Lecture-4 Dynamic Programming I
不是非常top的公司,merge sort 和 quick sort 都要必须会,网上资料非常多了,自己学会。
如果需要return多个结果的时候,那你可能就需要包装一个ResultType来返回结果了。
- 从递归到动规 - Triangle
- 什么样的题适合使用动态规划?
- 当我们谈论动态规划的时候,我们在谈论什么?
- 面试中常见动态规划的分类
- 坐标(矩阵)动态规划
我更愿意说动态规划是一种思想,不是一种算法。
每道动态规划题目解法不一样,但是蕴含的思想是一样的。
Triangle
Lintcode https://www.lintcode.com/problem/triangle/
Leetcode https://leetcode.cn/problems/triangle
Solution https://www.jiuzhang.com/solutions/triangle/
解决方法:
- DFS: Traverse
- DFS: Divide Conquer
- Divide Conquer + Memorization
- Traditional Dynamic Programming
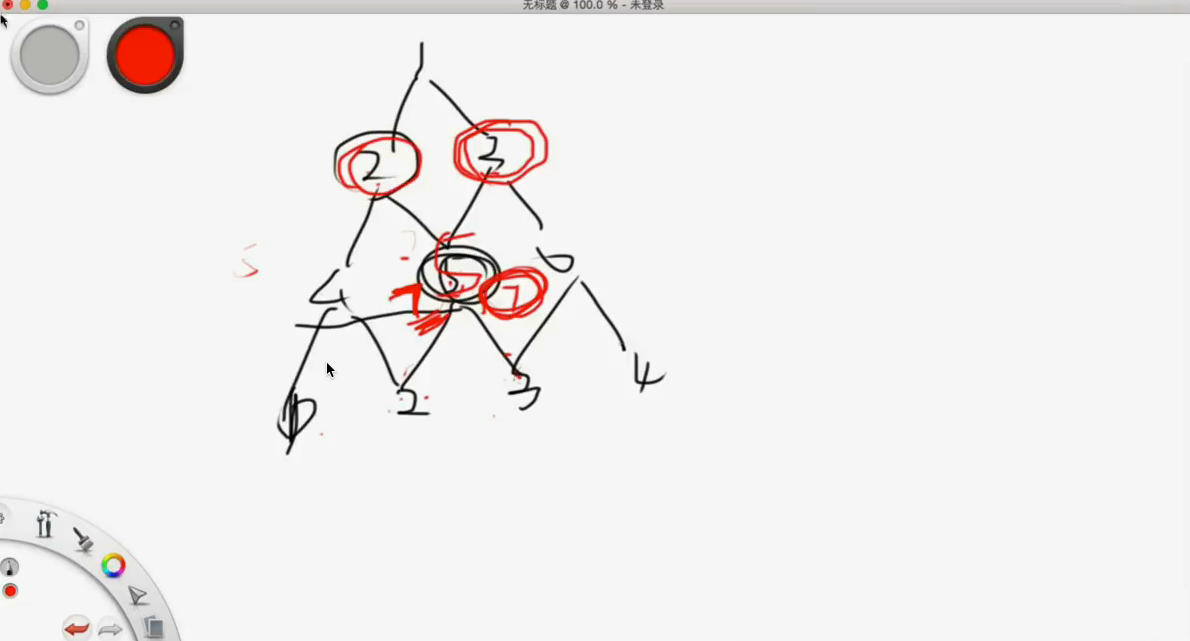
数字三角形,是我比较喜欢的一道入门题了。
这道题求最小,但是让你求最大也是没问题的
Description
Given a triangle array, return the minimum path sum from top to bottom. For each step, you may move to an adjacent number of the row below. More formally, if you are on index i on the current row, you may move to either index i or index i + 1 on the next row.
Example 1:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
Input: triangle = [[2],[3,4],[6,5,7],[4,1,8,3]]
Output: 11
Explanation: The triangle looks like:
2
3 4
6 5 7
4 1 8 3
The minimum path sum from top to bottom is 2 + 3 + 5 + 1 = 11 (underlined above).
Example 2:
1
2
Input: triangle = [[-10]]
Output: -10
Constraints:
- 1 <= triangle.length <= 200
- triangle[0].length == 1
- triangle[i].length == triangle[i - 1].length + 1
- -104 <= triangle[i][j] <= 104
Follow up
Could you do this using only O(n) extra space, where n is the total number of rows in the triangle?
DFS: Traverse
Depth-First Search
时间复杂度是:
A - O(n^2) / B - O(2^n) / C - (n!) / D - I don’t know.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
void traverse(int x, int y, int sum) {
if (x == n) {
// found a whole path from top to bottom
if (sum < best) {
best = sum;
}
return;
}
traverse(x + 1, y, sum + A[x][y]);
traverse(x + 1, y + 1, sum + A[x][y]);
}
best = MAXINT;
traverse(0, 0, 0);
// best is the answer
如果我们想把所有路径都找出来的话,可以用这个递归的方法。
这个复杂度仍然是O(2^n) 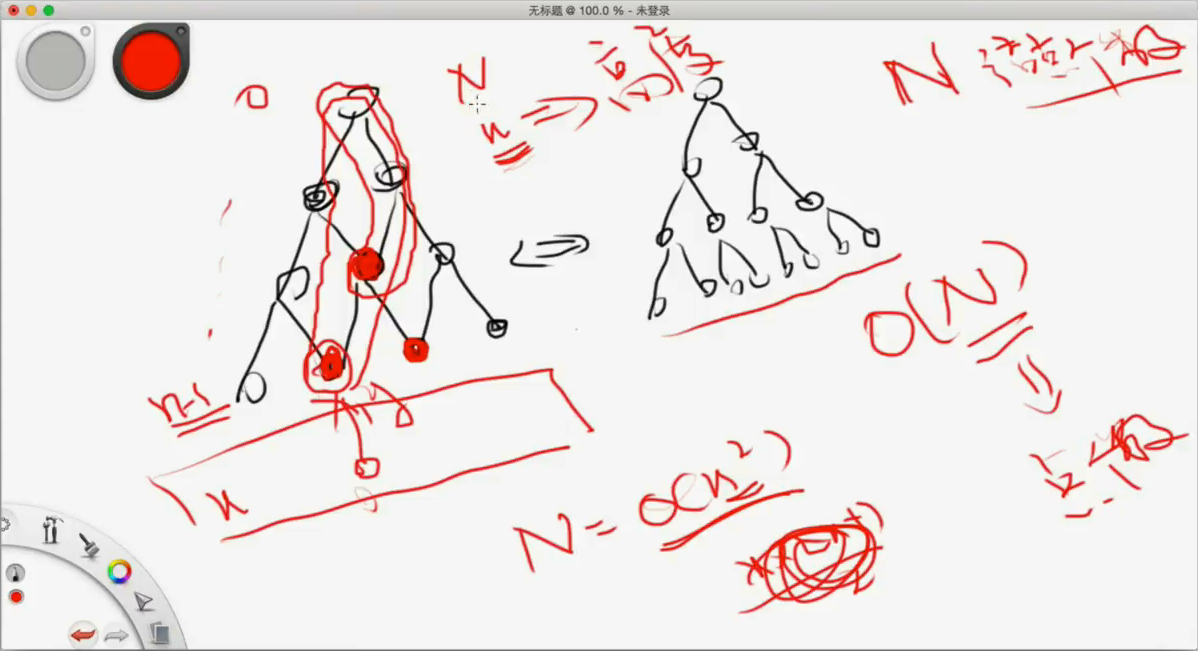 (1, 0) 和 (1, 1) 的有很多重复的地方,太多重复。
(1, 0) 和 (1, 1) 的有很多重复的地方,太多重复。 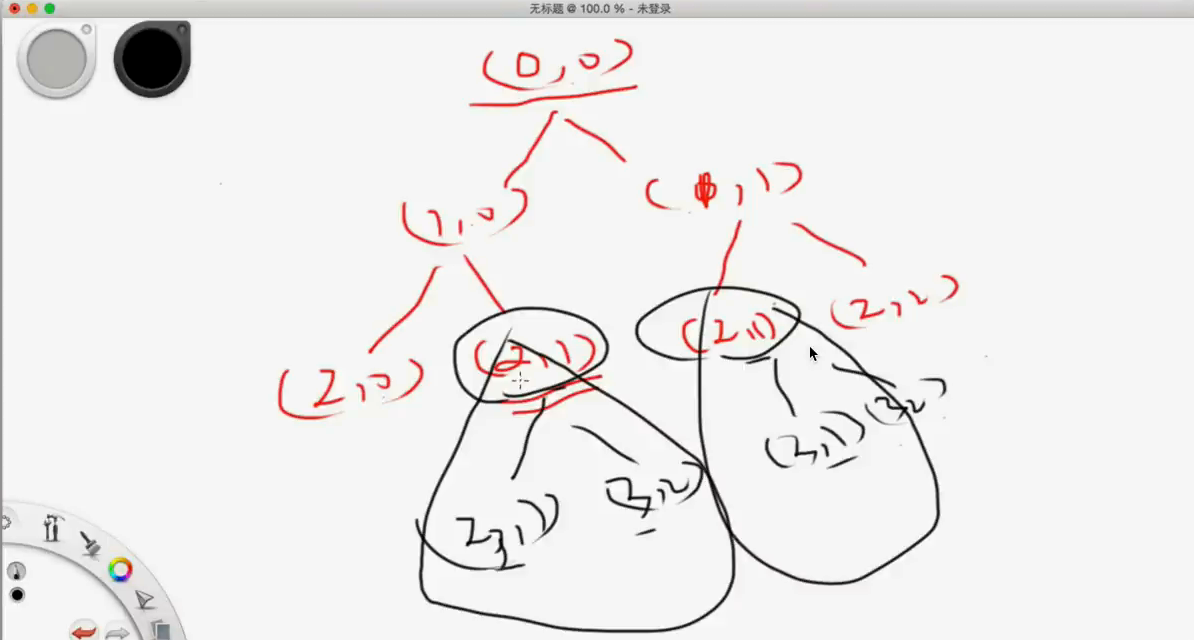
这个解法超时,有一个用例超时了!
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
class Solution {
private int best;
private int[][] A; // Triangle array
private int n; // Number of rows in the triangle
public int minimumTotal(List<List<Integer>> triangle) {
n = triangle.size();
A = new int[n][n];
best = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
// Convert the List of Lists to a 2D array for easier access
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j <= i; j++) {
A[i][j] = triangle.get(i).get(j);
}
}
traverse(0, 0, 0);
return best;
}
private void traverse(int x, int y, int sum) {
if (x == n) {
// Found a whole path from top to bottom
if (sum < best) {
best = sum;
}
return;
}
traverse(x + 1, y, sum + A[x][y]);
traverse(x + 1, y + 1, sum + A[x][y]);
}
}
DFS: Divide Conquer
A - O(n^2) / B - O(2^n) / C - (n!) / D - I don’t know.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
// return minimum path from (x, y) to bottom
int divideConquer(int x, int y) {
// x: 0 .. n-1
if (x == n) {
return 0;
}
return A[x][y] + Math.min(divideConquer(x + 1, y),
divideConquer(x + 1, y + 1));
}
// answer
divideConquer(0, 0);
- 每个点是不是只访问了一次
- 如果只访问了一次,那就统计一下(x, y)有多少个组合就好了
- 如果不是,那就要其他角度思考了
答案仍然是 O(2^n)
Divide Conquer + Memorization
我们想到的一个优化,分治就可以用这个优化。我们用哈希表来记住这个已经访问过的值比如上图的7这个值。
那么现在的时间复杂度降为了O(n^2)
这个思想,已经变为了动态规划了。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
// return minimum path from (x, y) to bottom
int divideConquer(int x, int y) {
if (x == n) {
return 0;
}
// Integer.MAX_VALUE 代表没有访问过 x, y 这个点
if (hash[x][y] != Integer.MAX_VALUE) {
return hash[x][xy];
}
hash[x][y] = A[x][y] + Math.min(divideConquer(x + 1, y), divideConquer(x + 1, y + 1));
return hash[x][y];
}
// answer
hash[*][*] = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
divideConquer(0, 0);
DC + HASH 时间复杂度就会降为 O(n^2)
下面这个 Solution 还是会超时!
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
class Solution {
private int best;
private int[][] A; // Triangle array
private int n; // Number of rows in the triangle
public int minimumTotal(List<List<Integer>> triangle) {
n = triangle.size();
A = new int[n][n];
best = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
// Convert the List of Lists to a 2D array for easier access
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j <= i; j++) {
A[i][j] = triangle.get(i).get(j);
}
}
return divideConquer(0, 0);
}
private int divideConquer(int x, int y) {
if (x == n) {
return 0;
}
return A[x][y] + Math.min(divideConquer(x + 1, y),
divideConquer(x + 1, y + 1));
}
}
Memorization Search
记忆化搜索的本质:动态规划
动态规划为什么会快?
动态规划与分治的区别? 看有无 重复计算!!
搜索基本都是指数级别的复杂度。
n^2是多项式级别的复杂度。
NP问题只能用搜索来做,N增长复杂度则是爆炸式的增长;对于P问题是一个多项式级别的复杂度。
分治是没有重复计算的。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
//Version 2 : Memorize Search
public class Solution {
private int n;
private int[][] minSum;
private int[][] triangle;
private int search(int x, int y) {
if (x >= n) {
return 0;
}
if (minSum[x][y] != Integer.MAX_VALUE) {
return minSum[x][y];
}
minSum[x][y] = Math.min(search(x + 1, y), search(x + 1, y + 1))
+ triangle[x][y];
return minSum[x][y];
}
public int minimumTotal(int[][] triangle) {
if (triangle == null || triangle.length == 0) {
return -1;
}
if (triangle[0] == null || triangle[0].length == 0) {
return -1;
}
this.n = triangle.length;
this.triangle = triangle;
this.minSum = new int[n][n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
minSum[i][j] = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
}
}
return search(0, 0);
}
}
动态规划的实现方式
多重循环 VS 记忆化搜索
| 多重循环 | 记忆化搜索 | |
|---|---|---|
| 优点 | 正规,大多数面试官可以接受,存在空间优化的可能性。 | 容易从搜索算法直接转化过来。有的时候可以节省更多的时间。 |
| 缺点 | 思考有难度。 | 递归。 |
多重循环:自底向上
时间复杂度?
空间复杂度?
A[][] 存储输入的三角形数组,方便用下标访问。
- 状态定义
f[i][j] 表示从i, j出发走到最后一层的最小路径长度
- 初始化,终点先有值
1
2
3
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
f[n - 1][i] = A[n - 1][i];
}
- 循环递推求解
1
2
3
4
5
for (int i = n - 2; i >= 0; i--) {
for (int j = 0; j <= i; j++) {
f[i][j] = Math.min(f[i + 1][j], f[i + 1][j + 1]) + A[i][j];
} // for j
} // for i
- 求结果:起点
1
f[0][0]
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
//Version 1: Bottom-Up
public class Solution {
/**
* @param triangle: a list of lists of integers.
* @return: An integer, minimum path sum.
*/
public int minimumTotal(int[][] triangle) {
if (triangle == null || triangle.length == 0) {
return -1;
}
if (triangle[0] == null || triangle[0].length == 0) {
return -1;
}
// state: f[x][y] = minimum path value from x,y to bottom
int n = triangle.length;
int[][] f = new int[n][n];
// initialize
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
f[n - 1][i] = triangle[n - 1][i];
}
// bottom up
for (int i = n - 2; i >= 0; i--) {
for (int j = 0; j <= i; j++) {
f[i][j] = Math.min(f[i + 1][j], f[i + 1][j + 1]) + triangle[i][j];
}
}
// answer
return f[0][0];
}
}
多重循环:自顶向下
时间复杂度?
空间复杂度?
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
// 初始化,起点
f[0][0] = A[0][0];
// 初始化三角形的左边和右边
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
f[i][0] = f[i][0] + A[i][0];
f[i][i] = f[i - 1][i - 1] + A[i][i];
}
// top down
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j < i; j++) {
f[i][j] = Math.min(f[i - 1][j], f[i - 1][j - 1]) + A[i][j];
} // for j
} // for i
Math.min(f[n - 1][0], f[n - 1][1], f[n - 1][2] ...)
- 多重循环的空间优化的可能性,我们暂不讨论
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
// version 0: top-down
public class Solution {
/**
* @param triangle: a list of lists of integers.
* @return: An integer, minimum path sum.
*/
public int minimumTotal(int[][] triangle) {
if (triangle == null || triangle.length == 0) {
return -1;
}
if (triangle[0] == null || triangle[0].length == 0) {
return -1;
}
// state: f[x][y] = minimum path value from 0,0 to x,y
int n = triangle.length;
int[][] f = new int[n][n];
// initialize
f[0][0] = triangle[0][0];
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
f[i][0] = f[i - 1][0] + triangle[i][0];
f[i][i] = f[i - 1][i - 1] + triangle[i][i];
}
// top down
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j < i; j++) {
f[i][j] = Math.min(f[i - 1][j], f[i - 1][j - 1]) + triangle[i][j];
}
}
// answer
int best = f[n - 1][0];
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
best = Math.min(best, f[n - 1][i]);
}
return best;
}
}
自底向上 VS 自顶向下
两种方法没有太大优劣区别
思维模式一个正向,一个逆向
后面统一采用自顶向下的方式。
什么情况下使用动态规划?
满足下面三个条件之一:
- 求最大值最小值
- 判断是否可行
- 统计方案个数
则极有可能是使用动态规划求解
做题的时候是一种尝试的思维,就是试一下暴力,不行再说,换别的方法。
十个题里面有9个
什么情况下不适用动态规划?
求出所有具体的方案而非方案个数 https://www.lintcode.com/problem/palindrome-partitioning/
输入数据是一个集合而不是序列 https://www.lintcode.com/problem/longest-consecutive-sequence/
则极不可能使用动态规划求解
剩下的一个,如果说题目让你求出所有的具体方案,都用搜索来做,不大可能用动态规划来做。
动态规划输入的需要是一个序列,两个数的位置不能随便换。
这些条件是来帮助我们来是不是用动态规划来解题。
动态规划的四要素
- 状态 State
- 灵感,创造力,存储小规模问题的结果
- 方程 Function
- 状态之间的联系,怎么通过小的状态,来算大的状态
- 初始化 Initialization
- 最极限的小状态是什么,起点
- 答案 Answer
- 最大的那个状态是什么,终点
一定要可以用自然语言来定义清清楚楚,明明白白的dp状态。
就是接收什么参数,返回什么值?
有了状态之后,我们再研究状态和状态之间的关系是什么?
这个关系表示为一个方程 Function
然后判断起点和终点。
初始化起点。
面试中常见的动态规划类型
- 坐标型动态规划15%
- 序列型动态规划30%
- 双序列动态规划30%
- 划分型动态规划10%
- 背包型动态规划10%
- 区间型动态规划5%
六种类型的动态规划,六种的比例大概是这样的
下面的三种动态规划会出现,但不常见。
坐标型动态规划
只能向下走和向右走,一看就是动态规划!!!
- State: f[x] 表示我从起点走到坐标x…… & f[x][y] 表示我从起点走到坐标x, y……
- function: 研究走到 x, y 这个点之前的一步
- intialize: 起点
- answer: 终点
初始化还初始化第0列和第0行
凡是二维的动态规划,反正都初始化f[i][0] 和 f[0][i]
Minimum Path Sum
Lintcode https://www.lintcode.com/problem/minimum-path-sum/
Leetcode https://leetcode.com/problems/minimum-path-sum/
Solution https://www.jiuzhang.com/solutions/minimum-path-sum/
Description
Given a m x n grid filled with non-negative numbers, find a path from top left to bottom right, which minimizes the sum of all numbers along its path.
Note: You can only move either down or right at any point in time.
Example 1:
1
2
3
4
5
6
Input: grid = [[1,3,1],[1,5,1],[4,2,1]]
[[1, 3, 1],
[1, 5, 1],
[4, 2, 1]]
Output: 7
Explanation: Because the path 1 -> 3 -> 1 -> 1 -> 1 minimizes the sum.
Example 2:
1
2
Input: grid = [[1,2,3],[4,5,6]]
Output: 12
Constraints:
- m == grid.length
- n == grid[i].length
- 1 <= m, n <= 200
- 0 <= grid[i][j] <= 200
Solutions
- state: f[x][y]从起点走到 x, y 的最短路径
- function: f[x][y] = min(f[x - 1][y], f[x][y - 1]) + A[x][y]
- intialize: f[i][0] = sum(0,0 ~ i,0) & f[0][i] = sum(0,0 ~ 0,i)
- answer: f[n-1][m-1]
Dpi 存储从(0, 0) 到(i, j)的最短路径。 Dpi = min(Dpi-1), Dpi) + gridi;
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
public class Solution {
public int minPathSum(int[][] grid) {
if (grid == null || grid.length == 0 || grid[0].length == 0) {
return 0;
}
int M = grid.length;
int N = grid[0].length;
int[][] sum = new int[M][N];
sum[0][0] = grid[0][0];
for (int i = 1; i < M; i++) {
sum[i][0] = sum[i - 1][0] + grid[i][0];
}
for (int i = 1; i < N; i++) {
sum[0][i] = sum[0][i - 1] + grid[0][i];
}
for (int i = 1; i < M; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j < N; j++) {
sum[i][j] = Math.min(sum[i - 1][j], sum[i][j - 1]) + grid[i][j];
}
}
return sum[M - 1][N - 1];
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
// 强化班滚动数组版本
public class Solution {
/**
* @param grid: a list of lists of integers.
* @return: An integer, minimizes the sum of all numbers along its path
*/
public int minPathSum(int[][] A) {
if (A == null || A.length == 0 || A[0].length == 0) {
return 0;
}
int m = A.length, n = A[0].length;
int[][] f = new int[2][n];
int i, j;
int old, now = 0; // f[i] is stored in rolling array f[0]
for (i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
old = now;
now = 1 - now; // 0 --> 1, 1 --> 0
for (j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if (i == 0 && j == 0) {
f[now][j] = A[0][0];
continue;
}
f[now][j] = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
if (i > 0) {
f[now][j] = Math.min(f[now][j], f[old][j]);
}
if (j > 0) {
f[now][j] = Math.min(f[now][j], f[now][j - 1]);
}
f[now][j] += A[i][j];
}
}
return f[now][n - 1];
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
// 动态规划专题班打印路径版本
public class Solution {
/**
* @param grid: a list of lists of integers
* @return: An integer, minimizes the sum of all numbers along its path
*/
public int minPathSum(int[][] A) {
if (A == null || A.length == 0 || A[0].length == 0) {
return 0;
}
int m = A.length, n = A[0].length;
int[][] f = new int[m][n];
int[][] pi = new int[m][n];
int i, j;
for (i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
for (j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if (i == 0 && j == 0) {
f[0][0] = A[0][0];
continue;
}
f[i][j] = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
if (i > 0) {
f[i][j] = Math.min(f[i][j], f[i - 1][j] + A[i][j]);
if (f[i][j] == f[i - 1][j] + A[i][j]) {
pi[i][j] = 0;
}
}
if (j > 0) {
f[i][j] = Math.min(f[i][j], f[i][j - 1] + A[i][j]);
if (f[i][j] == f[i][j - 1] + A[i][j]) {
pi[i][j] = 1;
}
}
}
}
// reverse order
// m-1,n-1
int[][] path = new int[m + n - 1][2];
int p;
i = m - 1;
j = n - 1;
for (p = m + n - 2; p >= 0; --p) {
path[p][0] = i;
path[p][1] = j;
if (p == 0) break;
if (pi[i][j] == 0) {
--i;
}
else {
--j;
}
}
for (p = 0; p < m + n - 1; ++p) {
System.out.println("(" + path[p][0] + ", " + path[p][1] + "):" + A[path[p][0]][path[p][1]]);
}
return f[m - 1][n - 1];
}
}
独孤九剑之破枪式
初始化一个二维的动态规划时,就去初始化第0行和第0列
Unique Path
Lintcode https://www.lintcode.com/problem/unique-paths/
Leetcode https://leetcode.com/problems/unique-paths/
Solution https://www.jiuzhang.com/solutions/unique-paths/
Description
There is a robot on an m x n grid. The robot is initially located at the top-left corner (i.e., grid[0][0]). The robot tries to move to the bottom-right corner (i.e., grid[m - 1][n - 1]). The robot can only move either down or right at any point in time.
Given the two integers m and n, return the number of possible unique paths that the robot can take to reach the bottom-right corner.
The test cases are generated so that the answer will be less than or equal to 2 * 10^9.
Solutions
- state: f[x][y]从起点到 x, y 的路径数
- function: (研究倒数第一步) f[x][y] = f[x - 1][y] + f[x][y - 1]
- intialize: f[0][i] = 1 & f[i][0] = 1
- answer: f[n-1][m-1]
Related Question: Unique Path II
解法1: 数学模型:在n-1 + m-1长度的序列中,有n-1个D,和m-1个R组成。 其中D表示向下,R表示向右。 因此满足组合数:C(n+m-2, n-1), 从n+m-2个位置中选n-1个位置放D的方案数。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
public class Solution {
public int uniquePaths(int m, int n) {
if (m == 0 || n == 0) {
return 1;
}
int[][] sum = new int[m][n];
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
sum[i][0] = 1;
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
sum[0][i] = 1;
}
for (int i = 1; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j < n; j++) {
sum[i][j] = sum[i - 1][j] + sum[i][j - 1];
}
}
return sum[m - 1][n - 1];
}
}
解法2: 可以用Dp过程来求解: Dpi 表示走到(i,j)的路径数, 考虑最后一步是从上往下走,还是从左往右走。 Dpi = Dpi-1 + Dpi;
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
// 方法二
public class Solution {
/**
* @param n, m: positive integer (1 <= n ,m <= 100)
* @return an integer
*/
public int uniquePaths(int m, int n) {
int[][] f = new int[m][n];
int i, j;
for (i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
for (j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if (i == 0 || j == 0) {
f[i][j] = 1;
}
else {
f[i][j] = f[i-1][j] + f[i][j-1];
}
}
}
return f[m-1][n-1];
}
}
- 完备性的
Climing Stairs
更简单的问题,爬楼梯
Lintcode https://www.lintcode.com/problem/climbing-stairs/
Leetcode https://leetcode.cn/problems/climbing-stairs/
Solution https://www.jiuzhang.com/solutions/climbing-stairs/
Description
You are climbing a staircase. It takes n steps to reach the top.
Each time you can either climb 1 or 2 steps. In how many distinct ways can you climb to the top?
Example 1:
1
2
3
4
5
Input: n = 2
Output: 2
Explanation: There are two ways to climb to the top.
1. 1 step + 1 step
2. 2 steps
Example 2:
1
2
3
4
5
6
Input: n = 3
Output: 3
Explanation: There are three ways to climb to the top.
1. 1 step + 1 step + 1 step
2. 1 step + 2 steps
3. 2 steps + 1 step
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 45
Solutions
- state: f[i]表示跳到第i个位置的方案总数
- function: f[i] = f[i-1] + f[i-2]
- intialize: f[0] = 1
- answer: f[n]
考虑最后一步走1阶还是走2阶。 方案数Dpn = 最后一步走1阶的方案数 + 最后一步走2阶的方案数。 Dpn = Dpn-1 + Dpn-2.
类比斐波那契数列
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
public class Solution {
public int climbStairs(int n) {
if (n <= 1) {
return n;
}
int last = 1, lastlast = 1;
int now = 0;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
now = last + lastlast;
lastlast = last;
last = now;
}
return now;
}
}
记忆化搜索版本
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
// 记忆化搜索
public class Solution {
/**
* @param n: An integer
* @return: An integer
*/
int[] result = null;
void f(int X) {
if (result[X] != -1) return;
if (X == 0 || X == 1) {
result[X] = 1;
return;
}
f(X - 1);
f(X - 2);
result[X] = result[X - 1] + result[X - 2];
}
public int climbStairs(int n) {
if (n == 0) {
return 0;
}
result = new int[n + 1];
for (int i = 0; i <= n; ++i) {
result[i] = -1;
}
f(n);
return result[n];
}
}
Jump Game
看一个稍微复杂一点的例子
Lintcode https://www.lintcode.com/problem/jump-game/
Leetcode https://leetcode.com/problems/jump-game/
Solution https://www.jiuzhang.com/solutions/jump-game/
Description
You are given an integer array nums. You are initially positioned at the array’s first index, and each element in the array represents your maximum jump length at that position.
Return true_ if you can reach the last index, or false otherwise_.
Example 1:
1
2
3
Input: nums = [2,3,1,1,4]
Output: true
Explanation: Jump 1 step from index 0 to 1, then 3 steps to the last index.
Example 2:
1
2
3
4
Input: nums = [3,2,1,0,4]
Output: false
Explanation: You will always arrive at index 3 no matter what.
Its maximum jump length is 0, which makes it impossible to reach the last index.
Constraints:
- 1 <= nums.length <= 104
- 0 <= nums[i] <= 105
其实这个贪心法的O(n),这是一个一定不要学的东西,不是所有的题目都能用贪心能解决。
贪心法容易导致nn你在某一步的时候只顾眼前的利益,对于贪心来说,比较眼瞎的。
来看Jump Game是判断可不可行的问题,很好满足条件。
Solutions
最优算法:贪心法,时间复杂度 O(n)
次优算法:动态规划,时间复杂度 O(n^2)
- state: f[i]代表我能否跳到第i个位置
- function: f[i] = OR(f[j], j < i && j能够跳到i)
- initialize: f[0] = true;
- answer: f[n-1]
在1的基础上,不仅问能不能跳的到,还问你最小用几步跳过去
如果有一个点跳不到怎么办?
那我们一般把这种情况赋值为正无穷大, Integer.MAX_VALUE
动态规划不是万能的。
Jump Game ii
Lintcode https://www.lintcode.com/problem/jump-game-ii/
Leetcode https://leetcode.cn/problems/jump-game-ii/
Solution https://www.jiuzhang.com/solutions/jump-game-ii/
Description
You are given a 0-indexed array of integers nums of length n. You are initially positioned at nums[0].
Each element nums[i] represents the maximum length of a forward jump from index i. In other words, if you are at nums[i], you can jump to any nums[i + j] where:
- 0 <= j <= nums[i] and
- i + j < n
Return _the minimum number of jumps to reach _nums[n - 1]. The test cases are generated such that you can reach nums[n - 1].
Example 1:
1
2
3
4
Input: nums = [2,3,1,1,4]
Output: 2
Explanation: The minimum number of jumps to reach the last index is 2.
Jump 1 step from index 0 to 1, then 3 steps to the last index.
Example 2:
1
2
Input: nums = [2,3,0,1,4]
Output: 2
Constraints:
- 1 <= nums.length <= 104
- 0 <= nums[i] <= 1000
- It’s guaranteed that you can reach nums[n - 1].
Solutions
- state: f[i]代表我跳到第i个位置最少需要几步
- function: f[i] = MIN{f[j]+1, j < i && j能够跳到i}
- initialize: f[0] = 0;
- answer: f[n-1]
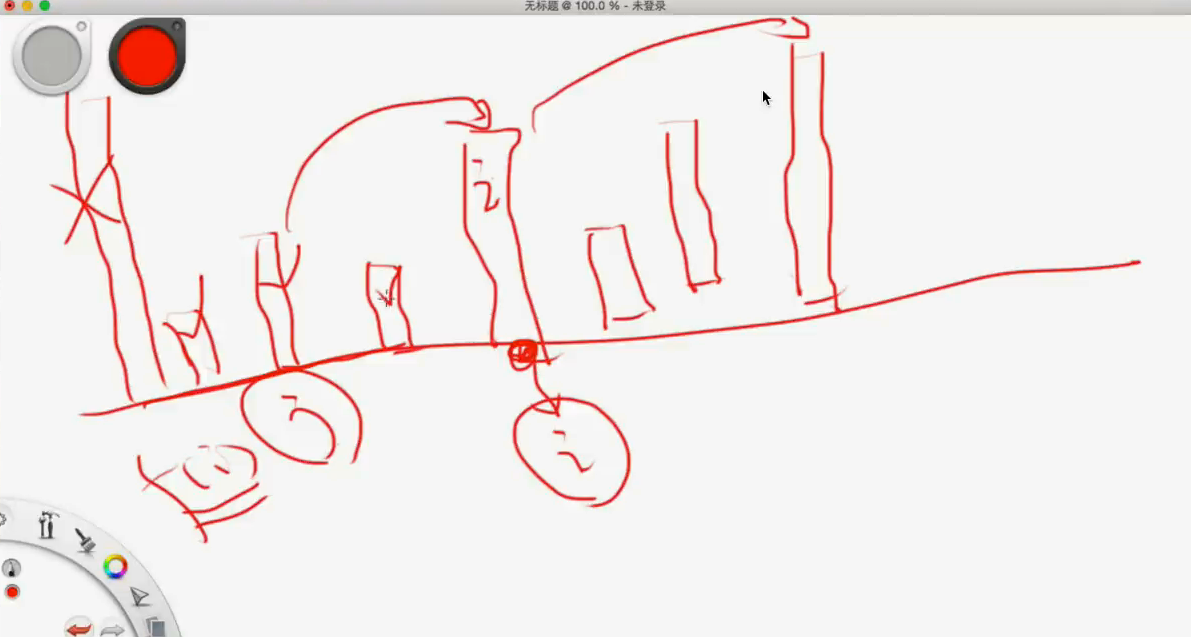
Longest Increasing Subsequence
还有一道非常经典的题目
如果你不会动态规划的话,这就是一道非常难的题目。
这道题一定大家会往贪心那边想的。
Solutions
这道题比较难的是起点和终点是什么。
状态方程再讲一下,如图
跳这个桩子,能从什么地方开始,从什么地方结束呢?
这道题是一定要掌握的,典型的坐标型动态规划,非常经典的非常经典的一道题。
如果让你给出具体方案呢,
动态规划的时候,面试的时候不大让你出方案。
把时间花在常考的类型上面。
我们总结一下
Conclusion
Why DP?
When DP?
How DP?
Homework
Required
- [Easy] 115 Unique Paths ii
- [Easy] 114 Unique Paths
- [Easy] 111 Climbing Stairs
- [Easy] 110 Minimum Path Sum
- [Easy] 109 Triangle
- [Medium] 117 Jump Game ii
- [Medium] 116 Jump Game
- [Medium] 107 Word Break
- [Medium] 108 Palindrome Partitioning ii
- [Medium] 76 Longest Increasing Subsequence