctx.close(); //关闭连接
}
}
hello.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
var socket;
//判断当前浏览器是否支持websocket
if(window.WebSocket) {
//go on
socket = new WebSocket("ws://localhost:7000/hello2");
//相当于channelReado, ev 收到服务器端回送的消息
socket.onmessage = function (ev) {
var rt = document.getElementById("responseText");
rt.value = rt.value + "\n" + ev.data;
}
//相当于连接开启(感知到连接开启)
socket.onopen = function (ev) {
var rt = document.getElementById("responseText");
rt.value = "连接开启了.."
}
//相当于连接关闭(感知到连接关闭)
socket.onclose = function (ev) {
var rt = document.getElementById("responseText");
rt.value = rt.value + "\n" + "连接关闭了.."
}
} else {
alert("当前浏览器不支持websocket")
}
//发送消息到服务器
function send(message) {
if(!window.socket) { //先判断socket是否创建好
return;
}
if(socket.readyState == WebSocket.OPEN) {
//通过socket 发送消息
socket.send(message)
} else {
alert("连接没有开启");
}
}
</script>
<form onsubmit="return false">
<textarea name="message" style="height: 300px; width: 300px"></textarea>
<input type="button" value="发生消息" onclick="send(this.form.message.value)">
<textarea id="responseText" style="height: 300px; width: 300px"></textarea>
<input type="button" value="清空内容" onclick="document.getElementById('responseText').value=''">
</form>
</body>
</html>
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.