Lecture-8 Data Structure
Outline
Linear Data Structure
Queue
Stack
Hash
Tree Data Structure
- Heap
What is Data Structure?
Data Structure is a way to organize data.
It provides some methods to handle data stream,
e.g. insert, delete, etc.
Queue
Operations
- O(1) Push
- O(1) Pop
- O(1) Top
Core data structure for BFS!
java.util.Queue
boolean add(E element)boolean offer(E element)如果队列没有满,将给定的元素添加到这个队列的队尾并返回 true。如果队列已满,第一个方法将抛出一个 IllegalStateException,而第二个方法返回 false。E remove()E poll()假如队列不为空,删除并返回这个队列队头的元素。如果队列是空的,第一个方法抛出 NoSuchElementException,而第二个方法返回 null。E element()E peek()如果队列不为空,返回这个队列队头的元素,但不删除。如果队列空,第一个方法将抛出一个 NoSuchElementException,而第二个方法返回 null。
Stack
Operations:
- O(1) Push
- O(1) Pop
- O(1) Top
java.util.Stack
E push(E item)将 item 压入栈并返回 item。E pop()弹出并返回栈顶的 item。如果栈为空,不要调用这个方法。E peek()返回栈顶元素,但不弹出。如果栈为空,不要调用这个方法。
Min Stack
Lintcode https://www.lintcode.com/problem/min-stack/
Leetcode https://leetcode.com/problems/min-stack/
Solution https://www.jiuzhang.com/solutions/min-stack/
Description
Design a stack that supports push, pop, top, and retrieving the minimum element in constant time.
Implement the MinStack class:
- MinStack() initializes the stack object.
- void push(int val) pushes the element val onto the stack.
- void pop() removes the element on the top of the stack.
- int top() gets the top element of the stack.
- int getMin() retrieves the minimum element in the stack.
You must implement a solution with O(1) time complexity for each function.
Example 1:
Input [“MinStack”,”push”,”push”,”push”,”getMin”,”pop”,”top”,”getMin”] [[],[-2],[0],[-3],[],[],[],[]]
Output [null,null,null,null,-3,null,0,-2]
Explanation MinStack
minStack = new MinStack();
minStack.push(-2);
minStack.push(0);
minStack.push(-3);
minStack.getMin(); // return -3
minStack.pop();
minStack.top(); // return 0
minStack.getMin(); // return -2
Constraints:
- -231 <= val <= 231 - 1
- Methods pop, top and getMin operations will always be called on non-empty stacks.
- At most 3 * 104 calls will be made to push, pop, top, and getMin.
Solutions
使用两个仅支持 pop 和 push 的栈就可以完成, stack 储存压入的数据, minStack 储存最小值.
- push 直接把元素压入 stack, 对于 minStack, 如果它为空则直接压入, 反之压入当前元素与 minStack 栈顶的最小值
- pop 两个栈都弹出一个元素, 返回 stack 弹出的元素
- min 返回 minStack 的栈顶
还可以令 minStack 为单调栈, 即push时只有元素更小的时候才放入这个栈, 而pop时只有栈顶与stack栈顶相同时才弹出
这样可以节约一定的空间, 但是实质上空间复杂度仍然是 O(n), 且多了一些判断, 并不一定更优
version 1:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
public class MinStack {
private Stack<Integer> stack;
private Stack<Integer> minStack;
public MinStack() {
stack = new Stack<Integer>();
minStack = new Stack<Integer>();
}
public void push(int number) {
stack.push(number);
if (minStack.isEmpty()) {
minStack.push(number);
} else {
minStack.push(Math.min(number, minStack.peek()));
}
}
public int pop() {
minStack.pop();
return stack.pop();
}
public int min() {
return minStack.peek();
}
}
version 2, save more space. but space complexity doesn’t change.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
public class MinStack {
private Stack<Integer> stack;
private Stack<Integer> minStack;
public MinStack() {
stack = new Stack<Integer>();
minStack = new Stack<Integer>();
}
public void push(int number) {
stack.push(number);
if (minStack.empty() == true)
minStack.push(number);
else if (minStack.peek() >= number) // 这里考虑的相等的情况也会继续push
minStack.push(number);
}
public int pop() {
if (stack.peek().equals(minStack.peek()))
minStack.pop();
return stack.pop();
}
public int min() {
return minStack.peek();
}
}
Implement Queue by Two Stacks
面试官一般就说一句话“你用栈实现一个队列”
(可以用两个!!)
Lintcode https://www.lintcode.com/problem/implement-queue-by-two-stacks/
Leetcode https://leetcode.com/problems/implement-queue-using-stacks/
SoluLtion https://www.jiuzhang.com/solutions/implement-queue-by-two-stacks/
Description
Implement a first in first out (FIFO) queue using only two stacks. The implemented queue should support all the functions of a normal queue (push, peek, pop, and empty).
Implement the MyQueue class:
- void push(int x) Pushes element x to the back of the queue.
- int pop() Removes the element from the front of the queue and returns it.
- int peek() Returns the element at the front of the queue.
- boolean empty() Returns true if the queue is empty, false otherwise.
Notes:
- You must use only standard operations of a stack, which means only push to top, peek/pop from top, size, and is empty operations are valid.
- Depending on your language, the stack may not be supported natively. You may simulate a stack using a list or deque (double-ended queue) as long as you use only a stack’s standard operations.
Example 1:
Input [“MyQueue”, “push”, “push”, “peek”, “pop”, “empty”] [[], [1], [2], [], [], []]
Output [null, null, null, 1, 1, false]
Explanation
MyQueue myQueue = new MyQueue();
myQueue.push(1); // queue is: [1]
myQueue.push(2); // queue is: [1, 2] (leftmost is front of the queue)
myQueue.peek(); // return 1
myQueue.pop(); // return 1, queue is [2]
myQueue.empty(); // return false
Constraints:
- 1 <= x <= 9
- At most 100 calls will be made to push, pop, peek, and empty.
- All the calls to pop and peek are valid.
Follow-up: Can you implement the queue such that each operation is amortized O(1) time complexity? In other words, performing n operations will take overall O(n) time even if one of those operations may take longer.
Solutions
push加入到栈中 top即从A栈出到B栈,执行完之后,B栈push出栈顶元素,作为返回值,然后继续入站栈,最后B栈出,返回A栈。 pop即从A栈出到B栈,执行完之后,B栈push出栈顶元素,然后B栈依次出,返回A栈。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
public class MyQueue {
private Stack<Integer> stack1;
private Stack<Integer> stack2;
public MyQueue() {
stack1 = new Stack<Integer>();
stack2 = new Stack<Integer>();
}
private void stack2ToStack1(){
while(! stack2.isEmpty()){
stack1.push(stack2.pop());
}
}
public void push(int element) {
stack2.push(element);
}
public int pop() {
if(stack1.empty() == true){
this.stack2ToStack1();
}
return stack1.pop();
}
public int top() {
if(stack1.empty() == true){
this.stack2ToStack1();
}
return stack1.peek();
}
}
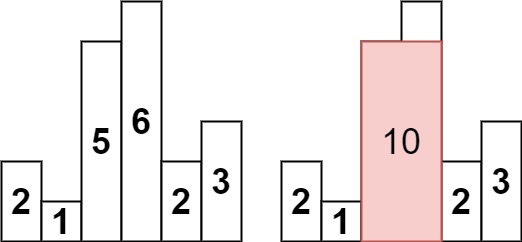
Largest Rectangle in Histogram
直方图的最大子矩阵
一道题经典的栈的运用。
Lintcode https://www.lintcode.com/problem/largest-rectangle-in-histogram/
Leetcode https://leetcode.com/problems/largest-rectangle-in-histogram/
Solution https://www.jiuzhang.com/solutions/largest-rectangle-in-histogram/
Description
Given an array of integers heights representing the histogram’s bar height where the width of each bar is 1, return the area of the largest rectangle in the histogram.
Example 1:
Input: heights = [2, 1, 5, 6, 2, 3]
Output: 10
Explanation: The above is a histogram where width of each bar is 1. The largest rectangle is shown in the red area, which has an area = 10 units.
Example 2:
Input: heights = [2, 4]
Output: 4
Constraints:
- 1 <= heights.length <= 10^5
- 0 <= heights[i] <= 10^4
Solutions
递增栈 / 递减栈
单调栈
单调栈专门就是来解决 O(n^2) => O(n) / O(nlogn)
而DP解决的是 => O(2^n) => O(n^2) 就是指数级到多项式
O(nlogn)
- 排序,nlogn,n*二分
- 借助一个logn的数据结构 heap / priority queue
单调栈的核心思想,是及时去掉无用数据。
用九章算法强化班中讲过的单调栈(stack)。维护一个单调递增栈,逐个将元素 push 到栈里。push 进去之前先把 >= 自己的元素 pop 出来。 每次从栈中 pop 出一个数的时候,就找到了往左数比它小的第一个数(当前栈顶)和往右数比它小的第一个数(即将入栈的数), 从而可以计算出这两个数中间的部分宽度 * 被pop出的数,就是以这个被pop出来的数为最低的那个直方向两边展开的最大矩阵面积。 因为要计算两个数中间的宽度,因此放在 stack 里的是每个数的下标。
考点:单调栈 很tricky
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
public class Solution {
public int largestRectangleArea(int[] height) {
if (height == null || height.length == 0) {
return 0;
}
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<Integer>(); //维护单调递增
int max = 0;
for (int i = 0; i <= height.length; i++) {
int curt = (i == height.length) ? -1 : height[i];
while (!stack.isEmpty() && curt <= height[stack.peek()]) { //如果栈顶高度大于当前高度
int h = height[stack.pop()]; //保存栈顶元素信息
int w = stack.isEmpty() ? i : i - stack.peek() - 1; //如果栈已经为空,宽度为i,否则i-s.top()-1
max = Math.max(max, h * w);
}
stack.push(i); //压入栈中
}
return max;
}
}
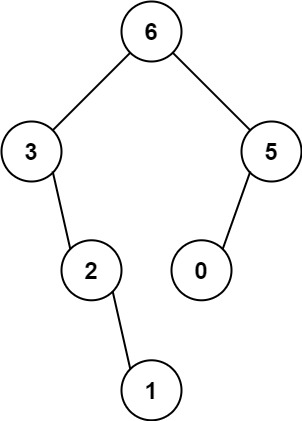
Max Tree
Lintcode https://www.lintcode.com/problem/max-tree/
Leetcode https://leetcode.com/problems/maximum-binary-tree/
Solution https://www.jiuzhang.com/solutions/max-tree/
Description
You are given an integer array nums with no duplicates. A maximum binary tree can be built recursively from nums using the following algorithm:
- Create a root node whose value is the maximum value in nums.
- Recursively build the left subtree on the subarray prefix to the left of the maximum value.
- Recursively build the right subtree on the subarray suffix to the right of the maximum value.
Return the maximum binary tree* *built from nums.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [3,2,1,6,0,5] Output: [6,3,5,null,2,0,null,null,1]
Explanation: The recursive calls are as follow:
The largest value in [3,2,1,6,0,5] is 6. Left prefix is [3,2,1] and right suffix is [0,5].
The largest value in [3,2,1] is 3. Left prefix is [] and right suffix is [2,1].
Empty array, so no child.
The largest value in [2,1] is 2. Left prefix is [] and right suffix is [1].
- Empty array, so no child.
- Only one element, so child is a node with value 1.
- Empty array, so no child.
The largest value in [0,5] is 5. Left prefix is [0] and right suffix is [].
Only one element, so child is a node with value 0.
Empty array, so no child.
Example 2:
Input: nums = [3, 2, 1]
Output: [3, null, 2, null, 1]
Constraints:
- 1 <= nums.length <= 1000
- 0 <= nums[i] <= 1000
- All integers in nums are unique.
Solutions
考点:
- 数据结构设计
- 树的调整
- 单调栈
题解: 利用数组实现基本数据结构的调整,当前遍历到的数字比stk中的最后一个大时,将stk中的最后一个数字转变为当前节点的左子树,循环调整至stk为空或者stk中的最后节点值大于新节点的值。如果stk不为空,说明stk中的最后一个节点值大于新节点值,则将新节点设为stk中的最后一个节点的右子树,将新节点存入stk。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
/**
* Definition of TreeNode: public class TreeNode { public int val; public
* TreeNode left, right; public TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; this.left =
* this.right = null; } }
*/
public class Solution {
/**
* @param A
* : Given an integer array with no duplicates.
* @return: The root of max tree.
*/
public static TreeNode maxTree(int[] A) {
// write your code here
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<TreeNode>(); //申请栈存放节点
TreeNode root = null;
for (int i = 0; i <= A.length; i++) {
TreeNode right = i == A.length ? new TreeNode(Integer.MAX_VALUE) //如果i==length,新建节点设置值为无穷大,否则值为A[i]
: new TreeNode(A[i]);
while (!stack.isEmpty()) { //如果栈不为空
if (right.val > stack.peek().val) { //如果新建节点的值比栈顶大
TreeNode nodeNow = stack.pop(); //临时保存栈顶节点并弹出
if (stack.isEmpty()) { //如果栈为空
right.left = nodeNow; //临时保存的栈顶的节点是当前新建节点的左子树
} else {
TreeNode left = stack.peek();
if (left.val > right.val) {
right.left = nodeNow; //新建节点的左子树为临时保存节点
} else {
left.right = nodeNow; //当前栈顶的节点的右子树为新建节点
}
}
} else
break;
}
stack.push(right); //将新建节点压入栈中
}
return stack.peek().left;
}
}
/**
* Definition of TreeNode:
* public class TreeNode {
* public int val;
* public TreeNode left, right;
* public TreeNode(int val) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = this.right = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
/**
* @param A: Given an integer array with no duplicates.
* @return: The root of max tree.
*/
public TreeNode maxTree(int[] A) {
// write your code here
int len = A.length;
TreeNode[] stk = new TreeNode[len];
for (int i = 0; i < len; ++i)
stk[i] = new TreeNode(0); //新建节点
int cnt = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < len; ++i) {
TreeNode tmp = new TreeNode(A[i]);
while (cnt > 0 && A[i] > stk[cnt-1].val) { //如果stk中的最后一个节点比新节点大
tmp.left = stk[cnt-1]; //当前新节点的左子树为stk的最后一个节点
cnt --;
}
if (cnt > 0) //如果stk不为空
stk[cnt - 1].right = tmp; //将新节点设为stk最后一个节点的右子树
stk[cnt++] = tmp;
}
return stk[0];
}
}
Hash
如果你用到了 HashMap,面试官就有可能追问
- HashMap 的具体实现是什么?
- 你能不能自己写一个 HashMap?
- HashMap 是怎么解决冲突问题的?
- Hash 为什么是 O(1) 的?
Operations
- O(1) Insert
- O(1) Delete
- O(1) Find
Hash Function
Collision
- Open Hashing (LinkedList)
- Closed Hashing (ArrayList)
Hash Function
Typical: From string to int.
1
2
3
4
5
int hashfunc(String key) {
// do something to key
// return a deterministic integer number
return md5(key) % hash_table_size;
}
Hash Function - Magic Number 33
有的库实现的时候会取31
这段是Apache的一个底层库扒下来的。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
int hashfunc(String key) {
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < key.length(); i++) {
sum = sum * 33 + (int)(key.charAt(i));
sum = sum % HASH_TABLE_SIZE;
}
return sum;
}
尽量不要不同的 Key 算出一个同样的结果出来,要尽量避免这个事情。
Collision
Open Hashing vs Closed Hashing
- 让链表长度尽量的小,让整个数组大一点,那么冲突出现的概率就会小一点
- 哈希函数设计的巧妙一点
Open Hashing
开放寻址法
Closed Hashing
类比上厕所,你占了我的坑,我去看看下一个坑是不是空的,如果是空的,我去占其他人的坑。
Rehashing
https://www.lintcode.com/problem/rehashing/
https://www.lintcode.com/problem/hash-function/
Hash in Java
- HashTable
- HashSet
- HashMap
Which on is Thread Safe? Ans: HashTable
java.util.HashSet
HashSet()构造一个空散列集。HashSet(Collection<? extends E> elements)构造一个散列集,并将集合中的所有元素添加到这个散列集中。HashSet(int initialCapacity)构造一个空的具有指定容量(桶数)的散列集。HashSet(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor)构造一个有指定容量和装填因子(0.0 ~ 1.0 之间的一个数,确定散列表填充的百分比,当大于这个百分比时,散列表进行再散列)的空散列集。
java.lang.Object
int hashCode()返回这个对象的散列码。散列码可以是任何整数,包括正数或负数。equals 和 hashCode 的定义必须兼容,即如果 x.equals(y) 为 true,x.hashCode() 必须等于 y.hashCode()。
java.util.Map<K, V>
- V get(Object key) 获取与键关联值;返回与键关联的对象,或者如果映射中没有这个对象,则返回 null。实现类可以禁止键位 null。
default V getOrDefault(Object key, V defaultValue)获得与键关联的值;返回与键关联的对象 ,或者如果未在映射中找到这个键,则返回 defaultValue。V put(K key, V value)将关联的一对键和值放到映射中。如果这个键已经存在 ,新对象将取代与这个键关联的旧对象。这个方法将返回键关联的旧值。如果之前没有这个键,则返回 null。实现类可以禁止键或值为 null。void putAll(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> entries)将指定映射中的所有映射条目添加到这个映射中。boolean containsKey(Object key)如果在映射中已经有这个键,返回 true。boolean containsValue(Object value)如果在映射中已经有这个值,返回 true。default void forEach(BiConsumer<? super K,? super V> action)对这个映射中的所有键 / 值对应用这个动作。
java.util.HashMap<K, V>
HashMap()HashMap(int initialCapacity)HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor)用给定的容量和装填因子构造一个空散列映射(装填因子时一个 0.0 ~ 1.0 之间的数。这个数决定散列表填充的百分比。一旦到了这个比例,就要将其再散列到更大的散列表中)。默认的装填因子时 0.75。
java.util.HashTable<K, V>
HashTable 是在集合框架出现之前已经存在的大量“遗留的”容器类。
HashTable 与 HashMap 作用相同,接口也基本相同,是同步的,但是推荐使用 HashMap。
如果需要并发访问,则要使用 ConcurrentHashMap.
LRU Cache
这道题一定要会做!!
Lintcode https://www.lintcode.com/problem/lru-cache/
Leetcode https://leetcode.com/problems/lru-cache/
Solution https://www.jiuzhang.com/solutions/lru-cache/
Example: [2 1 3 2 5 3 6 7]
Description
Design a data structure that follows the constraints of a Least Recently Used (LRU) cache.
Implement the LRUCache class:
- LRUCache(int capacity) Initialize the LRU cache with positive size capacity.
- int get(int key) Return the value of the key if the key exists, otherwise return -1.
- void put(int key, int value) Update the value of the key if the key exists. Otherwise, add the key-value pair to the cache. If the number of keys exceeds the capacity from this operation, evict the least recently used key.
The functions get and put must each run in O(1) average time complexity.
Example 1:
Input [“LRUCache”, “put”, “put”, “get”, “put”, “get”, “put”, “get”, “get”, “get”] [[2], [1, 1], [2, 2], [1], [3, 3], [2], [4, 4], [1], [3], [4]]
Output [null, null, null, 1, null, -1, null, -1, 3, 4]
Explanation LRUCache
lRUCache = new LRUCache(2);
lRUCache.put(1, 1); // cache is {1=1}
lRUCache.put(2, 2); // cache is {1=1, 2=2}
lRUCache.get(1); // return 1
lRUCache.put(3, 3); // LRU key was 2, evicts key 2, cache is {1=1, 3=3}
lRUCache.get(2); // returns -1 (not found)
lRUCache.put(4, 4); // LRU key was 1, evicts key 1, cache is {4=4, 3=3}
lRUCache.get(1); // return -1 (not found)
lRUCache.get(3); // return 3
lRUCache.get(4); // return 4
Constraints:
- 1 <= capacity <= 3000
- 0 <= key <= 10^4
- 0 <= value <= 10^5
- At most 2 * 10^5 calls will be made to get and put.
Solutions
LinkedHashMap = DoublyLinkedList + HashMap
1
2
3
HashMap<key, DoublyListNode> DoublyListNode {
prev, next, key, value;
}
Newest node append to tail.
Eldest node remove from head.
LinkedHashMap
但是面试的时候,还是用 LinkedList 和 HashMap 来实现。
Singly Linked List 的版本
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
public class LRUCache {
class ListNode {
public int key, val;
public ListNode next;
public ListNode(int key, int val) {
this.key = key;
this.val = val;
this.next = null;
}
}
private int capacity, size;
private ListNode dummy, tail;
private Map<Integer, ListNode> keyToPrev;
/*
* @param capacity: An integer
*/
public LRUCache(int capacity) {
this.capacity = capacity;
this.keyToPrev = new HashMap<Integer, ListNode>();
this.dummy = new ListNode(0, 0);
this.tail = this.dummy;
}
private void moveToTail(int key) {
ListNode prev = keyToPrev.get(key);
ListNode curt = prev.next;
if (tail == curt) {
return;
}
prev.next = prev.next.next;
tail.next = curt;
curt.next = null;
if (prev.next != null) {
keyToPrev.put(prev.next.key, prev);
}
keyToPrev.put(curt.key, tail);
tail = curt;
}
/*
* @param key: An integer
* @return: An integer
*/
public int get(int key) {
if (!keyToPrev.containsKey(key)) {
return -1;
}
moveToTail(key);
// the key has been moved to the end
return tail.val;
}
/*
* @param key: An integer
* @param value: An integer
* @return: nothing
*/
public void set(int key, int value) {
// get method will move the key to the end of the linked list
if (get(key) != -1) {
ListNode prev = keyToPrev.get(key);
prev.next.val = value;
return;
}
if (size < capacity) {
size++;
ListNode curt = new ListNode(key, value);
tail.next = curt;
keyToPrev.put(key, tail);
tail = curt;
return;
}
// replace the first node with new key, value
ListNode first = dummy.next;
keyToPrev.remove(first.key);
first.key = key;
first.val = value;
keyToPrev.put(key, dummy);
moveToTail(key);
}
}
涉及删除和移动操作,使用链表,链表是有序的,一直维护,近期最多使用的放于尾部,那么每次缓存达到上限的时候,删除头部即可,其余为链表的基础操作模拟即可。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
public class LRUCache {
private class Node{
Node prev;
Node next;
int key;
int value;
public Node(int key, int value) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.prev = null;
this.next = null;
}
}
private int capacity;
private HashMap<Integer, Node> hs = new HashMap<Integer, Node>();
private Node head = new Node(-1, -1);
private Node tail = new Node(-1, -1);
public LRUCache(int capacity) {
this.capacity = capacity;
tail.prev = head;
head.next = tail;
}
public int get(int key) {
if( !hs.containsKey(key)) { //key找不到
return -1;
}
// remove current
Node current = hs.get(key);
current.prev.next = current.next;
current.next.prev = current.prev;
// move current to tail
move_to_tail(current); //每次get,使用次数+1,最近使用,放于尾部
return hs.get(key).value;
}
public void set(int key, int value) { //数据放入缓存
// get 这个方法会把key挪到最末端,因此,不需要再调用 move_to_tail
if (get(key) != -1) {
hs.get(key).value = value;
return;
}
if (hs.size() == capacity) { //超出缓存上限
hs.remove(head.next.key); //删除头部数据
head.next = head.next.next;
head.next.prev = head;
}
Node insert = new Node(key, value); //新建节点
hs.put(key, insert);
move_to_tail(insert); //放于尾部
}
private void move_to_tail(Node current) { //移动数据至尾部
current.prev = tail.prev;
tail.prev = current;
current.prev.next = current;
current.next = tail;
}
}
Related Questions
https://www.lintcode.com/problem/subarray-sum/
https://www.lintcode.com/problem/copy-list-with-random-pointer/
https://www.lintcode.com/problem/anagrams/
https://www.lintcode.com/problem/longest-consecutive-sequence/
Heap
Operations
- O(logN) Add
- O(logN) Remove
O(1) Min/Max
- [] 整理这个位置的相关知识
Median Number
Lintcode https://www.lintcode.com/problem/data-stream-median/
Solution https://www.jiuzhang.com/solutions/median-in-data-stream/
Related Questions
https://www.lintcode.com/problem/heapify/
heapify 是帮助你理解堆的具体的存储时怎么存的
https://www.lintcode.com/problem/merge-k-sorted-lists/
https://www.lintcode.com/problem/merge-k-sorted-arrays/
https://www.lintcode.com/problem/ugly-number/