Lecture-5 Dynamic Programming II
Outline
- 复习上一节课的内容
- 单序列动态规划
- 双序列动态规划
什么情况下使用动态规划?
满足下满三个条件之一:
- 求最大值最小值
- 判断是否可行
- 统计方案个数
则极有可能是使用动态规划求解
什么情况下不使用动态规划?
求出所有具体的方案而非方案的个数 https://www.lintcode.com/problem/palindrome-partitioning/
输入数据是一个集合而不是序列 https://www.lintcode.com/problem/longest-consecutive-sequence/
则极不可能使用动态规划求解
Long Consecutive Sequence
简称LIS问题,是一个经典的DP
可以有各种变化的一道DP,也可以decreasing Subsequence
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
public class Solution {
/**
* @param nums: The integer array
* @return: The length of LTS (longest increasing subsequence)
*/
public int longestIncreasingSubsequence(int[] nums) {
int[] f = new int[nums.length];
状态:
f[i] 表示跳到第 i 个位置,所得到的 LTS 的长度是多少
起点:
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
f[i] = 1;
solution[i] = -1;
}
solution[...] = -1;
方程:
f[i] = max{f[j] + 1} | j < i && nums[j] <= nums[i];
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) {
if (nums[j] <= nums[i]) {
if (f[i] < f[j] + 1) {
f[i] = f[j] + 1;
solution[i] = j;
}
}
} // for j
} // for i
终点:
best_index = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
// best = Math.max(best, f[i]);
if (f[i] > f[best_index]) {
best_index = i;
}
}
best_index
solution[best_index]
solution[solution[best_index]]
......
int max = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
f[i] = 1;
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) {
if (nums[j] <= nums[i]) {
f[i] = f[i] > f[j] + 1 ? f[i] : f[j] + 1;
}
} // for j
} // for i
return max;
}
}
动态规划的四点要素
- 状态 State
- 灵感,创造力,存储小规模问题的结果
- 方程 Function
- 状态之间的联系,怎么通过小的状态,来算大的状态
- 初始化 Initialization
- 最极限的小状态时什么,起点
- 答案 Answer
- 最大的那个状态时什么,终点
面试中常见的动态规划类型
坐标型动态规划 15%
序列型动态规划 30%
双序列动态规划 30%
划分型动态规划 10%
背包型动态规划 10%
区间型动态规划 5%
pie
title 面试中常见的动态规划类型
"坐标型" : 15
"序列型" : 30
"双序列型" : 30
"划分型" : 10
"背包型" : 10
"区间型": 5
坐标型动态规划
state:
f[x] 表示我从起点走到坐标x ……
f[x][y] 表示我从起点走到坐标x, y ……
function: 研究走到 x, y 这个点之前的一步
intializa: 起点
answer: 终点
单序列动态规划
state: f[i] 表示前 i 个位置 / 数字 / 字母,第 i 个 …
function: f[i] = f[j] … j 是 i 之前的一个位置
initialize: f[0] …
answer: f[n-1] …
没有坐标的概念,有子串,前缀串的概念。
更改:answer: f[n] …
Palindrome Partitioning ii
Lintcode https://www.lintcode.com/problem/palindrome-partitioning-ii/
Leetcode https://leetcode.com/problems/palindrome-partitioning-ii/
Solution https://www.jiuzhang.com/solutions/palindrome-partitioning-ii/
Description
Given a string s, partition s such that every substring of the partition is a palindrome.
Return the minimum* *cuts needed for a palindrome partitioning of s.
Example 1:
Input: s = “aab”
Output: 1
Explanation: The palindrome partitioning [“aa”,”b”] could be produced using 1 cut.
Example 2:
Input: s = “a”
Output: 0
Example 3:
Input: s = “ab”
Output: 1
Constraints:
- 1 <= s.length <= 2000
- s consists of lowercase English letters only.
Solutions
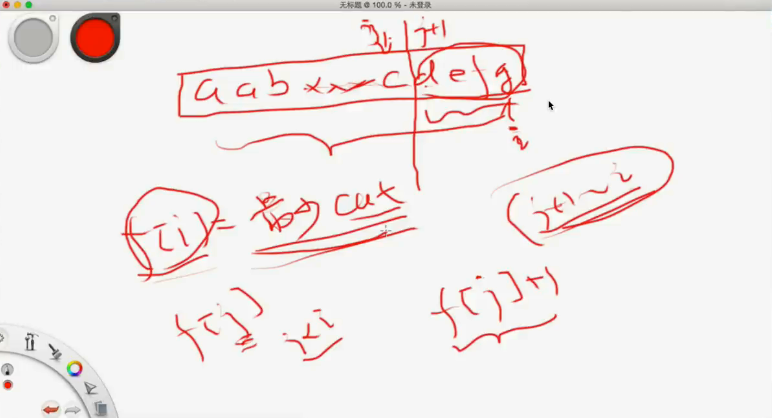
state: f[i] “前i”个字符组成的字符串需要最少几次 cut
// 最少能被分割为多少个字符串-1
function: f[i] = MIN{f[j]+1}, j<i && j+1 ~ i 这一段是一个回文串
initialize: f[i] = i - 1 (f[0] = -1)
answer: f[s.length()]
与 136. 分割回文串 不同, 这道题目不需要求所有方案, 而是求最小次数 – 最优解问题。
可以看作序列型动态规划问题,设定 dpi 表示原串的前 i 个字符最少分割多少次可以使得到的都是回文子串。
如果 s 前 i 个字符组成的子串本身就是回文串, 则 dpi = 0,否则:
dp[i] = min{dp[j] + 1} (j < i 并且 s[j + 1], s[j + 2], ... , s[i] 是回文串)
如果想要是 O(n^2) 的时间复杂度 (n 是 s 的长度),需要事先求出来回文串信息, 在状态转移时可以 O(1) 地知道一段子串是否回文的。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
// version 1
// f[i] 表示前i个字母,最少可以被分割为多少个回文串
// 最后return f[n] - 1
public class Solution {
private boolean[][] getIsPalindrome(String s) {
boolean[][] isPalindrome = new boolean[s.length()][s.length()];
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
isPalindrome[i][i] = true;
}
for (int i = 0; i < s.length() - 1; i++) {
isPalindrome[i][i + 1] = (s.charAt(i) == s.charAt(i + 1));
}
for (int length = 2; length < s.length(); length++) {
for (int start = 0; start + length < s.length(); start++) {
isPalindrome[start][start + length]
= isPalindrome[start + 1][start + length - 1] && s.charAt(start) == s.charAt(start + length);
}
}
return isPalindrome;
}
public int minCut(String s) {
if (s == null || s.length() == 0) {
return 0;
}
// preparation
boolean[][] isPalindrome = getIsPalindrome(s);
// initialize
int[] f = new int[s.length() + 1];
f[0] = 0;
// main
for (int i = 1; i <= s.length(); i++) {
f[i] = Integer.MAX_VALUE; // or f[i] = i
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) {
if (isPalindrome[j][i - 1]) {
f[i] = Math.min(f[i], f[j] + 1);
}
}
}
return f[s.length()] - 1;
}
}
先解决主程序main
如果是否是一个回文串,和动规没关系,就独立出来作为一个函数 getIsPalidrome(String s)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
// version 2
// f[i] 表示前i个字母,最少被切割几次可以切割为都是回文串。
// 最后return f[n]
public class Solution {
private boolean isPalindrome(String s, int start, int end) {
for (int i = start, j = end; i < j; i++, j--) {
if (s.charAt(i) != s.charAt(j)) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
private boolean[][] getIsPalindrome(String s) {
boolean[][] isPalindrome = new boolean[s.length()][s.length()];
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
isPalindrome[i][i] = true;
}
for (int i = 0; i < s.length() - 1; i++) {
isPalindrome[i][i + 1] = (s.charAt(i) == s.charAt(i + 1));
}
for (int length = 2; length < s.length(); length++) {
for (int start = 0; start + length < s.length(); start++) {
isPalindrome[start][start + length]
= isPalindrome[start + 1][start + length - 1] && s.charAt(start) == s.charAt(start + length);
}
}
return isPalindrome;
}
public int minCut(String s) {
if (s == null || s.length() == 0) {
return 0;
}
// preparation
boolean[][] isPalindrome = getIsPalindrome(s);
// initialize
int[] f = new int[s.length() + 1];
for (int i = 0; i <= s.length(); i++) {
f[i] = i - 1;
}
// main
for (int i = 1; i <= s.length(); i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) {
if (isPalindrome[j][i - 1]) {
f[i] = Math.min(f[i], f[j] + 1);
}
}
}
return f[s.length()];
}
}
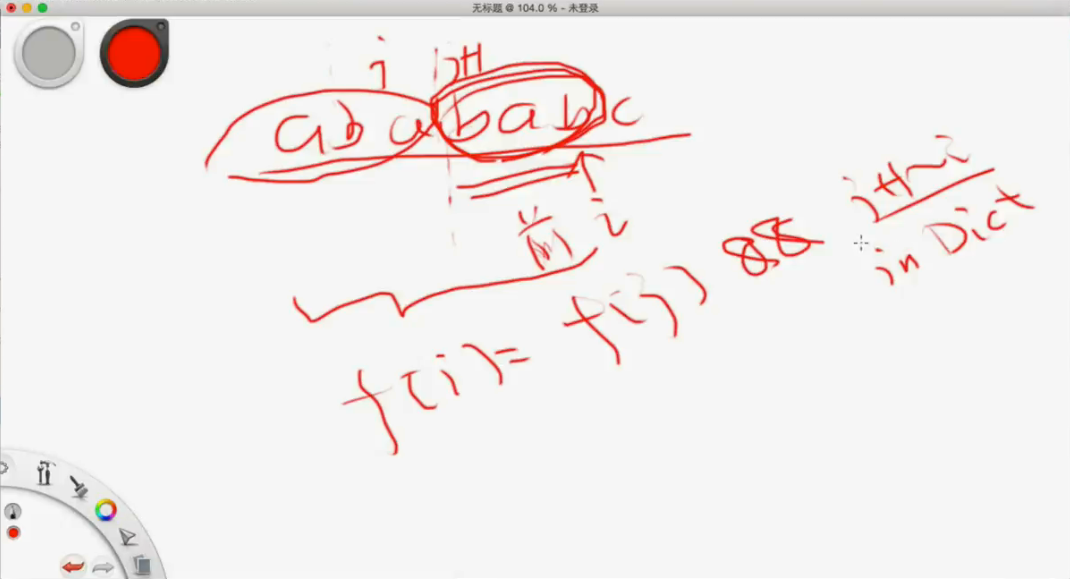
看f(j+1 到 i)是不是回文串,那么f[j] + 1就是一个候选方案。
区间型动态规划,这个就是一个区间型
那么看这个区间看存不存在一个推导的关系。
回文串,头尾要想等,中间也要是回文串。
所以就有公式 如图!!
可能for循环的顺序是不对的。
这样写在这里的时候,就错了。
在跑i的时候,i+1还没解决,所以这里错了
解决办法
倒过来!!
还有一种更本质的循环方案。
大区间 小区间
我们用区间的长度来进行第一重循环,再去计算区间的起始位置
我们初始化呢,就会初始化小的区间,比如[i][i]区间。
动规也是有选择性的,看这个方案,那个方案能不能行,我保存最优的那个。
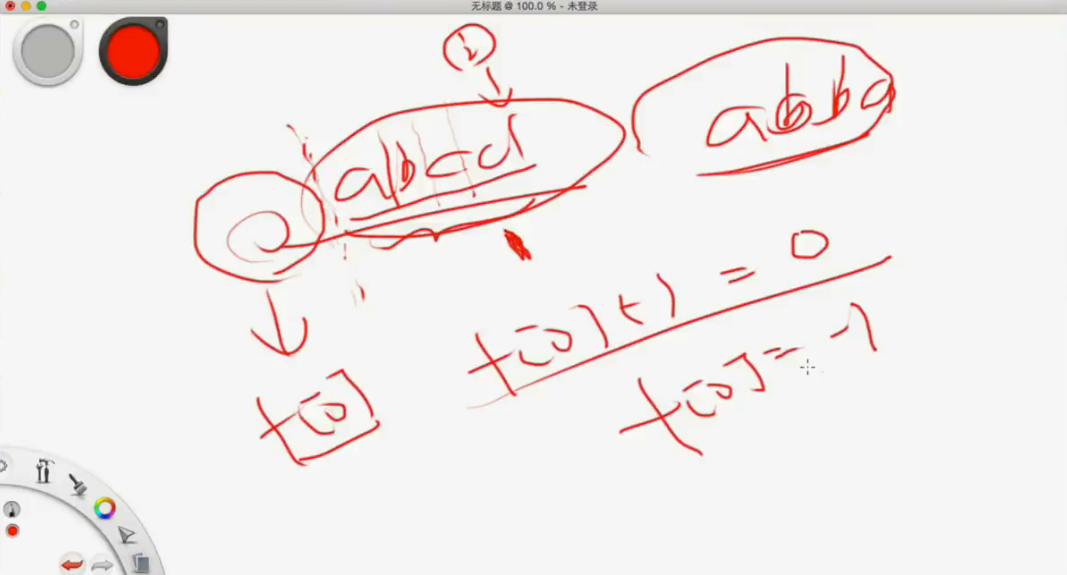
比如三个字符你要划几下能构成回文串。所以i需要i-1下才能回文串。
如果理解不了,我们换一个定义。
直接if掉,f[0]=0 f[1]=1
理解f[0] = -1的一种方式,如上图!!!
这道题就是两个动态规划,一个序列型的动规另一个是区间型的动规。
这里就会多一些代码,f[0]=-1就直接定义为-1就行
关键是f[0]定义为-1 f[i]其他的定义为无穷大都行。
关键是计算等号左边的时候,等号右边需要先计算好了。
独孤九剑 之 破鞭式
如果不是跟坐标相关的动态规划,一般有 N 个数/字符,就开 N+1 个位置的数组,第 0 个位置单独留出来做初始化。
类似的例子
Word Break
Lintcode https://www.lintcode.com/problem/word-break/
Leetcode https://leetcode.com/problems/word-break/
Solution https://www.jiuzhang.com/solutions/word-break/
Description
Given a string s and a dictionary of strings wordDict, return true if s can be segmented into a space-separated sequence of one or more dictionary words.
Note that the same word in the dictionary may be reused multiple times in the segmentation.
Example 1:
Input: s = “leetcode”, wordDict = [“leet”,”code”]
Output: true
Explanation: Return true because “leetcode” can be segmented as “leet code”.
Example 2:
Input: s = “applepenapple”, wordDict = [“apple”,”pen”]
Output: true
Explanation: Return true because “applepenapple” can be segmented as “apple pen apple”. Note that you are allowed to reuse a dictionary word.
Example 3:
Input: s = “catsandog”, wordDict = [“cats”,”dog”,”sand”,”and”,”cat”]
Output: false
Constraints:
- 1 <= s.length <= 300
- 1 <= wordDict.length <= 1000
- 1 <= wordDict[i].length <= 20
- s and wordDict[i] consist of only lowercase English letters.
- All the strings of wordDict are unique.
Solutions
对于这道题,我们首先考虑暴力的方法。本题相当于用多个字符串组成该字符串,那么我们就枚举所有可能的放入字符串的方法,通过深度优先搜索,尝试所有可能。 对于一个字符串,考虑字典中的每个前缀是否是这个字典中的单词。若不是,则跳过该单词。若是则将该前缀从字符串中删除后,判断剩下的字符串能否由字典里的单词组成。 由于题目的数据加强,此题已经无法使用常规的DFS方式通过,我们更推荐更优秀的DP来实现。
使用深度优先搜索,记录字符串,字典,以及当前需要判断的字符串的起始点 从当前字符串的起始点开始判断
定义dfs
递归的出口
如果起始点已经在字符串的尾部
停止,返回可以组成该字符串
如果还未到结尾,枚举下一个字符串的长度。
对于每种可能,判断该字符串是否在字典中
如果在字典中:
取出该字符串,判断剩下的是否可以
找完所有可能后,仍然不行,直接返回这段字符串无法找到答案
时间复杂度:O(2^n),考虑当s = “aaaaaaaaaaab”, dict = {“a”, “aa”, “aaa”, …., “aaaaaaaaa”} 空间复杂度:O(N),递归深度最深为N层
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
public class Solution {
public boolean wordBreak(String s, Set<String> dict) {
return dfs(s, dict, 0);
}
/**
* 递归的定义
* 判断字符串s[start: ]能否通过wordDict中的单词组成
**/
public boolean dfs(String s, Set<String> dict, int now) {
// 递归的出口
if (now == s.length()) {
return true;
}
// 递归的拆解,枚举下一个字符串的长度len
for (int len = 1; now + len <= s.length(); len++) {
// 判断s[now: now + len]是否满足条件
if (dict.contains(s.substring(now, now + len)) && dfs(s, dict, now + len)) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}
LintCode 582. Word Break II LintCode 683. Word break III LintCode 123. Word Search
同样这道题可能会有work break 2
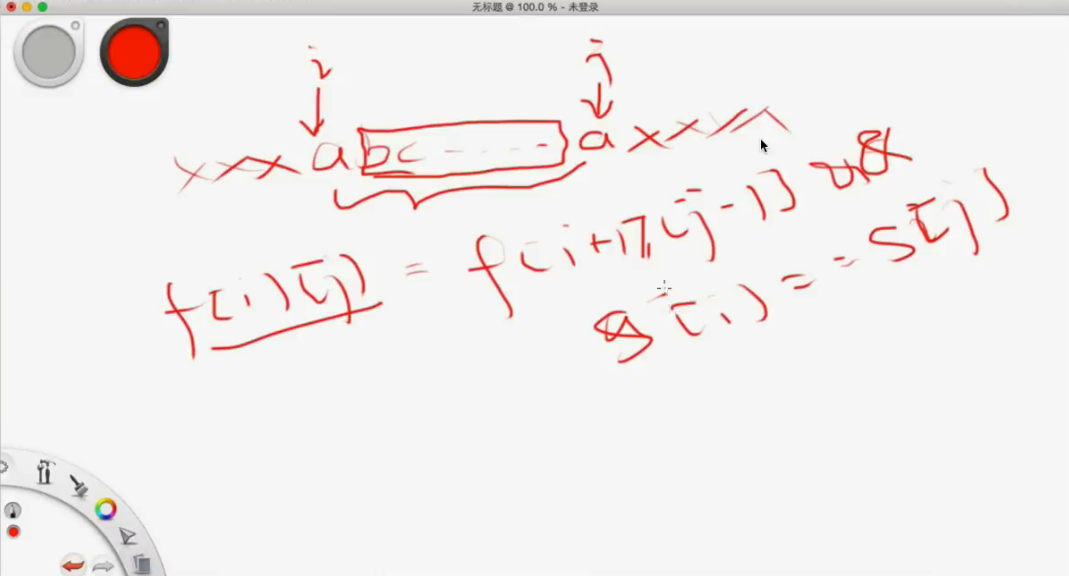
f[i] = f[j] && j+1 ~ i is in dict
state: f[i]表示“前i”个字符能否被完美切分
function: f[i] = OR{ f[j] }, j<i, j+1 ~ i 是一个词典中的单词
initialize: f[0] = true
answer: f[s.length()]
注意:切分位置的枚举 -> 单词长度枚举 O(NL)
- N: 字符串长度
L: 最长的单词的长度
- state: dp[i] 表示前 i 个字符是否能够被划分为若干个单词
- function: dp[i] = or{dp[j] and j + 1~i 是一个单词}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
public class Solution {
/*
* @param s: A string
* @param dict: A dictionary of words dict
* @return: A boolean
*/
public boolean wordBreak(String s, Set<String> dict) {
if (s == null) {
return true;
}
int maxLength = 0;
for (String word : dict) {
maxLength = Math.max(maxLength, word.length());
}
int n = s.length();
boolean[] dp = new boolean[n + 1];
dp[0] = true;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int l = 1; l <= maxLength; l++) {
if (i < l) {
break;
}
if (!dp[i - l]) {
continue;
}
String word = s.substring(i - l, i);
if (dict.contains(word)) {
dp[i] = true;
break;
}
}
}
return dp[n];
}
}
这道题要做一道小小的优化!!!
这里会超时了!!两重loop
优化:只循环最后一下最后那个单词。lastWordLength <= maxLength && lastWordLength <= i
严格来说 复杂度是 O(NL^2)
实现or逻辑,一旦发现满足条件就break
我们单序列的就讲到这里。。
双序列动态规划
state: f[i][j]代表了第一个 sequence 的前 i 个数字 / 字符,配上第二个 sequence 的前 j 个 …
function: f[i][j] = 研究第 i 个和第 j 个的匹配关系
initialize: f[i][0] 和 f[0][i]
answer: f[s1.length()][s2.length()]
Longest Common Subsequence
Lintcode https://www.lintcode.com/problem/longest-common-subsequence/
Solution https://www.jiuzhang.com/solutions/longest-common-subsequence/
Description
Given two strings text1 and text2, return the length of their longest common subsequence.
A subsequence of a string is a new string generated from the original string with some characters(can be none) deleted without changing the relative order of the remaining characters. (eg, “ace” is a subsequence of “abcde” while “aec” is not). A common subsequence of two strings is a subsequence that is common to both strings.
If there is no common subsequence, return 0.
Example 1:
Input: text1 = “abcde”, text2 = “ace”
Output: 3
Explanation: The longest common subsequence is “ace” and its length is 3.
Example 2:
Input: text1 = “abc”, text2 = “abc”
Output: 3
Explanation: The longest common subsequence is “abc” and its length is 3.
Example 3:
Input: text1 = “abc”, text2 = “def”
Output: 0
Explanation: There is no such common subsequence, so the result is 0.
Constraints:
- 1 <= text1.length <= 1000
- 1 <= text2.length <= 1000
- The input strings consist of lowercase English characters only.
Solutions
state: f[i][j]表示前 i 个字符配上前 j 个字符的 LCS 的长度
function: f[i][j] = MAX{ f[i-1][j], f[i][j-1], f[i-1][j-1]+1} // a[i] == b[j]
= MAC{ f[i-1][j], f[i][j-1] } // a[i] != b[j]
intialize: f[i][0] = 0 f[0][j] = 0
answer: f[a.length()][b.length()]
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
public class Solution {
/**
* @param A, B: Two strings.
* @return: The length of longest common subsequence of A and B.
*/
public int longestCommonSubsequence(String A, String B) {
int n = A.length();
int m = B.length();
int f[][] = new int[n + 1][m + 1];
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
for(int j = 1; j <= m; j++){
f[i][j] = Math.max(f[i - 1][j], f[i][j - 1]);
if(A.charAt(i - 1) == B.charAt(j - 1))
f[i][j] = f[i - 1][j - 1] + 1;
}
}
return f[n][m];
}
}
Related Question
Longest Common Substring https://www.lintcode.com/problem/longest-common-substring/
Edit Distance
Lintcode https://www.lintcode.com/problem/edit-distance/
Leetcode https://leetcode.com/problems/edit-distance/
Solution https://www.jiuzhang.com/solutions/edit-distance/
Description
Given two strings word1 and word2, return the minimum number of operations required to convert word1 to word2.
You have the following three operations permitted on a word:
- Insert a character
- Delete a character
- Replace a character
Example 1:
Input: word1 = “horse”, word2 = “ros”
Output: 3
Explanation: horse -> rorse (replace ‘h’ with ‘r’)
rorse -> rose (remove ‘r’)
rose -> ros (remove ‘e’)
Example 2:
Input: word1 = “intention”, word2 = “execution”
Output: 5
Explanation: intention -> inention (remove ‘t’)
inention -> enention (replace ‘i’ with ‘e’)
enention -> exention (replace ‘n’ with ‘x’)
exention -> exection (replace ‘n’ with ‘c’)
exection -> execution (insert ‘u’)
Constraints:
- 0 <= word1.length, word2.length <= 500
- word1 and word2 consist of lowercase English letters.
Solutions
state: f[i][j] a的前i个字符最少要用几次编辑可以变成b的前j个字符
function: f[i][j] = MIN{ f[i-1][j]+1, f[i][j-1]+1, f[i-1][j-1] } // a[i-1] == b[j-1]
= MIN{ f[i-1][j]+1, f[i][j-1]+1, f[i-1][j-1]+1 } // a[i] != b[j]
initialize: f[i][0] = i, f[0][j] = j
answer: f[a.length()][b.length()]
为了我要达到f[i][j]的状态,我可以有三种方法达到。
Dpi 表示A序列前i个数,与B的前j个数的LCS长度。 对A的每个位置i,枚举B的每个位置j。 转移方程见代码。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
public class Solution {
/**
* @param A, B: Two strings.
* @return: The length of longest common subsequence of A and B.
*/
public int longestCommonSubsequence(String A, String B) {
int n = A.length();
int m = B.length();
int f[][] = new int[n + 1][m + 1];
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
for(int j = 1; j <= m; j++){
f[i][j] = Math.max(f[i - 1][j], f[i][j - 1]);
if(A.charAt(i - 1) == B.charAt(j - 1))
f[i][j] = f[i - 1][j - 1] + 1;
}
}
return f[n][m];
}
}
Distinct Subsequences
Lintcode https://www.lintcode.com/problem/distinct-subsequences/
Leetcode https://leetcode.com/problems/distinct-subsequences/
Solution https://www.jiuzhang.com/solutions/distinct-subsequences/
Description
Given two strings s and t, return the number of distinct subsequences of s which equals t.
The test cases are generated so that the answer fits on a 32-bit signed integer.
Example 1:
Input: s = “rabbbit”, t = “rabbit”
Output: 3
Explanation: As shown below, there are 3 ways you can generate “rabbit” from s. rabbbit rabbbit rabbbit
Example 2:
Input: s = “babgbag”, t = “bag”
Output: 5
Explanation: As shown below, there are 5 ways you can generate “bag” from s. babgbag babgbag babgbag babgbag babgbag
Constraints:
- 1 <= s.length, t.length <= 1000
- s and t consist of English letters.
Solutions
有几种删除的方法使得 S -> T
state: f[i][j]表示S的前i个字符中选取T的前j个字符,有多少种方案
function: f[i][j] = f[i-1][j] + f[i-1][j-1] // S[i-1] == T[j-1]
= f[i-1][j] (S[i-1] != T[j-1])
initialize: f[i][0] = 1, f[0][j] = 0 (j > 0)
answer: f[n][m] (n = sizeof(S), m = sizeof(T))
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
public class Solution {
public int numDistinct(String S, String T) {
if (S == null || T == null) {
return 0;
}
int[][] nums = new int[S.length() + 1][T.length() + 1];
for (int i = 0; i <= S.length(); i++) {
nums[i][0] = 1;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= S.length(); i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= T.length(); j++) {
nums[i][j] = nums[i - 1][j];
if (S.charAt(i - 1) == T.charAt(j - 1)) {
nums[i][j] += nums[i - 1][j - 1];
}
}
}
return nums[S.length()][T.length()];
}
}
多达5种解法与详细解释 https://www.cnblogs.com/yuzhangcmu/p/4196373.html
Interleaving String
Lintcode https://www.lintcode.com/problem/interleaving-string/
Leetcode https://leetcode.com/problems/interleaving-string/
Solution https://www.jiuzhang.com/solutions/interleaving-string/
Description
Given strings s1, s2, and s3, find whether s3 is formed by an interleaving of s1 and s2.
An interleaving of two strings s and t is a configuration where s and t are divided into n and m substrings respectively, such that:
- s = s1 + s2 + … + sn
- t = t1 + t2 + … + tm
n - m <= 1 - The interleaving is s1 + t1 + s2 + t2 + s3 + t3 + … or t1 + s1 + t2 + s2 + t3 + s3 + …
Note: a + b is the concatenation of strings a and b.
Example 1:
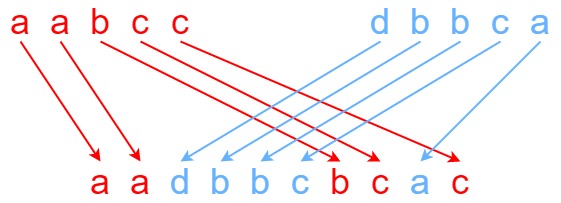
Input: s1 = “aabcc”, s2 = “dbbca”, s3 = “aadbbcbcac”
Output: true
Explanation: One way to obtain s3 is: Split s1 into s1 = “aa” + “bc” + “c”, and s2 into s2 = “dbbc” + “a”. Interleaving the two splits, we get “aa” + “dbbc” + “bc” + “a” + “c” = “aadbbcbcac”. Since s3 can be obtained by interleaving s1 and s2, we return true.
Example 2:
Input: s1 = “aabcc”, s2 = “dbbca”, s3 = “aadbbbaccc”
Output: false
Explanation: Notice how it is impossible to interleave s2 with any other string to obtain s3.
Example 3:
Input: s1 = “”, s2 = “”, s3 = “”
Output: true
Constraints:
- 0 <= s1.length, s2.length <= 100
- 0 <= s3.length <= 200
- s1, s2, and s3 consist of lowercase English letters.
Solutions
state: f[i][j] 表示 s1 的前 i 个字符和 s2 的前 j 个字符能否交替组成 s3 的前 i+j 个字符
| function: f[][] = (f[i-1][k] && (s1[i-1]==s3[i+j-1])) | (f[i][j-1] && (s2[j-1]==s3[i+j-1])) |
initialize: f[i][0] = (s1[0 … i-1] == s3[0 … i-1])
f[0][j] = (s2[0 … j-1] == s3[0 … j-1])
answer: f[n][m], n = sizeof(s1), m = sizeof(s2)
动态规划。 dpi代表由s1的前i个字母和s2的前j个字母是否能构成当前i+j个字母。 然后状态转移即可。(看第i+j+1个是否能被s1的第i+1个构成或被s2的第j+1个构成)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
public class Solution {
public boolean isInterleave(String s1, String s2, String s3) {
if (s1.length() + s2.length() != s3.length()) {
return false;
}
boolean [][] interleaved = new boolean[s1.length() + 1][s2.length() + 1];
interleaved[0][0] = true;
for (int i = 1; i <= s1.length(); i++) {
if(s3.charAt(i - 1) == s1.charAt(i - 1) && interleaved[i - 1][0])
interleaved[i][0] = true;
}
for (int j = 1; j <= s2.length(); j++) {
if(s3.charAt(j - 1) == s2.charAt(j - 1) && interleaved[0][j - 1])
interleaved[0][j] = true;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= s1.length(); i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= s2.length(); j++) {
if(((s3.charAt(i + j - 1) == s1.charAt(i - 1) && interleaved[i - 1][j]))
|| ((s3.charAt(i + j - 1)) == s2.charAt(j - 1) && interleaved[i][j - 1]))
interleaved[i][j] = true;
}
}
return interleaved[s1.length()][s2.length()];
}
}
这类的程序实现大都大同小异的。
Follow up
Could you solve it using only O(s2.length) additional memory space?
动态规划总结
面试的时候你都可以和面试官来讨论这个,它的状态是什么。
- 什么情况下可能使用 / 不使用动态规划?
- 最大值最小值 / 是否可行 / 方案总数
- 求所有方案 / 集合而不是序列
- 解决动态规划问题的四点要素
- 状态
- 方程
- 初始化
- 答案
- 三种面试常见的动态规划类别及状态特点
- 坐标、单序列、双序列
- 一些奇技淫巧
- 初始化第 0 行和第 0 列
- n 个数开 n+1 个位置的数组
其他类型的动态规划习题
- 背包类:
https://www.lintcode.com/problem/backpack/
https://www.lintcode.com/problem/backpack-ii/
https://www.lintcode.com/problem/minimum-adjustment-cost/
https://www.lintcode.com/problem/k-sum/
- 区间类:
https://www.lintcode.com/problem/coins-in-a-line-iii/
https://www.lintcode.com/problem/scramble-string/
- 划分类:
https://www.lintcode.com/problem/best-time-to-buy-and-sell-stock-iv/
https://www.lintcode.com/problem/maximum-subarray-iii/
有一个背包9讲,前三讲就可以了,后面竞赛难度了。
Homework
Required
- [Medium] 119 Edit Distance
- [Medium] 118 Distinct Subsequences
- [Medium] 79 Longest Common Substring
- [Medium] 77 Longest Common Subsequence
- [Medium] 29 Interleaving String
Optional
- [Medium] 25 Backpack ii
- [Medium] 92 Backpack
- [Medium] 91 Minimum Adjustment Cost
- [Hard] 192 Wildcard Matching
- [Hard] 89 K Sum