Lecture-6 Linked List
链表只是一个载体,实际上是让你实现一些其他题目。
Outline
- Introduce Dummy Node
- Basic Linked List Skills
- Two Pointers in Linked List (Fast-slow pointers)
Basic Knowledge Test
What’s the output of the following code?
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
void print() {
for (ListNode node = head; node != null; node = node.next) {
System.out.print(node.val);
System.out.print("->");
}
System.out.println("null");
}
void main() {
ListNode node1 = new ListNode(1);
ListNode node2 = new ListNode(2);
ListNode node3 = new ListNode(3);
ListNode head = node1;
node1.next = node2;
node2.next = node3;
print(head);
node1 = node2;
print(head);
}
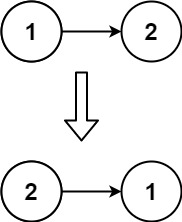
解释一下node1 = node2;代码的意思。
类似 a=b b=c c=e 赋值语句,但是实际上链表在内存中的结构是不会变化的。
如果要改变的话,需要node.val node.next来赋值改变。
node1 = node2; 这只是改变了指针的引用。
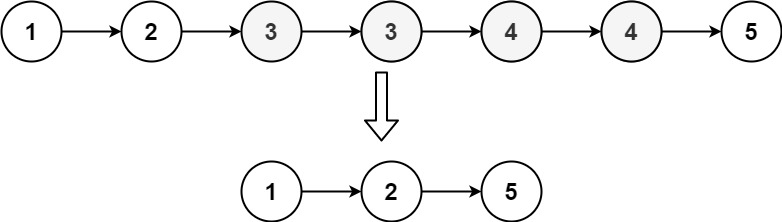
Remove Duplicates from Sorrted List ii
Lintcode https://www.lintcode.com/problem/remove-duplicates-from-sorted-list-ii/
Leetcode https://leetcode.com/problems/remove-duplicates-from-sorted-list-ii/
Solution https://www.jiuzhang.com/solutions/remove-duplicates-from-sorted-list-ii/
Description
Given the head of a sorted linked list, delete all nodes that have duplicate numbers, leaving only distinct numbers from the original list. Return the linked list sorted as well.
Example 1:
Input: head = [1,2,3,3,4,4,5]
Output: [1,2,5]
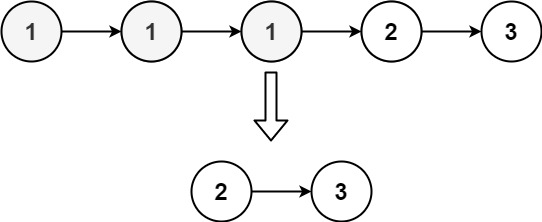
Example 2:
Input: head = [1,1,1,2,3]
Output: [2,3]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the list is in the range [0, 300].
- -100 <= Node.val <= 100
- The list is guaranteed to be sorted in ascending order.
Solutions
我们经常的操作就是
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0);
dummy.next = head;
head = dummy;
// 亦或者多加两个变量来处理
ListNode prev = dummy;
ListNode curt = head;
最后是 return dummy.next;
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
public class Solution {
public ListNode deleteDuplicates(ListNode head) {
if(head == null || head.next == null)
return head;
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0);
dummy.next = head;
head = dummy;
while (head.next != null && head.next.next != null) {
if (head.next.val == head.next.next.val) {
int val = head.next.val;
while (head.next != null && head.next.val == val) {
head.next = head.next.next;
}
} else {
head = head.next;
}
}
return dummy.next;
}
}
如果不用 Dummy Node 程序就会变得复杂很多,思考更多的东西。
soft delete / hard delete / logic delete
Related Question
Remove Duplicates from Sorrted List https://leetcode.cn/problems/remove-duplicates-from-sorted-list/
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
class Solution {
public ListNode deleteDuplicates(ListNode head) {
if (head == null) {
return head;
}
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur.next != null) {
if (cur.val == cur.next.val) {
cur.next = cur.next.next;
} else {
cur = cur.next;
}
}
return head;
}
}
Delete Node in the Middle of Singly Linked List
只给了要删除的节点,没给 head,那只能 soft delete。
node.val = node.next.val;
node.next = node.next.next;
如果只给了 node2 ,但是要删除2,我们把下一个点 node3 拷贝到 node2,并把下一个点 node3 删掉,一个很巧妙的方法,删除了 node2。
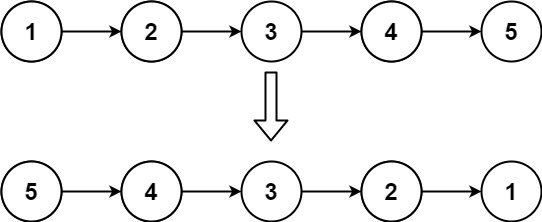
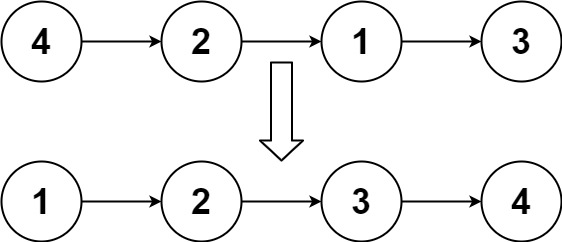
Reverse Linked List
Leetcode https://leetcode.com/problems/reverse-linked-list/
Description
Given the head of a singly linked list, reverse the list, and return the reversed list.
Example 1:
Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5]
Output: [5,4,3,2,1]
Example 2:
Input: head = [1,2]
Output: [2,1]
Example 3:
Input: head = []
Output: []
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the list is the range [0, 5000].
- -5000 <= Node.val <= 5000
Follow up: A linked list can be reversed either iteratively or recursively. Could you implement both?
Solutions
单纯的reverse list 理解背下来了。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
public class Solution {
public ListNode reverse(ListNode head) {
ListNode prev = null;
while (head != null) {
ListNode temp = head.next;
head.next = prev;
prev = head;
head = temp;
}
return prev;
}
}
解释这个逆转过程。交换两个数
类似于两个节点逆转,
这样子可以借助swap(a, b)来记住反转链表的代码
Reverse Linked List ii
Lintcode https://www.lintcode.com/problem/reverse-linked-list-ii/
Leetcode https://leetcode.cn/problems/reverse-linked-list-ii/
Solution https://www.jiuzhang.com/solutions/reverse-linked-list-ii/
Description
Given the head of a singly linked list and two integers left and right where left <= right, reverse the nodes of the list from position left to position right, and return the reversed list.
Example 1:
Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5], left = 2, right = 4
Output: [1,4,3,2,5]
Example 2:
Input: head = [5], left = 1, right = 1 Output: [5]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the list is n.
- 1 <= n <= 500
- -500 <= Node.val <= 500
- 1 <= left <= right <= n
Follow up: Could you do it in one pass?
Solutions
容易写错的地方:你有没有冒出一个NPE,出现空指针的情况。
所有需要来确认非空。
1
2
3
4
5
6
for (int i = 1; i < m; i++) {
if (head == null) {
return null;
}
head = head.next;
}
- 创建head.
- 找到m的前一个节点-Pre
- 记录Pre的下一个节点,它会是翻转链的尾部。
- 翻转指定区间的链表,翻到最后一个节点时,把reverseTail.next指向它的next。这样就把翻转链表与之后 的链表接起来了。
- 返回dummynode的下一个节点。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
/**
* Definition for ListNode
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode reverseBetween(ListNode head, int m, int n) {
if (m >= n || head == null) {
return head;
}
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0);
dummy.next = head;
head = dummy;
for (int i = 1; i < m; i++) {
if (head == null) {
return null;
}
head = head.next;
}
ListNode premNode = head;
ListNode mNode = head.next;
ListNode nNode = mNode, postnNode = mNode.next;
for (int i = m; i < n; i++) {
if (postnNode == null) {
return null;
}
ListNode temp = postnNode.next;
postnNode.next = nNode;
nNode = postnNode;
postnNode = temp;
}
mNode.next = postnNode;
premNode.next = nNode;
return dummy.next;
}
}
这没什么算法可言,就是细心来做链表题目。
Dummy Node
Scenario: When the head is not determinated
当我的头不是确定的时候,head 节点不一定是谁的时候,用 Dummy Node
Related Questions:
- Merge Two Sorted Lists
- Partition List
- …
Partition List
还有一道类似的叫做 Partition Array
Lintcode https://www.lintcode.com/problem/partition-list/
Leetcode https://leetcode.com/problems/partition-list/
Solution https://www.jiuzhang.com/solutions/partition-list/
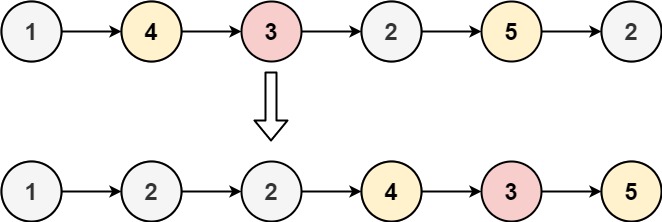
Description
Given the head of a linked list and a value x, partition it such that all nodes less than x come before nodes greater than or equal to x.
You should preserve the original relative order of the nodes in each of the two partitions.
Example 1:
Input: head = [1,4,3,2,5,2], x = 3
Output: [1,2,2,4,3,5]
Example 2:
Input: head = [2,1], x = 2
Output: [1,2]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the list is in the range [0, 200].
- -100 <= Node.val <= 100
- -200 <= x <= 200
Solutions
双指针方法,用两个指针将两个部分分别串起来。最后在将两个部分拼接起来。 left指针用来串起来所有小于x的结点, right指针用来串起来所有大于等于x的结点。 得到两个链表,一个是小于x的,一个是大于等于x的,做一个拼接即可。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode partition(ListNode head, int x) {
if (head == null) {
return null;
}
ListNode leftDummy = new ListNode(0);
ListNode rightDummy = new ListNode(0);
ListNode left = leftDummy, right = rightDummy;
while (head != null) {
if (head.val < x) {
left.next = head;
left = head;
} else {
right.next = head;
right = head;
}
head = head.next;
}
right.next = null;
left.next = rightDummy.next;
return leftDummy.next;
}
}
[] 没写过归并排序的写一写!!
Basic Linked List Skills
- Insert a Node in Sorted List
- Remove a Node from Linked List
- Reverse a Linked List
- Merge Two Linked Lists
- Middle of a Linked List
Middle of Linked List
Lintcode
Leetcode https://leetcode.com/problems/middle-of-the-linked-list/
Solution https://www.jiuzhang.com/solutions/middle-of-the-linked-list/
Description
Given the head of a singly linked list, return the middle node of the linked list.
If there are two middle nodes, return the second middle node.
Example 1:
Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5]
Output: [3,4,5]
Explanation: The middle node of the list is node 3.
Example 2:
Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5,6]
Output: [4,5,6]
Explanation: Since the list has two middle nodes with values 3 and 4, we return the second one.
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the list is in the range [1, 100].
- 1 <= Node.val <= 100
Solutions
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
class Solution {
public ListNode middleNode(ListNode head) {
ListNode slow = head, fast = head;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
return slow;
}
}
有一种题是数据流问题,data stream 问题。先数一下总长度再除以2的方法就不行了。
当我快指针走到最后的时候,或者空的时候,慢指针就是中间的位置。
也就是说快指针每走一步,慢指针的位置都是快指针的中间位置。
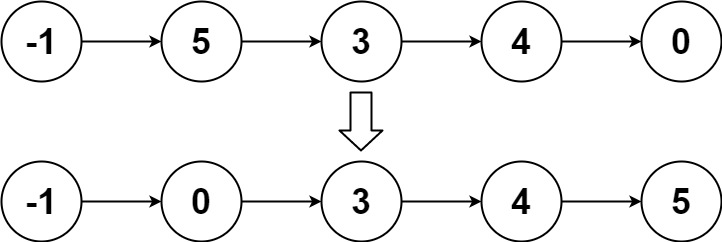
Sort List
Lintcode https://www.lintcode.com/problem/sort-list/
Leetcode https://leetcode.com/problems/sort-list/
Solution https://www.jiuzhang.com/solutions/sort-list/
Merge Sort vs Quick Sort
Description
Given the head of a linked list, return the list after sorting it in ascending order.
Example 1:
Input: head = [4,2,1,3]
Output: [1,2,3,4]
Example 2:
Input: head = [-1,5,3,4,0]
Output: [-1,0,3,4,5]
Example 3:
Input: head = [] Output: []
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the list is in the range [0, 5 * 104].
- -10^5 <= Node.val <= 10^5
Follow up: Can you sort the linked list in O(n logn) time and O(1) memory (i.e. constant space)?
Solutions
一定是已知的排序算法来解决。
O(nlogn) 有三种排序 heap sort, merge sort, quick sort 其中 Quick Sort 完胜,然后 Merge Sort 是一个稳定排序(两个相等的值相对位置不变)
Quick Sort 是原地排序 O(1) extra M
Merge Sort O(n) extra M
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
// version 1: Merge Sort
public class Solution {
private ListNode findMiddle(ListNode head) {
ListNode slow = head, fast = head.next;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return slow;
}
private ListNode merge(ListNode head1, ListNode head2) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0);
ListNode tail = dummy;
while (head1 != null && head2 != null) {
if (head1.val < head2.val) {
tail.next = head1;
head1 = head1.next;
} else {
tail.next = head2;
head2 = head2.next;
}
tail = tail.next;
}
if (head1 != null) {
tail.next = head1;
} else {
tail.next = head2;
}
return dummy.next;
}
public ListNode sortList(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return head;
}
ListNode mid = findMiddle(head);
ListNode right = sortList(mid.next);
mid.next = null;
ListNode left = sortList(head);
return merge(left, right);
}
}
面试 Heap Sort 不要求??
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
// version 2: Quick Sort 1
public class Solution {
public ListNode sortList(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return head;
}
ListNode mid = findMedian(head); // O(n)
ListNode leftDummy = new ListNode(0), leftTail = leftDummy;
ListNode rightDummy = new ListNode(0), rightTail = rightDummy;
ListNode middleDummy = new ListNode(0), middleTail = middleDummy;
while (head != null) {
if (head.val < mid.val) {
leftTail.next = head;
leftTail = head;
} else if (head.val > mid.val) {
rightTail.next = head;
rightTail = head;
} else {
middleTail.next = head;
middleTail = head;
}
head = head.next;
}
leftTail.next = null;
middleTail.next = null;
rightTail.next = null;
ListNode left = sortList(leftDummy.next);
ListNode right = sortList(rightDummy.next);
return concat(left, middleDummy.next, right);
}
private ListNode findMedian(ListNode head) {
ListNode slow = head, fast = head.next;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
return slow;
}
private ListNode concat(ListNode left, ListNode middle, ListNode right) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0), tail = dummy;
tail.next = left; tail = getTail(tail);
tail.next = middle; tail = getTail(tail);
tail.next = right; tail = getTail(tail);
return dummy.next;
}
private ListNode getTail(ListNode head) {
if (head == null) {
return null;
}
while (head.next != null) {
head = head.next;
}
return head;
}
}
// version 3: Quick Sort 2
/**
* Definition for ListNode.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int val) {
* this.val = val;
* this.next = null;
* }
* }
*/
class Pair {
public ListNode first, second;
public Pair(ListNode first, ListNode second) {
this.first = first;
this.second = second;
}
}
public class Solution {
/**
* @param head: The head of linked list.
* @return: You should return the head of the sorted linked list,
using constant space complexity.
*/
public ListNode sortList(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return head;
}
ListNode mid = findMedian(head); // O(n)
Pair pair = partition(head, mid.val); // O(n)
ListNode left = sortList(pair.first);
ListNode right = sortList(pair.second);
getTail(left).next = right; // O(n)
return left;
}
// 1->2->3 return 2
// 1->2 return 1
private ListNode findMedian(ListNode head) {
ListNode slow = head, fast = head.next;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
return slow;
}
// < value in the left, > value in the right
private Pair partition(ListNode head, int value) {
ListNode leftDummy = new ListNode(0), leftTail = leftDummy;
ListNode rightDummy = new ListNode(0), rightTail = rightDummy;
ListNode equalDummy = new ListNode(0), equalTail = equalDummy;
while (head != null) {
if (head.val < value) {
leftTail.next = head;
leftTail = head;
} else if (head.val > value) {
rightTail.next = head;
rightTail = head;
} else {
equalTail.next = head;
equalTail = head;
}
head = head.next;
}
leftTail.next = null;
rightTail.next = null;
equalTail.next = null;
if (leftDummy.next == null && rightDummy.next == null) {
ListNode mid = findMedian(equalDummy.next);
leftDummy.next = equalDummy.next;
rightDummy.next = mid.next;
mid.next = null;
} else if (leftDummy.next == null) {
leftTail.next = equalDummy.next;
} else {
rightTail.next = equalDummy.next;
}
return new Pair(leftDummy.next, rightDummy.next);
}
private ListNode getTail(ListNode head) {
if (head == null) {
return null;
}
while (head.next != null) {
head = head.next;
}
return head;
}
}
分治法,先左排序,再右边排序
对于给定的head所代表的list,排好序之后返回他新的head
- Basic Knowledge 找中点函数、merge函数、bfs, binary search, dfs -> subsets, permutation
面试可以直接写出来,其他的才是你需要考虑的。
面试中你需要先写出main,先写出大的逻辑写全了。
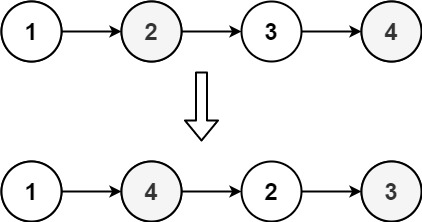
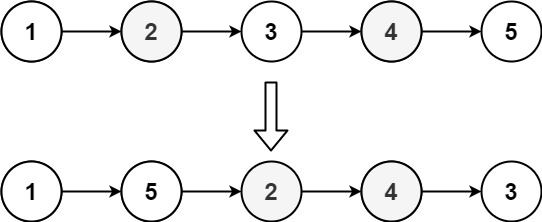
Reorder List
Lintcode https://www.lintcode.com/problem/reorder-list/
Leetcode https://leetcode.com/problems/reorder-list/
Solution https://www.jiuzhang.com/solutions/reorder-list/
Description
You are given the head of a singly linked-list. The list can be represented as:
L0 → L1 → … → Ln - 1 → Ln
Reorder the list to be on the following form:
L0 → Ln → L1 → Ln - 1 → L2 → Ln - 2 → …
You may not modify the values in the list’s nodes. Only nodes themselves may be changed.
Example 1:
Input: head = [1,2,3,4]
Output: [1,4,2,3]
Example 2:
Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5]
Output: [1,5,2,4,3]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the list is in the range [1, 5 * 104].
- 1 <= Node.val <= 1000
Solutions
先找到中点,然后把后半段倒过来,然后前后交替合并。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
public class Solution {
private ListNode reverse(ListNode head) {
ListNode newHead = null;
while (head != null) {
ListNode temp = head.next;
head.next = newHead;
newHead = head;
head = temp;
}
return newHead;
}
private void merge(ListNode head1, ListNode head2) {
int index = 0;
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0);
while (head1 != null && head2 != null) {
if (index % 2 == 0) {
dummy.next = head1;
head1 = head1.next;
} else {
dummy.next = head2;
head2 = head2.next;
}
dummy = dummy.next;
index ++;
}
if (head1 != null) {
dummy.next = head1;
} else {
dummy.next = head2;
}
}
private ListNode findMiddle(ListNode head) {
ListNode slow = head, fast = head.next;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return slow;
}
public void reorderList(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return;
}
ListNode mid = findMiddle(head);
ListNode tail = reverse(mid.next);
mid.next = null;
merge(head, tail);
}
}
本质上还是三个函数 findMiddle() reverse() merge() 来处理这个问题!
实际上就是基本功的一个运用
Fast Slow Pointers
- Middle of Linked List
- Remove Nth Node From End of List
- Linked List Cycle i, ii
- Rotate List
…
Linked List Cycle
Lintcode https://www.lintcode.com/problem/linked-list-cycle/
Leetcode https://leetcode.com/problems/linked-list-cycle/
Solution https://www.jiuzhang.com/solutions/linked-list-cycle/
Description
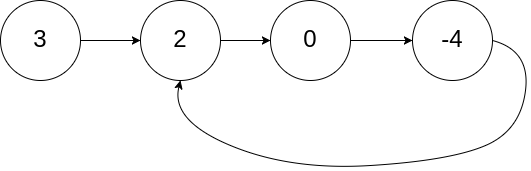
Given head, the head of a linked list, determine if the linked list has a cycle in it.
There is a cycle in a linked list if there is some node in the list that can be reached again by continuously following the next pointer. Internally, pos is used to denote the index of the node that tail’s next pointer is connected to. Note that pos is not passed as a parameter.
Return true if there is a cycle in the linked list. Otherwise, return false.
Example 1:
Input: head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1
Output: true
Explanation: There is a cycle in the linked list, where the tail connects to the 1st node (0-indexed).
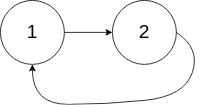
Example 2:
Input: head = [1,2], pos = 0
Output: true
Explanation: There is a cycle in the linked list, where the tail connects to the 0th node.
Example 3:
Input: head = [1], pos = -1
Output: false
Explanation: There is no cycle in the linked list.
Constraints:
- The number of the nodes in the list is in the range [0, 10^4].
- -10^5 <= Node.val <= 10^5
- pos is -1 or a valid index in the linked-list.
Solutions
快慢指针的经典题。 快指针每次走两步,慢指针一次走一步。 在慢指针进入环之后,快慢指针之间的距离每次缩小1,所以最终能相遇。
Linked List Cycle i, ii 这种题目就是背答案题目。。你不太可能在面试现场想到这个办法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
public class Solution {
public Boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return false;
}
ListNode fast, slow;
fast = head.next;
slow = head;
while (fast != slow) {
if(fast==null || fast.next==null)
return false;
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return true;
}
}
Follow Up
Can you solve it using O(1) (i.e. constant) memory?
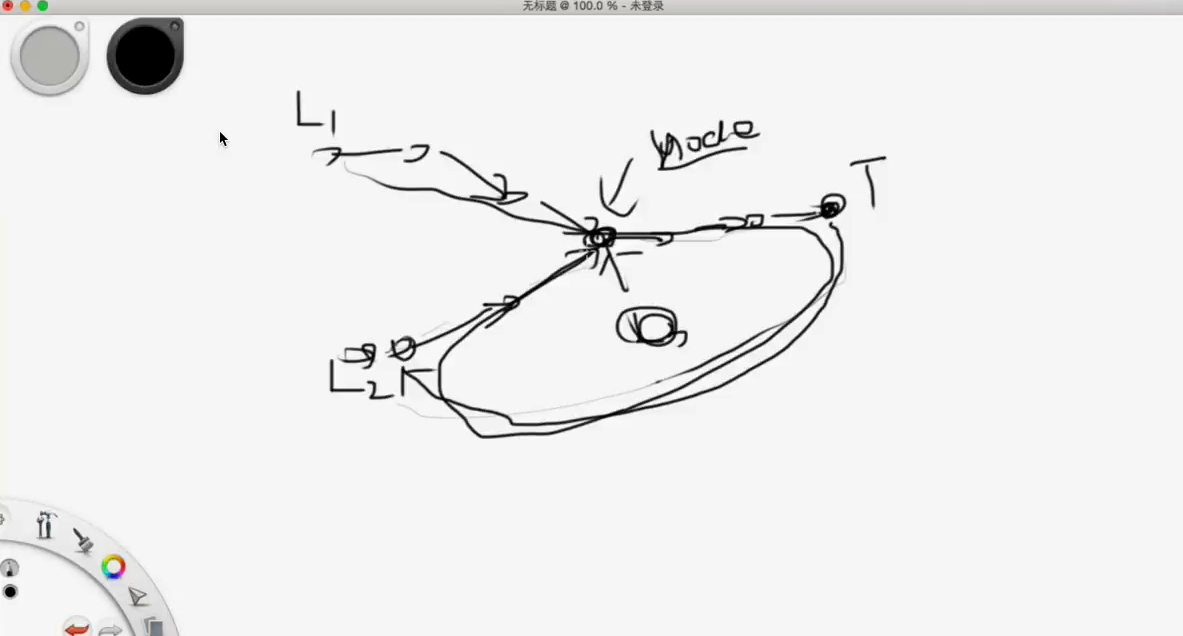
环的入口在哪???
首先第一次相遇,这里操作把Slow慢指针放到第一个节点,然后再次相遇就是入口。
还有一道题,求链表的交点!
把L2和tail连起来,就是“环的入口”这道题的思路来解决。
实际上用一个hash表就都解决了,为什么用这个呢,要用O(1)的来实现
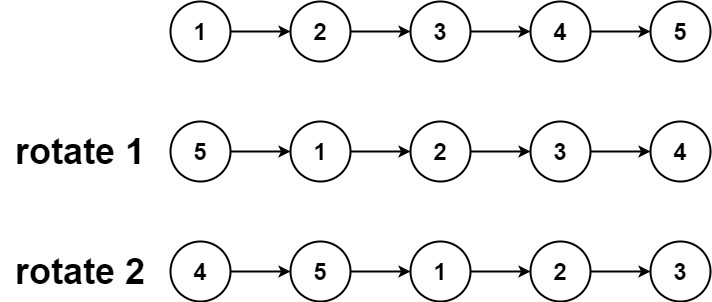
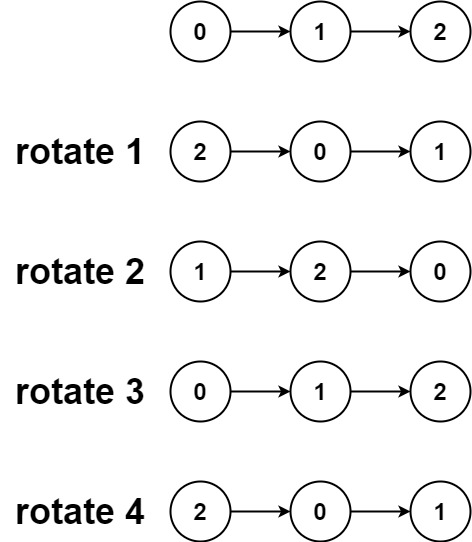
Rotate List
Lintcode https://www.lintcode.com/problem/rotate-list/
Leetcode https://leetcode.com/problems/rotate-list/
Solution https://www.jiuzhang.com/solutions/rotate-list/
Description
Given the head of a linked list, rotate the list to the right by k places.
Example 1:
Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 2
Output: [4,5,1,2,3]
Example 2:
Input: head = [0,1,2], k = 4
Output: [2,0,1]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the list is in the range [0, 500].
- -100 <= Node.val <= 100
- 0 <= k <= 2 * 10^9
Solutions
一种方法,我先找到它的长度,我 rotate 到哪里。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
public class Solution {
private int getLength(ListNode head) {
int length = 0;
while (head != null) {
length ++;
head = head.next;
}
return length;
}
public ListNode rotateRight(ListNode head, int n) {
if (head == null) {
return null;
}
int length = getLength(head);
n = n % length;
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0);
dummy.next = head;
head = dummy;
ListNode tail = dummy;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
head = head.next;
}
while (head.next != null) {
tail = tail.next;
head = head.next;
}
head.next = dummy.next;
dummy.next = tail.next;
tail.next = null;
return dummy.next;
}
}
Merge k Sorted Lists
Lintcode https://www.lintcode.com/problem/merge-k-sorted-lists/
Leetcode https://leetcode.com/problems/merge-k-sorted-lists/
Solution https://www.jiuzhang.com/solutions/merge-k-sorted-lists/
PriorityQueue / Heap vs Divide Conquer
Description
You are given an array of k linked-lists lists, each linked-list is sorted in ascending order.
Merge all the linked-lists into one sorted linked-list and return it.
Example 1:
Input: lists = [ [1, 4, 5], [1, 3, 4], [2, 6] ]
Output: [1, 1, 2, 3, 4, 4, 5, 6]
Explanation: The linked-lists are: [ 1->4->5, 1->3->4, 2->6 ] merging them into one sorted list: 1->1->2->3->4->4->5->6
Example 2:
Input: lists = []
Output: []
Example 3:
Input: lists = [[]]
Output: []
Constraints:
- k == lists.length
- 0 <= k <= 10^4
- 0 <= lists[i].length <= 500
- -10^4 <= lists[i][j] <= 10^4
- lists[i] is sorted in ascending order.
- The sum of lists[i].length will not exceed 10^4.
Solutions
三种方法,这是一个非常有区分度的题目。我很喜欢。
要求三种方法都要AC。你就会掌握优先级队列,归并排序,两两合并的方法。
想到了优先级队列。
如果你会用comparator函数来做,谁小谁出列。
答案 是 nlogk
有序数组合并,使用两个指针向后移动,每次比较,小的一个数字取出来,并将指针后移一位。
K个有序链表可以每次合并一个链表进结果链表中。合并k次
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
// version 1: Divide & Conquer
/**
* Definition for ListNode.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int val) {
* this.val = val;
* this.next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
/**
* @param lists: a list of ListNode
* @return: The head of one sorted list.
*/
public ListNode mergeKLists(List<ListNode> lists) {
if (lists.size() == 0) {
return null;
}
return mergeHelper(lists, 0, lists.size() - 1);
}
private ListNode mergeHelper(List<ListNode> lists, int start, int end) {
if (start == end) {
return lists.get(start);
}
int mid = start + (end - start) / 2;
ListNode left = mergeHelper(lists, start, mid);
ListNode right = mergeHelper(lists, mid + 1, end);
return mergeTwoLists(left, right);
}
private ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0);
ListNode tail = dummy;
while (list1 != null && list2 != null) {
if (list1.val < list2.val) {
tail.next = list1;
tail = list1;
list1 = list1.next;
} else {
tail.next = list2;
tail = list2;
list2 = list2.next;
}
}
if (list1 != null) {
tail.next = list1;
} else {
tail.next = list2;
}
return dummy.next;
}
}
// version 2: Heap
public class Solution {
private Comparator<ListNode> ListNodeComparator = new Comparator<ListNode>() {
public int compare(ListNode left, ListNode right) {
return left.val - right.val;
}
};
public ListNode mergeKLists(List<ListNode> lists) {
if (lists == null || lists.size() == 0) {
return null;
}
Queue<ListNode> heap = new PriorityQueue<ListNode>(lists.size(), ListNodeComparator);
for (int i = 0; i < lists.size(); i++) {
if (lists.get(i) != null) {
heap.add(lists.get(i));
}
}
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0);
ListNode tail = dummy;
while (!heap.isEmpty()) {
ListNode head = heap.poll();
tail.next = head;
tail = head;
if (head.next != null) {
heap.add(head.next);
}
}
return dummy.next;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
// Version 3: merge two by two
/**
* Definition for ListNode.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int val) {
* this.val = val;
* this.next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
/**
* @param lists: a list of ListNode
* @return: The head of one sorted list.
*/
public ListNode mergeKLists(List<ListNode> lists) {
if (lists == null || lists.size() == 0) {
return null;
}
while (lists.size() > 1) {
List<ListNode> new_lists = new ArrayList<ListNode>();
for (int i = 0; i + 1 < lists.size(); i += 2) {
ListNode merged_list = merge(lists.get(i), lists.get(i+1));
new_lists.add(merged_list);
}
if (lists.size() % 2 == 1) {
new_lists.add(lists.get(lists.size() - 1));
}
lists = new_lists;
}
return lists.get(0);
}
private ListNode merge(ListNode a, ListNode b) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0);
ListNode tail = dummy;
while (a != null && b != null) {
if (a.val < b.val) {
tail.next = a;
a = a.next;
} else {
tail.next = b;
b = b.next;
}
tail = tail.next;
}
if (a != null) {
tail.next = a;
} else {
tail.next = b;
}
return dummy.next;
}
}
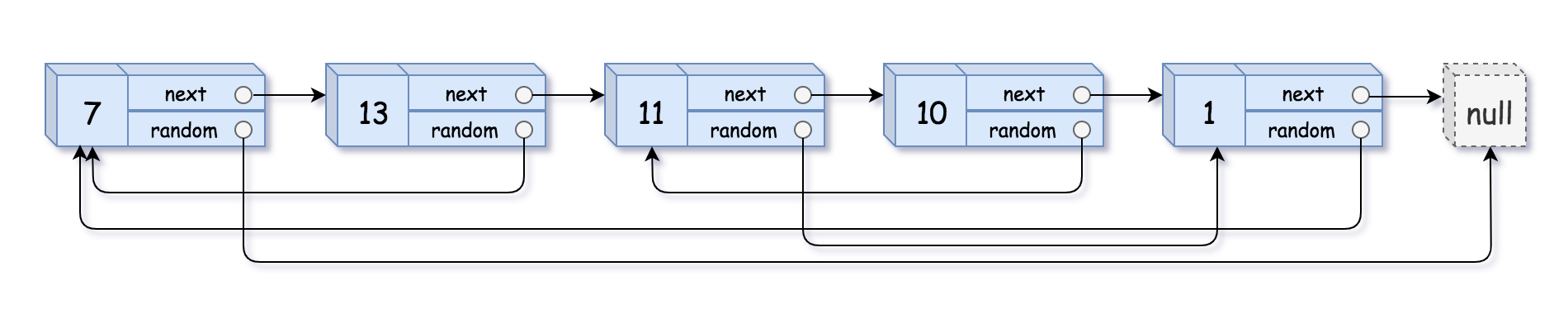
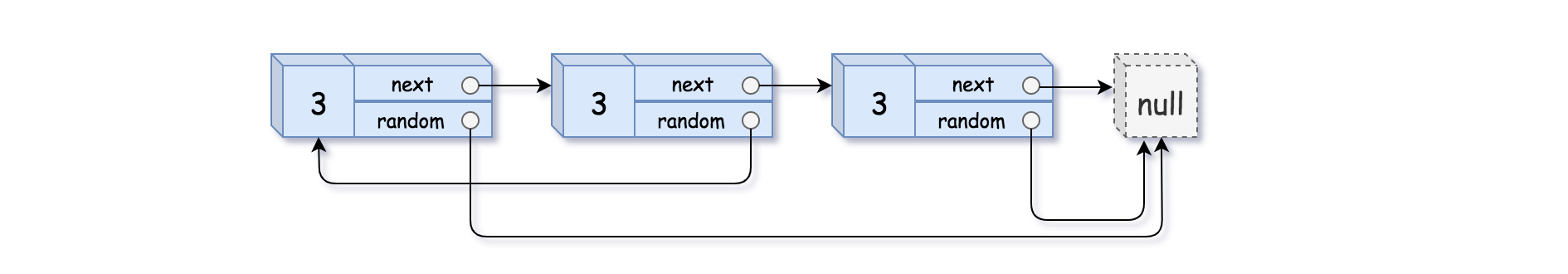
Copy List with Random Pointer
Lintcode https://www.lintcode.com/problem/copy-list-with-random-pointer/
Leetcode https://www.leetcode.com/problems/copy-list-with-random-pointer/
Solution https://www.jiuzhang.com/solutions/copy-list-with-random-pointer/
Description
A linked list of length n is given such that each node contains an additional random pointer, which could point to any node in the list, or null.
Construct a deep copy of the list. The deep copy should consist of exactly n brand new nodes, where each new node has its value set to the value of its corresponding original node. Both the next and random pointer of the new nodes should point to new nodes in the copied list such that the pointers in the original list and copied list represent the same list state. None of the pointers in the new list should point to nodes in the original list.
For example, if there are two nodes X and Y in the original list, where X.random –> Y, then for the corresponding two nodes x and y in the copied list, x.random –> y.
Return the head of the copied linked list.
The linked list is represented in the input/output as a list of n nodes. Each node is represented as a pair of [val, random_index] where:
- val: an integer representing Node.val
- random_index: the index of the node (range from 0 to n-1) that the random pointer points to, or null if it does not point to any node.
Your code will only be given the head of the original linked list.
Example 1:
Input: head = [[7, null], [13, 0], [11, 4], [10,2], [1,0]]
Output: [[7, null], [13, 0], [11, 4], [10, 2], [1, 0]]
Example 2:
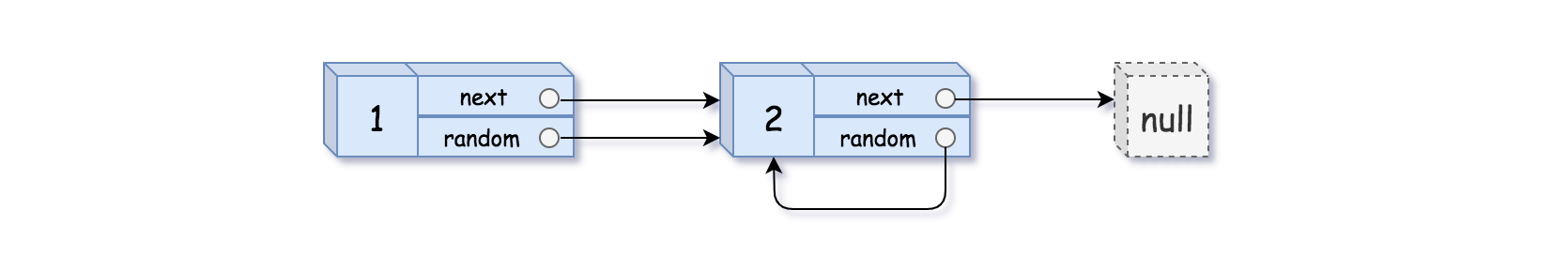
Input: head = [[1, 1], [2, 1]]
Output: [[1, 1], [2, 1]]
Example 3:
Input: head = [[3,null],[3,0],[3,null]]
Output: [[3,null],[3,0],[3,null]]
Constraints:
- 0 <= n <= 1000
- -104 <= Node.val <= 104
- Node.random is null or is pointing to some node in the linked list.
Solutions
深拷贝要对每个点都新建一遍。ALL
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
// HashMap version
public class Solution {
public RandomListNode copyRandomList(RandomListNode head) {
if (head == null) {
return null;
}
HashMap<RandomListNode, RandomListNode> map = new HashMap<RandomListNode, RandomListNode>();
RandomListNode dummy = new RandomListNode(0);
RandomListNode pre = dummy, newNode;
while (head != null) {
if (map.containsKey(head)) {
newNode = map.get(head);
} else {
newNode = new RandomListNode(head.label);
map.put(head, newNode);
}
pre.next = newNode;
if (head.random != null) {
if (map.containsKey(head.random)) {
newNode.random = map.get(head.random);
} else {
newNode.random = new RandomListNode(head.random.label);
map.put(head.random, newNode.random);
}
}
pre = newNode;
head = head.next;
}
return dummy.next;
}
}
剩下hashmap 的空间,算是奇技淫巧了
第三步,我拆开就行了
这道题同样需要函数化!!
第一遍扫的时候巧妙运用next指针, 开始数组是 1->2->3->4 。
然后扫描过程中 先建立copy节点 1->1->2->2->3->3->4->4, 然后第二遍copy的时候去建立边的copy, 拆分节点, 一边扫描一边拆成两个链表,这里用到两个dummy node。
第一个链表变回 1->2->3 , 然后第二变成 1->2->3`
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
//No HashMap version
public class Solution {
private void copyNext(RandomListNode head) {
while (head != null) {
RandomListNode newNode = new RandomListNode(head.label);
newNode.random = head.random;
newNode.next = head.next;
head.next = newNode;
head = head.next.next;
}
}
private void copyRandom(RandomListNode head) {
while (head != null) {
if (head.next.random != null) {
head.next.random = head.random.next;
}
head = head.next.next;
}
}
private RandomListNode splitList(RandomListNode head) {
RandomListNode newHead = head.next;
while (head != null) {
RandomListNode temp = head.next;
head.next = temp.next;
head = head.next;
if (temp.next != null) {
temp.next = temp.next.next;
}
}
return newHead;
}
public RandomListNode copyRandomList(RandomListNode head) {
if (head == null) {
return null;
}
copyNext(head);
copyRandom(head);
return splitList(head);
}
}
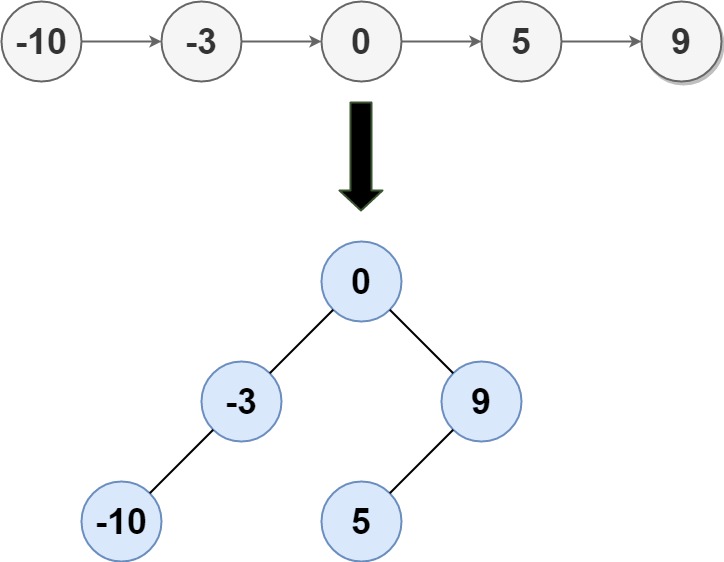
Convert Sorted List to Balanced BST
Lintcode https://www.lintcode.com/problem/convert-sorted-list-to-balanced-bst/
Leetcode https://leetcode.com/problems/convert-sorted-list-to-binary-search-tree/
Solution https://www.jiuzhang.com/solutions/convert-sorted-list-to-balanced-bst/
Description
Given the head of a singly linked list where elements are sorted in ascending order, convert it to a height-balanced binary search tree.
Example 1:
Input: head = [-10,-3,0,5,9]
Output: [0,-3,9,-10,null,5]
Explanation: One possible answer is [0,-3,9,-10,null,5], which represents the shown height balanced BST.
Example 2:
Input: head = []
Output: []
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in head is in the range [0, 2 * 10^4].
- -10^5 <= Node.val <= 10^5
Solutions
在链表上使用分治的方法。 这个算法的时间复杂度是 O(n)的。 要诀在于,先把整个链表的长度取一次,然后拿着这个长度和链表头一起作为参数来进行递归构造。 convert(head, length) 表示把从 head 开头的长度为 length 的那么多个节点,转化为 bst。 return 两个值,一个是转化后的 bst 根节点,一个是链表上从 head 开始第 length + 1 个节点是谁。 这样做的好处是,你不需要用 O(n) 的时间去找链表的中点了,直接 O(1) 从 return 里得到。
也是属于奇技淫巧吧,也是要记住会写就行。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
/**
* Definition for ListNode.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int val) {
* this.val = val;
* this.next = null;
* }
* }
* Definition of TreeNode:
* public class TreeNode {
* public int val;
* public TreeNode left, right;
* public TreeNode(int val) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = this.right = null;
* }
* }
*/
class Pair {
TreeNode root;
ListNode next;
public Pair(TreeNode root, ListNode next) {
this.root = root;
this.next = next;
}
}
public class Solution {
/*
* @param head: The first node of linked list.
* @return: a tree node
*/
public TreeNode sortedListToBST(ListNode head) {
if (head == null) {
return null;
}
int length = getLinkedListLength(head);
Pair pair = convert(head, length);
return pair.root;
}
public int getLinkedListLength(ListNode head) {
int length = 0;
while (head != null) {
length++;
head = head.next;
}
return length;
}
public Pair convert(ListNode head, int length) {
/**
* Convert head -> head.next .... head.next.next... -> next
* |_______________________________|
* length
* to a Balanced-BST and return the root of the BST and the
* (length + 1)th node from head.
*/
if (length == 0) {
return new Pair(null, head);
}
// convert the first length / 2 nodes to a left child tree node.
Pair leftPair = convert(head, length / 2);
// convert linked list from (length / 2 + 2)th node as head to a right child tree node
Pair rightPair = convert(leftPair.next.next, length - length / 2 - 1);
// so the (length / 2 + 1)th node will be directly converted to the root node.
// pair.root
// / \
// leftPair.root rightPair.root
Pair pair = new Pair(new TreeNode(leftPair.next.val), null);
pair.root.left = leftPair.root;
pair.root.right = rightPair.root;
pair.next = rightPair.next;
return pair;
}
}
把current开头的,长度为size的那么多个点,变成BST。
并且“顺便”把current,挪动到size + 1的那个点。
把current开头的,长度为size的那么多个点,变成bst. 并且顺便,把current,挪动到size+1的那个点。
Related Questions
https://www.lintcode.com/problem/reverse-nodes-in-k-group/
https://www.lintcode.com/problem/delete-node-in-the-middle-of-singly-linked-list/
https://www.lintcode.com/problem/convert-binary-search-tree-to-doubly-linked-list/
Homework
Required
- [Easy] 174 Remove Nth Node from End of List
- [Easy] 96 Partition List
- [Medium] 113 Remove Duplicates from Sorted List ii
- [Medium] 106 Convert Sorted List To Balanced BST
- [Medium] 105 Copy List With Random Pointer
- [Medium] 104 Merge k Sorted Lists
- [Medium] 99 Reorder List
- [Medium] 98 Sort List
- [Medium] 36 Reverse Linked List ii
- [Hard] 103 Linked List Cycle ii
Optional
- [Naive] 228 Middle of Linked List
- [Naive] 452 Remove Linked List Elements
- [Easy] 217 Remove Duplicates from
- [Easy] 415 Swap Nodes in Pairs
- [Easy] 372 Delete Node in the Middle of Singly Linked List
- [Easy] 173 Insertion Sort List
- [Easy] 167 Add Two Numbers
- [Easy] 166 Nth to Last Node in List
- [Easy] 165 Merge Two Sorted Lists
- [Easy] 112 Remove Duplicates from Sorted List
- [Easy] 35 Reverse Linked List
- [Medium] 221 Add Two Numbers ii
- [Medium] 223 Palindrome Linked List
- [Medium] 378 Convert Binary Search Tree to Doubly Linked List
- [Medium] 170 Rotate List
- [Medium] 102 Linked List Cycle
- [Hard] 450 Reverse Nodes in k-Group