Lecture-9 Graph And Search
做一下这道题
Binary Search Tree Iterator
非递归的 inorder 的遍历这个树。
如果是数组嵌套数组,你怎么去定义这种数据类型?你可以自己去定义自己的class!
Outline
Graph
- Clone Graph
- Topological Sorting
Search
- DFS (Depth First Search)
- BFS (Breadth First Search)
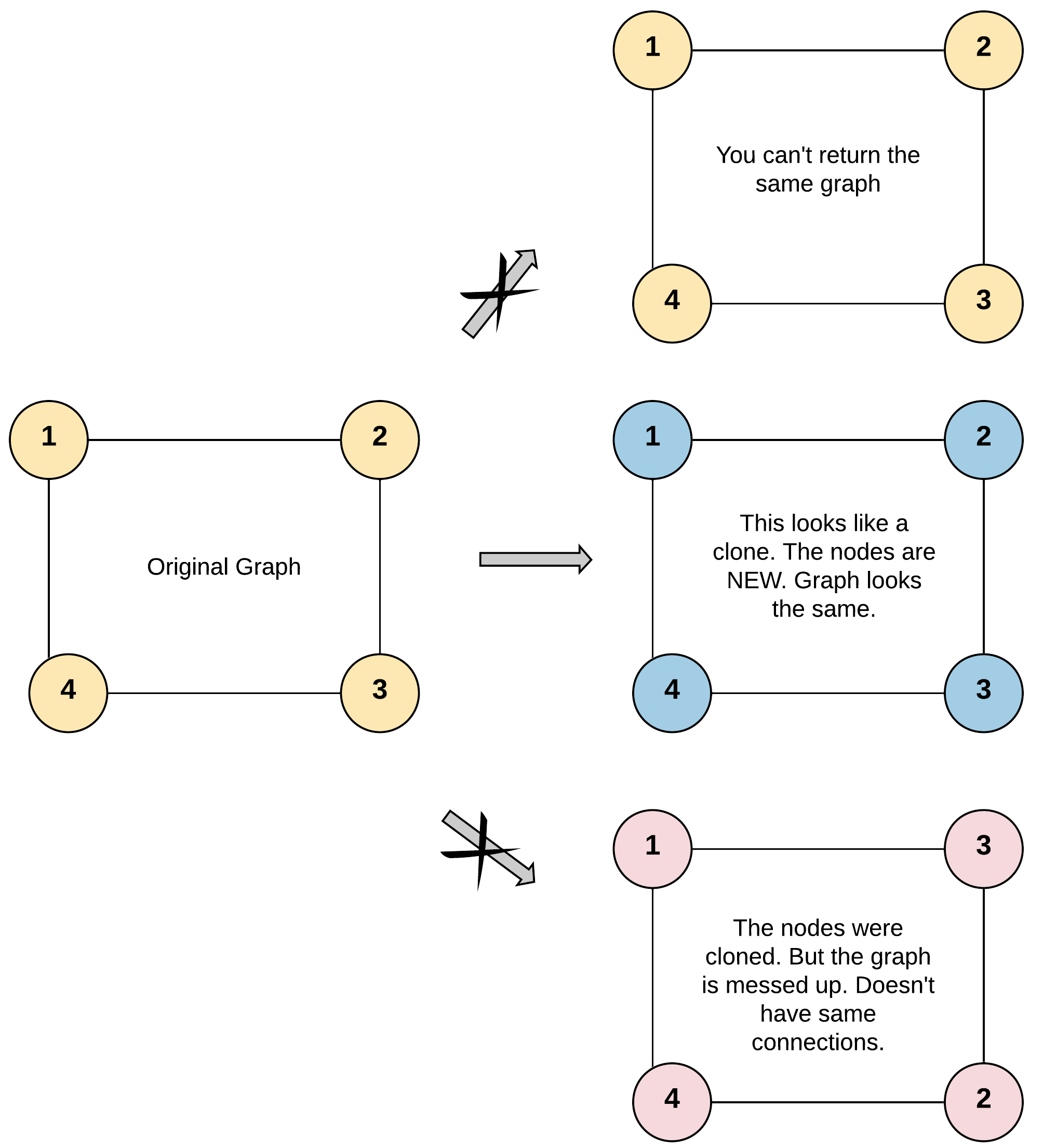
Clone Graph
它本质上还是一道搜索题
Lintcode https://www.lintcode.com/problem/clone-graph/
Leetcode https://leetcode.com/problems/clone-graph/
Solution https://www.jiuzhang.com/solutions/clone-graph/
Description
Given a reference of a node in a connected undirected graph.
Return a deep copy (clone) of the graph.
Each node in the graph contains a value (int) and a list (List[Node]) of its neighbors.
class Node { public int val; public List
Test case format:
For simplicity, each node’s value is the same as the node’s index (1-indexed). For example, the first node with val == 1, the second node with val == 2, and so on. The graph is represented in the test case using an adjacency list.
An adjacency list is a collection of unordered lists used to represent a finite graph. Each list describes the set of neighbors of a node in the graph.
The given node will always be the first node with val = 1. You must return the copy of the given node as a reference to the cloned graph.
Example 1:
Input: adjList = [[2,4],[1,3],[2,4],[1,3]]
Output: [[2,4],[1,3],[2,4],[1,3]]
Explanation: There are 4 nodes in the graph.
1st node (val = 1)’s neighbors are 2nd node (val = 2) and 4th node (val = 4).
2nd node (val = 2)’s neighbors are 1st node (val = 1) and 3rd node (val = 3).
3rd node (val = 3)’s neighbors are 2nd node (val = 2) and 4th node (val = 4).
4th node (val = 4)’s neighbors are 1st node (val = 1) and 3rd node (val = 3).
Example 2:
Input: adjList = [[]]
Output: [[]]
Explanation: Note that the input contains one empty list. The graph consists of only one node with val = 1 and it does not have any neighbors.
Example 3:
Input: adjList = [] Output: [] Explanation: This an empty graph, it does not have any nodes.
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the graph is in the range [0, 100].
- 1 <= Node.val <= 100
- Node.val is unique for each node.
- There are no repeated edges and no self-loops in the graph.
- The Graph is connected and all nodes can be visited starting from the given node.
Solutions
- 从原图给定的点找到所有点
- 复制所有的点
- 复制所有的边
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
/**
* Definition for undirected graph.
* class UndirectedGraphNode {
* int label;
* ArrayList<UndirectedGraphNode> neighbors;
* UndirectedGraphNode(int x) { label = x; neighbors = new ArrayList<UndirectedGraphNode>(); }
* };
*/
public class Solution {
/**
* @param node: A undirected graph node
* @return: A undirected graph node
*/
public UndirectedGraphNode cloneGraph(UndirectedGraphNode node) {
if (node == null) {
return node;
}
// use bfs algorithm to traverse the graph and get all nodes.
ArrayList<UndirectedGraphNode> nodes = getNodes(node);
// copy nodes, store the old->new mapping information in a hash map
HashMap<UndirectedGraphNode, UndirectedGraphNode> mapping = new HashMap<>();
for (UndirectedGraphNode n : nodes) {
mapping.put(n, new UndirectedGraphNode(n.label));
}
// copy neighbors(edges)
for (UndirectedGraphNode n : nodes) {
UndirectedGraphNode newNode = mapping.get(n);
for (UndirectedGraphNode neighbor : n.neighbors) {
UndirectedGraphNode newNeighbor = mapping.get(neighbor);
newNode.neighbors.add(newNeighbor);
}
}
return mapping.get(node);
}
private ArrayList<UndirectedGraphNode> getNodes(UndirectedGraphNode node) {
Queue<UndirectedGraphNode> queue = new LinkedList<UndirectedGraphNode>();
HashSet<UndirectedGraphNode> set = new HashSet<>();
queue.offer(node);
set.add(node);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
UndirectedGraphNode head = queue.poll();
for (UndirectedGraphNode neighbor : head.neighbors) {
if (!set.contains(neighbor)) {
set.add(neighbor);
queue.offer(neighbor);
}
}
}
return new ArrayList<UndirectedGraphNode>(set);
}
}
- node -> graph
copy nodes: old nodes -> new nodes; // 存储映射关系,hash
for node in nodes =>
- new node;
Hash[old_node] = new_node;
copy edges
for node in nodes =>
for edge in node.edges =>
- 从hash表里找到(node, edge.otherNode)对应的点是啥
- 链接对应的点
BFS在图上最经典的应用就是通过图上一个点,找出图上所有的点,也就是整个图。
去重/判重 这个不就是哈希表最擅长 HashSet/HashMap
BFS非常非常的重要!!!!
- 从一个点找到其他的所有点
- 它能做的另一件是它通过一个点,分层的找到其他的所有点。
BFS Template <www.jiuzhang.com/solutions/bfs-template/>
Q: 为什么不用DFS?
Ans: 可以用的,但是不用递归就不用递归!!!能用BFS的就用BFS!!!
Topological Sorting
拓扑排序
Lintcode https://www.lintcode.com/problem/topological-sorting/
Solution https://www.jiuzhang.com/solutions/topological-sorting/
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/topological-sorting/
Solutions
有向图,只能A->B。
无向图,A<->B。
这道题本质上也是一道BFS的题目。
除非面试官说必须用DFS来实现,否则就用BFS来写就行。
要求:掌握BFS。
BFS
When?
- Find connected graph
- Shortest Path in Simple Graph
Graph BFS vs Tree BFS?
Search
Search = { DFS, BFS }
DFS = Permutation + Subset
DFS基本上是一个排列问题或者是一个组合问题。
Permutation 是所有的排列,Subsets实际上是Combination,所有的组合。
Subsets -> Lecture-1 strStr
Permutations
Lintcode https://www.lintcode.com/problem/permutations/
Leetcode https://leetcode.com/problems/permutations/
Solution https://www.jiuzhang.com/solutions/permutations/
Description
Given an array nums of distinct integers, return all the possible permutations. You can return the answer in any order.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [1, 2, 3]
Output: [[1, 2, 3], [1, 3, 2], [2, 1, 3], [2, 3, 1], [3, 1, 2], [3, 2, 1]]
Example 2:
Input: nums = [0, 1]
Output: [[0, 1], [1, 0]]
Example 3:
Input: nums = [1]
Output: [[1]]
Constraints:
- 1 <= nums.length <= 6
- -10 <= nums[i] <= 10
- All the integers of nums are unique.
Solutions
使用深度优先搜索算法。 使用 visited 数组记录某个数是否被放到 permutation 里了。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
public class Solution {
/*
* @param nums: A list of integers.
* @return: A list of permutations.
*/
public List<List<Integer>> permute(int[] nums) {
List<List<Integer>> results = new ArrayList<>();
if (nums == null) {
return results;
}
dfs(nums, new boolean[nums.length], new ArrayList<Integer>(), results);
return results;
}
private void dfs(int[] nums,
boolean[] visited,
List<Integer> permutation,
List<List<Integer>> results) {
if (nums.length == permutation.size()) {
results.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(permutation));
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (visited[i]) {
continue;
}
permutation.add(nums[i]);
visited[i] = true;
dfs(nums, visited, permutation, results);
visited[i] = false;
permutation.remove(permutation.size() - 1);
}
}
}
递归版本
想清楚搜索这棵树是长什么样子的?就是这颗递归树是长什么样子的?
递归的一定要有的三件事情
- 给递归一个定义(他做了一件什么样的事情):找到以 permutation 开头的加到 results 中
- 递归完成的子任务
- 递归的出口:找出一眼能看出来的极端情况,这道题就是
permutation.size() == nums.length。一般的的递归最好是加上return显式的表明出口。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
public class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> permute(int[] nums) {
List<List<Integer>> results = new ArrayList<>();
if (nums == null) {
return results;
}
if (nums.length == 0) {
results.add(new ArrayList<Integer>());
return results;
}
List<Integer> permutation = new ArrayList<Integer>();
Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<>();
helper(nums, permutation, set, results);
return results;
} // end permute
// 1. 定义:找到所有以 permutation 开头的排列
public void helper(int[] nums,
List<Integer> permutation,
Set<Integer> set,
List<List<Integer>> results) {
// 3. 递归的出口
if (permutation.size() == nums.length) {
results.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(permutation));
return;
}
// 2. 用一个循环来实现递归的子任务
// [3] => [3,1], [3,2], [3,4] ...
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (set.contains(nums[i])) {
continue;
}
permutation.add(nums[i]);
set.add(nums[i]);
helper(nums, permutation, set, results);
set.remove(nums[i]);
permutation.remove(permutation.size() - 1);
} // for i
} // end helper
}
public class Solution {
public ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> permute(int[] num) {
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> results = new ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>>();
if (num == null || num.length == 0) {
return results;
}
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>();
helper(results, list, num);
return results;
} // end permute
public void helper(ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> results, ArrayList<Integer> list, int[] num) {
if (list.size() == num.length) {
results.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(list));
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < num.length; i++) {
if (list.contains(num[i])) {
continue;
}
list.add(num[i]);
helper(results, list, num);
list.remove(list.size() - 1);
} // end for loop
} // end helper
} // end Solution
Non-Recursion
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
class Solution {
/**
* @param nums: A list of integers.
* @return: A list of permutations.
*/
public List<List<Integer>> permute(int[] nums) {
ArrayList<List<Integer>> permutations
= new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();
if (nums == null) {
return permutations;
}
if (nums.length == 0) {
permutations.add(new ArrayList<Integer>());
return permutations;
}
int n = nums.length;
ArrayList<Integer> stack = new ArrayList<Integer>();
stack.add(-1);
while (stack.size() != 0) {
Integer last = stack.get(stack.size() - 1);
stack.remove(stack.size() - 1);
// increase the last number
int next = -1;
for (int i = last + 1; i < n; i++) {
if (!stack.contains(i)) {
next = i;
break;
}
}
if (next == -1) {
continue;
}
// generate the next permutation
stack.add(next);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (!stack.contains(i)) {
stack.add(i);
}
}
// copy to permutations set
ArrayList<Integer> permutation = new ArrayList<Integer>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
permutation.add(nums[stack.get(i)]);
}
permutations.add(permutation);
}
return permutations;
}
}
如果想用 Divide & Conquer 的话,需要能够很明显的看出来一半一半的结构。Permutations 并不明显。
Permutations II
Lintcode https://www.lintcode.com/problem/permutations-ii/
Leetcode https://www.leetcode.com/problems/permutations-ii/
Solution https://www.jiuzhang.com/solutions/permutations-ii/
Description
Given a collection of numbers, nums, that might contain duplicates, return all possible unique permutations in any order.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [1, 1, 2]
Output: [ [1, 1, 2], [1, 2, 1], [2, 1, 1] ]
Example 2:
Input: nums = [1, 2, 3]
Output: [ [1, 2, 3], [1, 3, 2], [2, 1, 3], [2, 3, 1], [3, 1, 2], [3, 2, 1] ]
Constraints:
- 1 <= nums.length <= 8
- -10 <= nums[i] <= 10
Solutions
用哈希表的方式来去重,只是代码中的哈希表方式单纯用了一个数组。
做递归,深搜的时候,在结束递归的时候要把之前改了什么再改回来。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
public class Solution {
public ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> permuteUnique(int[] num) {
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>>();
if (numm == null || num.length == 0) {
return result;
}
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>();
int[] visited = new int[num.length];
Arrays.sort(num);
helper(result, list, visited, num);
return result;
} // end permuteUnique
public void helper(ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> result,
ArrayList<Integer> list, int[] visited, int[] num) {
if (list.size() == num.length) {
result.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(list));
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < num.length; i++) {
if (visited[i] == 1 || (i != 0 &&
num[i] == num[i-1] && visited[i-1] == 0)) {
continue;
}
visited[i] = 1;
list.add(num[i]);
helper(result, list, visited, num);
list.remove(list.size() - 1);
visited[i] = 0;
} // end for i loop
} // end helper
} // end Solution
使用排列式深度优先搜索算法。
和没有重复元素的 Permutation 一题相比,只加了两句话:
- Arrays.sort(nums) // 排序这样所有重复的数
- if (i > 0 && numsi == numsi - 1 && !visitedi - 1) { continue; } // 跳过会造成重复的情况
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
public class Solution {
/*
* @param : A list of integers
* @return: A list of unique permutations
*/
public List<List<Integer>> permuteUnique(int[] nums) {
List<List<Integer>> results = new ArrayList<>();
if (nums == null) {
return results;
}
Arrays.sort(nums);
dfs(nums, new boolean[nums.length], new ArrayList<Integer>(), results);
return results;
}
private void dfs(int[] nums,
boolean[] visited,
List<Integer> permutation,
List<List<Integer>> results) {
if (nums.length == permutation.size()) {
results.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(permutation));
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (visited[i]) {
continue;
}
if (i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1] && !visited[i - 1]) {
continue;
}
permutation.add(nums[i]);
visited[i] = true;
dfs(nums, visited, permutation, results);
visited[i] = false;
permutation.remove(permutation.size() - 1);
}
}
};
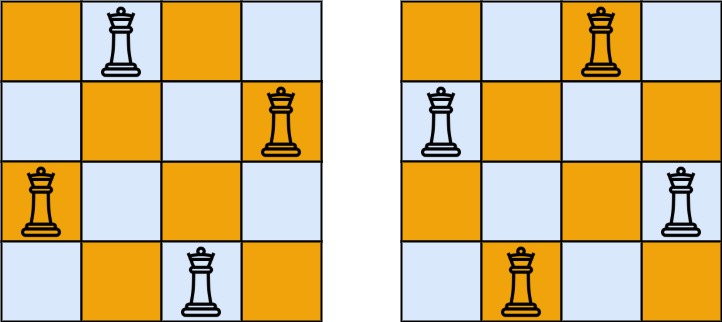
N Queens
Eight Quenes Puzzle https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Eight_queens_puzzle
Lintcode https://www.lintcode.com/problem/n-queens/
Leetcode https://www.leetcode.com/problems/n-queens/
Solution https://www.jiuzhang.com/solutions/n-queens/
Description
The n-queens puzzle is the problem of placing n queens on an n x n chessboard such that no two queens attack each other.
Given an integer n, return all distinct solutions to the n-queens puzzle. You may return the answer in any order.
Each solution contains a distinct board configuration of the n-queens’ placement, where ‘Q’ and ‘.’ both indicate a queen and an empty space, respectively.
Example 1:
Input: n = 4
Output: [ [“.Q..”, “…Q”, “Q…”, “..Q.”],
[”..Q.”, “Q…”, “…Q”, “.Q..”] ]
Explanation: There exist two distinct solutions to the 4-queens puzzle as shown above
Example 2:
Input: n = 1
Output: [[“Q”]]
Constraints:
- 1 <= n <= 9
Solutions
这道题有两种问法,一道题是问所有的方案,另一种问法是问所有的方案总数。(N-Queens II)
=> [2, 4, 1, 3] // 2位置放,第二行放在4位置,还需要检查斜对角线上是否满足。
相当于 Permutations 的过程中,多一层的检查。
- 很认真的写好几遍!
- 输出的数组单独一个函数
- 搜索过程用一个 search 函数来用,相当于一个 helper 函数
- 除了这个数我又没有用过,斜对角线是否存在
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
public class Solution {
private String[] drawChessBoard(ArrayList<Integer> cols) {
String[] chessboard = new String[cols.size()];
for (int i = 0; i < cols.size(); i++) {
chessboard[i] = "";
for (int j = 0; j < cols.size(); j++) {
if (j == cols.get(i)) {
chessboard[i] += "Q";
} else {
chessboard[i] += ".";
}
} // for j
} // for i
return chessboard;
} // end drawChessBoard
private boolean isValid(ArrayList<Integer> cols, int col) {
int row = cols.size();
for (int i = 0; i < row; i++) {
// same column
if (cols.get(i) == col) {
return false;
}
// left-top to right-bottom
if (i - cols.get(i) == row - col) {
return false;
}
// right-top to left-bottom
if (i + cols.get(i) == row + col) {
return false;
}
} // for i
return true;
} // end isValid
private void search(int n, ArrayList<Integer> cols, ArrayList<String[]> result) {
if (cols.size() == n) {
result.add(drawChessBoard(cols));
return;
}
for (int col = 0; col < n; col++) {
if (!isValid(cols, col)) {
continue;
}
cols.add(col);
search(n, cols, result);
cols.remove(cols.size() - 1);
} // end for col
} // end search
public ArrayList<String[]> solveNQueens(int n) {
ArrayList<String[]> result = new ArrayList<String[]>();
if (n <= 0) {
return result;
}
search(n, new ArrayList<Integer>(), result);
return result;
} // end solveNQueens
} // end Solution
暴力搜索,尝试可以放置的地点,返回每个方案即可
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
class Solution {
/**
* Get all distinct N-Queen solutions
* @param n: The number of queens
* @return: All distinct solutions
* For example, A string '...Q' shows a queen on forth position
*/
List<List<String>> solveNQueens(int n) {
List<List<String>> results = new ArrayList<>();
if (n <= 0) {
return results;
}
search(results, new ArrayList<Integer>(), n);
return results;
}
/*
* results store all of the chessboards
* cols store the column indices for each row
*/
private void search(List<List<String>> results,
List<Integer> cols,
int n) {
if (cols.size() == n) {
results.add(drawChessboard(cols));
return;
}
for (int colIndex = 0; colIndex < n; colIndex++) {
if (!isValid(cols, colIndex)) {
continue;
}
cols.add(colIndex);
search(results, cols, n);
cols.remove(cols.size() - 1);
}
}
private List<String> drawChessboard(List<Integer> cols) {
List<String> chessboard = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < cols.size(); i++) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for (int j = 0; j < cols.size(); j++) {
sb.append(j == cols.get(i) ? 'Q' : '.');
}
chessboard.add(sb.toString());
}
return chessboard;
}
private boolean isValid(List<Integer> cols, int column) {
int row = cols.size();
for (int rowIndex = 0; rowIndex < cols.size(); rowIndex++) {
if (cols.get(rowIndex) == column) {
return false;
}
if (rowIndex + cols.get(rowIndex) == row + column) {
return false;
}
if (rowIndex - cols.get(rowIndex) == row - column) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
Palindrome Patitioning
Lintcode https://www.lintcode.com/problem/palindrome-partitioning/
Leetcode https://leetcode.com/problems/palindrome-partitioning/
Solution https://www.jiuzhang.com/solutions/palindrome-partitioning/
Description
Given a string s, partition s such that every substring of the partition is a palindrome. Return all possible palindrome partitioning of s.
Example 1:
Input: s = “aab”
Output: [[“a”, “a”, “b”], [“aa”, “b”]]
Example 2:
Input: s = “a”
Output: [[“a”]]
Constraints:
- 1 <= s.length <= 16
- s contains only lowercase English letters.
Solutions
使用回溯法枚举所有可能的分割方案即可.
关于判断回文串, 最简单的可以写一个函数, 遍历一次字符串即可. 但是这样效率不高, 可以先预处理一下, 可以使用动态规划或者Manacher算法.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
// version 1: shorter but slower
public class Solution {
/**
* @param s: A string
* @return: A list of lists of string
*/
public List<List<String>> partition(String s) {
List<List<String>> results = new ArrayList<>();
if (s == null || s.length() == 0) {
return results;
}
List<String> partition = new ArrayList<String>();
helper(s, 0, partition, results);
return results;
}
private void helper(String s,
int startIndex,
List<String> partition,
List<List<String>> results) {
if (startIndex == s.length()) {
results.add(new ArrayList<String>(partition));
return;
}
for (int i = startIndex; i < s.length(); i++) {
String subString = s.substring(startIndex, i + 1);
if (!isPalindrome(subString)) {
continue;
}
partition.add(subString);
helper(s, i + 1, partition, results);
partition.remove(partition.size() - 1);
}
}
private boolean isPalindrome(String s) {
for (int i = 0, j = s.length() - 1; i < j; i++, j--) {
if (s.charAt(i) != s.charAt(j)) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
// version 2: longer but faster
public class Solution {
List<List<String>> results;
boolean[][] isPalindrome;
/**
* @param s: A string
* @return: A list of lists of string
*/
public List<List<String>> partition(String s) {
results = new ArrayList<>();
if (s == null || s.length() == 0) {
return results;
}
getIsPalindrome(s);
helper(s, 0, new ArrayList<Integer>());
return results;
}
private void getIsPalindrome(String s) {
int n = s.length();
isPalindrome = new boolean[n][n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
isPalindrome[i][i] = true;
}
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
isPalindrome[i][i + 1] = (s.charAt(i) == s.charAt(i + 1));
}
for (int i = n - 3; i >= 0; i--) {
for (int j = i + 2; j < n; j++) {
isPalindrome[i][j] = isPalindrome[i + 1][j - 1] && s.charAt(i) == s.charAt(j);
}
}
}
private void helper(String s,
int startIndex,
List<Integer> partition) {
if (startIndex == s.length()) {
addResult(s, partition);
return;
}
for (int i = startIndex; i < s.length(); i++) {
if (!isPalindrome[startIndex][i]) {
continue;
}
partition.add(i);
helper(s, i + 1, partition);
partition.remove(partition.size() - 1);
}
}
private void addResult(String s, List<Integer> partition) {
List<String> result = new ArrayList<>();
int startIndex = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < partition.size(); i++) {
result.add(s.substring(startIndex, partition.get(i) + 1));
startIndex = partition.get(i) + 1;
}
results.add(result);
}
}
Combination Sum
Lintcode https://www.lintcode.com/problem/combination-sum/
Leetcode https://www.leetcode.com/problems/combination-sum/
Solution https://www.jiuzhang.com/solutions/combination-sum/
Description
Given an array of distinct integers candidates and a target integer target, return a list of all unique combinations of candidates where the chosen numbers sum to target. You may return the combinations in any order.
The same number may be chosen from candidates an unlimited number of times. Two combinations are unique if the frequency of at least one of the chosen numbers is different.
The test cases are generated such that the number of unique combinations that sum up to target is less than 150 combinations for the given input.
Example 1:
Input: candidates = [2, 3, 6, 7], target = 7
Output: [ [2, 2, 3], [7] ]
Explanation: 2 and 3 are candidates, and 2 + 2 + 3 = 7. Note that 2 can be used multiple times. 7 is a candidate, and 7 = 7. These are the only two combinations.
Example 2:
Input: candidates = [2, 3, 5], target = 8
Output: [ [2, 2, 2, 2], [2, 3, 3], [3, 5] ]
Example 3:
Input: candidates = [2], target = 1
Output: []
Constraints:
- 1 <= candidates.length <= 30
- 2 <= candidates[i] <= 40
- All elements of candidates are distinct.
- 1 <= target <= 40
Solutions
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
public class Solution {
public ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> combinationSum(int[] candidates, int target) {
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>>();
if (candidates == null) {
return result;
}
ArrayList<Integer> path = new ArrayList<Integer>();
Arrays.sort(candidates);
helper(candidates, target, path, 0, result);
return result;
} // end combinationSum
void helper(int[] candidates, int target, ArrayList<Integer> path, int index,
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> result) {
if (target == 0) {
result.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(path));
return;
}
int prev = -1;
for (int i = index; i < candidates.length; i++) {
if (candidates[i] > target) {
break;
}
if (prev != -1 && prev == candidates[i]) {
continue;
}
path.add(candidates[i]);
helper(candidates, target - candidates[i], path, i, result);
path.remove(path.size() - 1);
prev = candidates[i];
} // for i
} // end helper
} // end Solution
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
// version 1: Remove duplicates & generate a new array
public class Solution {
/**
* @param candidates: A list of integers
* @param target:An integer
* @return: A list of lists of integers
*/
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum(int[] candidates, int target) {
List<List<Integer>> results = new ArrayList<>();
if (candidates == null || candidates.length == 0) {
return results;
}
int[] nums = removeDuplicates(candidates);
dfs(nums, 0, new ArrayList<Integer>(), target, results);
return results;
}
private int[] removeDuplicates(int[] candidates) {
Arrays.sort(candidates);
int index = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < candidates.length; i++) {
if (candidates[i] != candidates[index]) {
candidates[++index] = candidates[i];
}
}
int[] nums = new int[index + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < index + 1; i++) {
nums[i] = candidates[i];
}
return nums;
}
private void dfs(int[] nums,
int startIndex,
List<Integer> combination,
int remainTarget,
List<List<Integer>> results) {
if (remainTarget == 0) {
results.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(combination));
return;
}
for (int i = startIndex; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (remainTarget < nums[i]) {
break;
}
combination.add(nums[i]);
dfs(nums, i, combination, remainTarget - nums[i], results);
combination.remove(combination.size() - 1);
}
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
// version 2: reuse candidates array
public class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum(int[] candidates, int target) {
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
if (candidates == null) {
return result;
}
List<Integer> combination = new ArrayList<>();
Arrays.sort(candidates);
helper(candidates, 0, target, combination, result);
return result;
}
void helper(int[] candidates,
int index,
int target,
List<Integer> combination,
List<List<Integer>> result) {
if (target == 0) {
result.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(combination));
return;
}
for (int i = index; i < candidates.length; i++) {
if (candidates[i] > target) {
break;
}
if (i != 0 && candidates[i] == candidates[i - 1]) {
continue;
}
combination.add(candidates[i]);
helper(candidates, i, target - candidates[i], combination, result);
combination.remove(combination.size() - 1);
}
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
public class Solution {
/**
* @param candidates: A list of integers
* @param target: An integer
* @return: A list of lists of integers
*/
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum(int[] candidates, int target) {
Arrays.sort(candidates);
List<List<Integer>> results = new ArrayList<>();
dfs(candidates, 0, target, new ArrayList<Integer>(), results);
return results;
}
private void dfs(int[] candidates, int index, int target, List<Integer> combination, List<List<Integer>> results) {
if (index == candidates.length) {
if (target == 0) {
results.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(combination));
}
return;
}
if (target < 0) {
return;
}
dfs(candidates, index + 1, target, combination, results);
if (index > 0 && candidates[index] == candidates[index - 1]) {
return;
}
combination.add(candidates[index]);
dfs(candidates, index, target - candidates[index], combination, results);
combination.remove(combination.size() - 1);
}
}
Combination Sum II
Lintcode https://www.lintcode.com/problem/combination-sum-ii/
Leetcode https://www.leetcode.com/problems/combination-sum-ii/
Solution https://www.jiuzhang.com/solutions/combination-sum-ii/
Description
Given a collection of candidate numbers (candidates) and a target number (target), find all unique combinations in candidates where the candidate numbers sum to target.
Each number in candidates may only be used once in the combination.
Note: The solution set must not contain duplicate combinations.
Example 1:
Input: candidates = [10, 1, 2, 7, 6, 1, 5], target = 8
Output: [ [1, 1, 6], [1, 2, 5], [1, 7], [2, 6] ]
Example 2:
Input: candidates = [ 2, 5, 2, 1, 2 ], target = 5
Output: [ [ 1, 2, 2 ], [5] ]
Constraints:
- 1 <= candidates.length <= 100
- 1 <= candidates[i] <= 50
- 1 <= target <= 30
Solutions
使用回溯法搜索所有可能的组合. 很基础的题目, 有多种不同的写法, 再次不多赘述.
有一个显而易见的小优化: 我们在搜索的过程中会记录已经选择的数字的和, 如果这个和超过了 target, 停止搜索. 除此之外还有很多可以优化的细节, 慢慢探索吧!
另外, 这个题目还可以有非递归的形式: 用一个整型的 num.length 个二进制位表示一个组合, 第 i 位为 1 表示这个组合内含有 num[i]. 这样可以从0自增这个整型来达到枚举所有组合的效果. 避免了递归的开销 (但是也不一定比递归快, 因为递归可以有优化, 而这样枚举就只能老老实实把所有的组合都查看一遍)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
public class Solution {
/**
* @param num: Given the candidate numbers
* @param target: Given the target number
* @return: All the combinations that sum to target
*/
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum2(int[] candidates,
int target) {
List<List<Integer>> results = new ArrayList<>();
if (candidates == null || candidates.length == 0) {
return results;
}
Arrays.sort(candidates);
List<Integer> combination = new ArrayList<Integer>();
helper(candidates, 0, combination, target, results);
return results;
}
private void helper(int[] candidates,
int startIndex,
List<Integer> combination,
int target,
List<List<Integer>> results) {
if (target == 0) {
results.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(combination));
return;
}
for (int i = startIndex; i < candidates.length; i++) {
if (i != startIndex && candidates[i] == candidates[i - 1]) {
continue;
}
if (target < candidates[i]) {
break;
}
combination.add(candidates[i]);
helper(candidates, i + 1, combination, target - candidates[i], results);
combination.remove(combination.size() - 1);
}
}
}
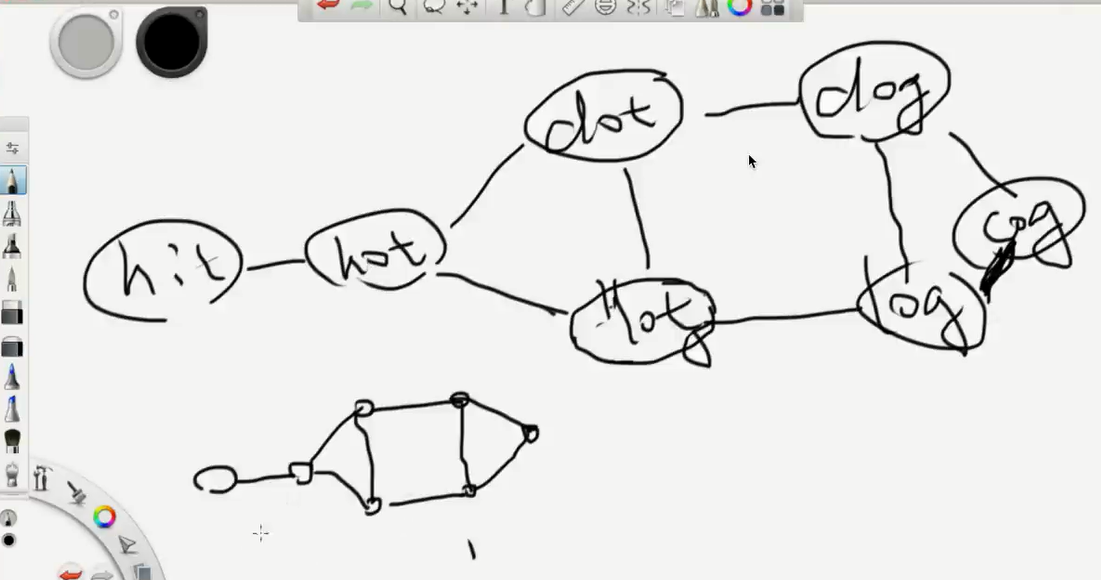
Word Ladder
Lintcode https://www.lintcode.com/problem/word-ladder/
Leetcode https://www.leetcode.com/problems/word-ladder/
Solution https://www.jiuzhang.com/solutions/word-ladder/
很具有代表性的一类题,给你一个 start 给你一个 end ,再给你一个规则。
这就是一个图。问你从起点到终点,求最短路径。简单图,Simple Graph。
最专业的做法就是宽度优先搜索。
还有一类BFS的问题,叫做九宫格类问题。
Description
A transformation sequence from word beginWord to word endWord using a dictionary wordList is a sequence of words beginWord -> s1 -> s2 -> … -> sk such that:
- Every adjacent pair of words differs by a single letter.
- Every si for 1 <= i <= k is in wordList. Note that beginWord does not need to be in wordList.
- sk == endWord
Given two words, beginWord and endWord, and a dictionary wordList, return the number of words in the shortest transformation sequence from beginWord to endWord, or 0 if no such sequence exists.
Example 1:
Input: beginWord = “hit”, endWord = “cog”, wordList = [“hot”,”dot”,”dog”,”lot”,”log”,”cog”]
Output: 5
Explanation: One shortest transformation sequence is “hit” -> “hot” -> “dot” -> “dog” -> cog”, which is 5 words long.
Example 2:
Input: beginWord = “hit”, endWord = “cog”, wordList = [“hot”,”dot”,”dog”,”lot”,”log”]
Output: 0
Explanation: The endWord “cog” is not in wordList, therefore there is no valid transformation sequence.
Constraints:
- 1 <= beginWord.length <= 10
- endWord.length == beginWord.length
- 1 <= wordList.length <= 5000
- wordList[i].length == beginWord.length
- beginWord, endWord, and wordList[i] consist of lowercase English letters.
- beginWord != endWord
- All the words in wordList are unique.
Solutions
从头部开始枚举替换字母,每次替换一个字母,即为一步,每次得到新单词如果在dict中就继续搜索。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
// version: LintCode ( Set<String> )
public class Solution {
public int ladderLength(String start, String end, Set<String> dict) {
if (dict == null) {
return 0;
}
if (start.equals(end)) {
return 1;
}
dict.add(start);
dict.add(end);
HashSet<String> hash = new HashSet<String>();
Queue<String> queue = new LinkedList<String>();
queue.offer(start);
hash.add(start);
int length = 1;
while(!queue.isEmpty()) { //开始bfs
length++;
int size = queue.size(); //当前步数的队列大小
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
String word = queue.poll();
for (String nextWord: getNextWords(word, dict)) { //得到新单词
if (hash.contains(nextWord)) {
continue;
}
if (nextWord.equals(end)) {
return length;
}
hash.add(nextWord);
queue.offer(nextWord); //存入队列继续搜索
}
}
}
return 0;
}
// replace character of a string at given index to a given character
// return a new string
private String replace(String s, int index, char c) {
char[] chars = s.toCharArray();
chars[index] = c;
return new String(chars);
}
// get connections with given word.
// for example, given word = 'hot', dict = {'hot', 'hit', 'hog'}
// it will return ['hit', 'hog']
private ArrayList<String> getNextWords(String word, Set<String> dict) {
ArrayList<String> nextWords = new ArrayList<String>();
for (char c = 'a'; c <= 'z'; c++) { //枚举当前替换字母
for (int i = 0; i < word.length(); i++) { //枚举替换位置
if (c == word.charAt(i)) {
continue;
}
String nextWord = replace(word, i, c);
if (dict.contains(nextWord)) {//如果dict中包含新单词,存入nextWords
nextWords.add(nextWord);
}
} // for i
} // for c
return nextWords; //构造当前单词的全部下一步方案
} // end getNextWords
} // end Solution
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
// version: LeetCode
public class Solution {
public int ladderLength(String start, String end, List<String> wordList) {
Set<String> dict = new HashSet<>();
for (String word : wordList) { //将wordList中的单词加入dict
dict.add(word);
}
if (start.equals(end)) {
return 1;
}
HashSet<String> hash = new HashSet<String>();
Queue<String> queue = new LinkedList<String>();
queue.offer(start);
hash.add(start);
int length = 1;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) { //开始bfs
length++;
int size = queue.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { //枚举当前步数队列的情况
String word = queue.poll();
for (String nextWord: getNextWords(word, dict)) {
if (hash.contains(nextWord)) {
continue;
}
if (nextWord.equals(end)) {
return length;
}
hash.add(nextWord); //存入新单词
queue.offer(nextWord);
}
}
}
return 0;
}
// replace character of a string at given index to a given character
// return a new string
private String replace(String s, int index, char c) {
char[] chars = s.toCharArray();
chars[index] = c;
return new String(chars);
}
// get connections with given word.
// for example, given word = 'hot', dict = {'hot', 'hit', 'hog'}
// it will return ['hit', 'hog']
private ArrayList<String> getNextWords(String word, Set<String> dict) {
ArrayList<String> nextWords = new ArrayList<String>();
for (char c = 'a'; c <= 'z'; c++) { //枚举替换字母
for (int i = 0; i < word.length(); i++) { //枚举替换位置
if (c == word.charAt(i)) {
continue;
}
String nextWord = replace(word, i, c);
if (dict.contains(nextWord)) { //如果dict中包含新单词,存入nextWords
nextWords.add(nextWord);
}
}
}
return nextWords; //构造当前单词的全部下一步方案
}
}
Word Ladder II
Lintcode https://www.lintcode.com/problem/word-ladder-ii/
Leetcode https://www.leetcode.com/problems/word-ladder-ii/
Solution https://www.jiuzhang.com/solutions/word-ladder-ii/
Description
A transformation sequence from word beginWord to word endWord using a dictionary wordList is a sequence of words beginWord -> s1 -> s2 -> … -> sk such that:
- Every adjacent pair of words differs by a single letter.
- Every si for 1 <= i <= k is in wordList. Note that beginWord does not need to be in wordList.
- sk == endWord
Given two words, beginWord and endWord, and a dictionary wordList, return all the shortest transformation sequences from beginWord to endWord, or an empty list if no such sequence exists. Each sequence should be returned as a list of the words [beginWord, s1, s2, …, sk].
Example 1:
Input: beginWord = “hit”, endWord = “cog”, wordList = [“hot”,”dot”,”dog”,”lot”,”log”,”cog”]
Output: [[“hit”,”hot”,”dot”,”dog”,”cog”],[“hit”,”hot”,”lot”,”log”,”cog”]]
Explanation: There are 2 shortest transformation sequences: “hit” -> “hot” -> “dot” -> “dog” -> “cog” “hit” -> “hot” -> “lot” -> “log” -> “cog”
Example 2:
Input: beginWord = “hit”, endWord = “cog”, wordList = [“hot”,”dot”,”dog”,”lot”,”log”]
Output: []
Explanation: The endWord “cog” is not in wordList, therefore there is no valid transformation sequence.
Constraints:
- 1 <= beginWord.length <= 5
- endWord.length == beginWord.length
- 1 <= wordList.length <= 500
- wordList[i].length == beginWord.length
- beginWord, endWord, and wordList[i] consist of lowercase English letters.
- beginWord != endWord
- All the words in wordList are unique.
- The sum of all shortest transformation sequences does not exceed 10^5.
Solutions
end -> start : bfs start -> end : dfs
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
public class Solution {
public List<List<String>> findLadders(String start, String end,
Set<String> dict) {
List<List<String>> ladders = new ArrayList<List<String>>();
Map<String, List<String>> map = new HashMap<String, List<String>>();
Map<String, Integer> distance = new HashMap<String, Integer>();
dict.add(start);
dict.add(end);
bfs(map, distance, end, start, dict);
List<String> path = new ArrayList<String>();
dfs(ladders, path, start, end, distance, map);
return ladders;
}
void dfs(List<List<String>> ladders, List<String> path, String crt,
String end, Map<String, Integer> distance,
Map<String, List<String>> map) {
path.add(crt);
if (crt.equals(end)) {
ladders.add(new ArrayList<String>(path));
} else {
for (String next : map.get(crt)) {
if (distance.containsKey(next) && distance.get(crt) == distance.get(next) + 1) {
dfs(ladders, path, next, end, distance, map);
}
}
}
path.remove(path.size() - 1);
}
void bfs(Map<String, List<String>> map, Map<String, Integer> distance,
String start, String end, Set<String> dict) {
Queue<String> q = new LinkedList<String>();
q.offer(start);
distance.put(start, 0);
for (String s : dict) {
map.put(s, new ArrayList<String>());
}
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
String crt = q.poll();
List<String> nextList = expand(crt, dict);
for (String next : nextList) {
map.get(next).add(crt);
if (!distance.containsKey(next)) {
distance.put(next, distance.get(crt) + 1);
q.offer(next);
}
}
}
}
List<String> expand(String crt, Set<String> dict) {
List<String> expansion = new ArrayList<String>();
for (int i = 0; i < crt.length(); i++) {
for (char ch = 'a'; ch <= 'z'; ch++) {
if (ch != crt.charAt(i)) {
String expanded = crt.substring(0, i) + ch
+ crt.substring(i + 1);
if (dict.contains(expanded)) {
expansion.add(expanded);
}
}
}
}
return expansion;
}
}
start -> end: bfs end -> start: dfs
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
public class Solution {
public List<List<String>> findLadders(String start, String end,
Set<String> dict) {
List<List<String>> ladders = new ArrayList<List<String>>();
Map<String, List<String>> map = new HashMap<String, List<String>>();
Map<String, Integer> distance = new HashMap<String, Integer>();
dict.add(start);
dict.add(end);
bfs(map, distance, start, end, dict);
List<String> path = new ArrayList<String>();
dfs(ladders, path, end, start, distance, map);
return ladders;
}
void dfs(List<List<String>> ladders, List<String> path, String crt,
String start, Map<String, Integer> distance,
Map<String, List<String>> map) {
path.add(crt);
if (crt.equals(start)) {
Collections.reverse(path);
ladders.add(new ArrayList<String>(path));
Collections.reverse(path);
} else {
for (String next : map.get(crt)) {
if (distance.containsKey(next) && distance.get(crt) == distance.get(next) + 1) {
dfs(ladders, path, next, start, distance, map);
}
}
}
path.remove(path.size() - 1);
}
void bfs(Map<String, List<String>> map, Map<String, Integer> distance,
String start, String end, Set<String> dict) {
Queue<String> q = new LinkedList<String>();
q.offer(start);
distance.put(start, 0);
for (String s : dict) {
map.put(s, new ArrayList<String>());
}
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
String crt = q.poll();
List<String> nextList = expand(crt, dict);
for (String next : nextList) {
map.get(next).add(crt);
if (!distance.containsKey(next)) {
distance.put(next, distance.get(crt) + 1);
q.offer(next);
}
}
}
}
List<String> expand(String crt, Set<String> dict) {
List<String> expansion = new ArrayList<String>();
for (int i = 0; i < crt.length(); i++) {
for (char ch = 'a'; ch <= 'z'; ch++) {
if (ch != crt.charAt(i)) {
String expanded = crt.substring(0, i) + ch
+ crt.substring(i + 1);
if (dict.contains(expanded)) {
expansion.add(expanded);
}
}
}
}
return expansion;
}
}
- 本题基于搜索完成。
- 首先使用bfs,调用getnext()方法寻找当前单词的下一步单词,如果单词在dict中,就存入ret。
- 然后使用dfs,枚举当前字符串的下一步方案,方案存入path,然后枚举搜索,搜索完成后,再将其删除。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
// 九章算法求职集训营版本 (只用DFS+剪枝)
public class Solution {
/*
* @param start: a string
* @param end: a string
* @param dict: a set of string
* @return: a list of lists of string
*/
List<List<String> > res = new ArrayList<List<String> >();
int T;
int[] f;
int endid;
HashMap<String, Integer> word2id = new HashMap<String, Integer>();
String[] id2word;
HashMap<Integer, List<Integer>> graph = new HashMap<Integer, List<Integer>>();
int[] lb;
public void dfs(int id, int idx) {
if (idx > T) {
return;
}
if (idx + lb[id] > T) {
return;
}
f[idx] = id;
int i;
if (id == endid) {
List<String> flist = new ArrayList<String>();
for (i = 0; i < f.length; ++i) flist.add(id2word[f[i]]);
res.add(flist);
return;
}
int next;
for (i = 0; i < graph.get(id).size(); ++i) { //枚举下一步进行搜索
next = graph.get(id).get(i);
dfs(next, idx + 1);
}
if (res.size() == 0) {
lb[id] = Math.max(lb[id], T - idx + 1);
}
}
private void buildWordIds(String start, String end, Set<String> dict) { //将各个单词存入word2id
int n = 0;
for (String s : dict) {
word2id.put(s, n);
++n;
}
if (!word2id.containsKey(start)) {
word2id.put(start, n);
++n;
}
if (!word2id.containsKey(end)) {
word2id.put(end, n);
++n;
}
id2word = new String[word2id.size()];
for (String s: word2id.keySet()) {
id2word[word2id.get(s)] = s; //建立数字对字符串的映射关系
}
}
private void buildGraph() {
for (String s : word2id.keySet()) {
int id = word2id.get(s);
graph.put(id, new ArrayList<Integer>());
char[] now = s.toCharArray();
for (int i = 0; i < now.length; ++i) { //枚举当前单词替换位置
char tmp = now[i];
for (char c = 'a'; c <= 'z'; ++c) { //枚举替换字母
if (c == tmp) {
continue;
}
now[i] = c;
if (word2id.containsKey(String.valueOf(now))) {//如果新单词在word2id中
graph.get(id).add(word2id.get(String.valueOf(now)));
}
}
now[i] = tmp;
}
}
}
// calculate lower bound to go from word i to end
private void initLb(String end) { //统计字符串不同字母的数量
int n = id2word.length;
lb = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
String now = id2word[i];
lb[i] = 0;
for (int p = 0; p < now.length(); ++p) {
if (now.charAt(p) != end.charAt(p)) {
++lb[i];
}
}
}
}
public List<List<String>> findLadders(String start, String end, Set<String> dict) {
if (start.equals(end)) {
List<String> t = new ArrayList<String>();
t.add(start);
res.add(t);
return res;
}
buildWordIds(start, end, dict);
buildGraph();
initLb(end);
endid = word2id.get(end);
for (T = 1; ; ++T) {
System.out.println(T);
f = new int[T + 1];
dfs(word2id.get(start), 0); //dfs
if (res.size() > 0) {
return res;
}
}
}
}
//集训营 version 2
public class Solution {
/*
* @param start: a string
* @param end: a string
* @param dict: a set of string
* @return: a list of lists of string
*/
Map<String, List<String>> graph = new HashMap<>();
List<List<String>> ans = new ArrayList<>();
Map<String, Integer> lb = new HashMap<>();
private void dfs(int limit, int x, String word, String end, List<String> path) {
if (x == limit + 1) {
if (word.equals(end)) { //如果当前单词和end相同
ans.add(new ArrayList<>(path)); //答案将当前path存入
}
return;
}
if (x - 1 + lb.get(word) > limit) {//如果当前单词的变换次数加上不同的字母数超出限制就退出
return;
}
for (String next : graph.get(word)) {
path.add(next); //将下一个单词加入path
dfs(limit, x + 1, next, end, path); //继续搜索
path.remove(path.size() - 1); //搜索完成后删除
}
if (ans.isEmpty()) {
lb.put(word, Math.max(lb.get(word), limit - (x - 1) + 1));
}
}
private List<String> getNext(String word, Set<String> dict) {
List<String> ret = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < word.length(); i++) { //枚举当前单词替换位置
char[] sc = word.toCharArray();
for (char c = 'a'; c <= 'z'; c++) { //枚举当前可替换字母
sc[i] = c;
String next = String.valueOf(sc);
if (dict.contains(next) && !word.equals(next)) { //如果替换字母后的单词在dict中
ret.add(next); //加入ret中
}
}
}
return ret;
}
private int getDiff(String a, String b) { //比较两个字符串不同的字母个数
int ret = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < a.length(); i++) {
if (a.charAt(i) != b.charAt(i)) {
ret++;
}
}
return ret;
}
public List<List<String>> findLadders(String start, String end, Set<String> dict) {
// write your code here
dict.add(start);
dict.add(end);
for (String word : dict) {
graph.put(word, getNext(word, dict)); //存入当前单词和下一步方案
lb.put(word, getDiff(word, end));
}
int limit = 0;
List<String> path = new ArrayList<>();
path.add(start);
while (ans.isEmpty()) {
dfs(limit, 1, start, end, path); //开始搜索
limit++; //每一步limit++
}
return ans;
}
}
Conclusion
DFS (O(2^n), O(n!)) 思想是构建搜索树 + 判断可行性
- Find all possible solutions
- Permutations / Subsets
如果题目让你找出所有方案,那么需要用DFS
BFS (O(m), O(n))
- Graph traversal (每个点只遍历一次)
- Find shortest path in a simple graph